
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
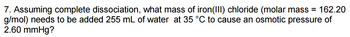
Transcribed Image Text:7. Assuming complete dissociation, what mass of iron(III) chloride (molar mass = 162.20
g/mol) needs to be added 255 mL of water at 35 °C to cause an osmotic pressure of
2.60 mmHg?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7. Because carbon tetrachloride (CCL4) is not soluble in water, a test tube containing the two liquids will form two layers. Predict which layer is on top and justify your answer. If molecular iodine (I2) is added to the test tube, predict which liquid layer will dissolve most of the iodine and justify your answer.arrow_forwardCalculate the molality of a solution prepared by dissolving 50.0 g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in 555 g of H2O.arrow_forward6.) A saturated aqueous solution of NO(g) at 25 °C has [NO] = 9.5x10-4 M when PNO = 380 torr. What is the [NO], in M, when PNO = (1.7x10^2) torr at this temperature? Note: Your answer is assumed to be reduced to the highest power possible. Your Answer:arrow_forward
- At 70 °C, the solubility of an unknown solute is 65.7 g/100.0 g of water. What mass of the solute can dissolve in 125.5 g of water at the same temperature?arrow_forwardThe solubility limit of a solute at 20. °C and 1.0 atm is 13.8 g of solute per 1 L of water. What will MOST likely happen when 12.0 g of solute are added to 1 L of pure water and the solution is mixed well (at the same conditions)?arrow_forwardAt 25 °C, the solubility of NaCl is 36.0g/100g H20. How much NaCl can dissolve in 450 g of water at that temperature? * 8.0 g 162 g 0.080 g O 1.62 garrow_forward
- The freezing point of a liquid will change when a solute is added. Explain how the addition of salt impacts the boiling point of water. Calculate the freezing point change for a given concentration. Given that water's freezing point is 0.00°C and the freezing point depression constant (Kf) is 1.86 °C·kg/mol, calculate the freezing point depression for a 2.80 molal solution (moles/kg) of CaCl, in water. Assume ideal behavior of the ions. 21 MacBook Air 吕0 888 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F7 ! @ $ % & 1 3 6. 7 8. Q W E R Yarrow_forwardWhen 4.13 g of a certain molecular compound X are dissolved in 35. g of cyclohexane (C6H₁2), the freezing point of the solution is measured to be 3.7 °C. Calculate the molar mass of X.arrow_forwardRemember that the boiling point elevation constant for water is Kb = 0.512 C/kg, and the freezing point depression constant for water is Kf = 1.86 C/kg Use the table provided to answer the question. 1.00 g of Lead (II) Sulfate is mixed into 5.75 L of water. a) How many moles of the Lead (III) Sulfate will actually dissolve into the water? b) How many grams of Lead (III) Sulfate will be left un-dissolved? c) At what temperature will the solution now boil and freeze?arrow_forward
- -A solution is made by dissolving 16.0 g of CaCl2 in 4560 g of water.Calculate the freezing point of this solution. -Calculate the osmotic pressure of a 0.75 M solution of ferric nitrate, Fe(NO3)3, at 25 oCarrow_forwardA 1.35 m aqueous solution of Compound X had a boiling point of 102.8°C. Which one of the following is most likely to be Compound X? Hint: The boiling point elevation constant for water is 0.52°C/m. Na3PO4 CaCl₂ X OKCI CH3CH₂OHarrow_forwardThe freezing point of a solution that contains 1.1 g of an unknown compound, (A), dissolved in 12 g of benzene is found to be 2.97 °C. The freezing point of pure benzene is 5.48 °C. The freezing point depression constant of benzene is 5.12 °C/molal. What is the molecular weight of the unknown compound?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY