
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Human centrifuges are often used to simulate different acceleration levels for pilots. When aerospace physiologists say that a pilot is pulling 9 g,s , they mean that the resultant normal force on the pilot from the bottom of the seat is nine times their weight. Knowing that the centrifuge starts from rest and has a constant angular acceleration of 1.5 RPM per second until the pilot is pulling 9 g's and then continues with a constant angular velocity, determine (a) how long it will take for the pilot to reach 9 g's (b) the angle 0 of the normal force once the pilot reaches 9 g’s. Assume that the force parallel to the seat is zero.
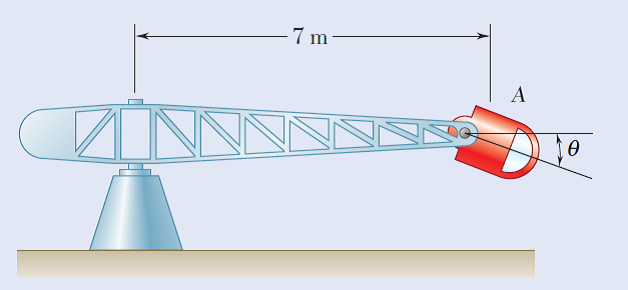
Transcribed Image Text:7 m
Ө
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A block of mass m1 = 3.60 kg on a frictionless inclined plane of angle 30.0° is connected by a cord over a massless, frictionless pulley to a second block of mass m2 = 2.00 kg hanging vertically. (a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of each block? m1 = m/s2 m2 = m/s2 (b) What is the direction of the acceleration of m2? m2 accelerates downwardsnot enough information m2 accelerates upwards (c) What is the magnitude of the tension in the cord? Narrow_forward5. A 2-kg sphere is attached to a massless rigid rod attached to a fixed pivot point O. The rigid rod and mass rotate in the horizontal plane. A moment is applied to the rod of magnitude M = 0.5t² N. m, where t is in seconds. The length of the rod is 0.5 m. Determine the speed of the sphere after the moment is applied for 5 seconds. M(t)arrow_forward7.5 kg The pulley in the system shown made of two uniform disks that are glued together. The smaller disk has a mass of 0.95 kg and radius of 38 cm. The larger disk has a mass of 3 kg and radius of 76 cm. The pulley is mounted on a frictionless axle that runs through the center of the smaller disk and the midpoint between the center and edge of the larger disk. A rope is wrapped around the smaller disk such that it does not slip. Use work-energy principles to determine how far the hanging mass has fallen when the kinetic energy of the pulley is 250 J, if the system started at rest. d marrow_forward
- A 5003-lb truck is being used to lift a 1003 lb boulder B that is on a 230 lb pallet A. The acceleration of the truck is 1 ft/s2 and g = 32.2 ft/s2. Determine the horizontal force between the tires and the ground. The horizontal friction force between the tires and the ground is ______ lb.arrow_forwardProblem (4) When the power to an electric motor is turned on the motor reaches its rated speed of 2400 rpm in 4 s, and when the power is turned off the motor coasts to rest in 40 s. Assuming uniformly accelerated motion, determine the number of revolutions that the motor executes: (a) in reaching its rated speed, (b) in coasting to rest.arrow_forwardA solid sphere of mass M and radius R rolls without slipping along a table at speed v. What is its kinetic energy? Mv2/5 Mv2/2 Mv2 3Mv2/2 7Mv2/10arrow_forward
- PROBLEM 4.8 A gyroscope slows from an initial rate of 32.0 rad/s at a rate of 0.9 rad s² 9. How long does it take to come to rest? c. 37.56 s d. 38.56 s 10. How many revolutions does it make before stopping? с. 262 d. 292 а. 35.56 s b. 36.56 s а. 282 b. 272arrow_forwardTwo objects with masses of 2.55 kg and 4.15 kg are connected by a light string that passes over a light frictionless pulley to form an Atwood machine. (a) Determine the tension in the string. (b) Determine the acceleration of each object. (c) Determine the distance each object will move in the first second of motion if they start from rest.arrow_forwardA stone of mass 3 kg is dropped into a water tank. The stone has negligible speed when entering the water surface and takes 3 seconds to sink to the bottom. While sinking, the resistance of the water is 9N. The acceleration of the stone and the height of water column are respectively: O 1.6.81 ms 2, 30.64 m O 2. 9.81 ms¯4, 44.1 m O 3. (-) 9.81 ms Z, 44.1 m O 4. 12.81 ms¯2, 57.6 marrow_forward
- . An object of mass 12 kg is suspended from a pulley which has a mass of 6 kg and a radius of rotation of 0.25 m. If at that time the pulley rotates with an angular velocity of 5 rad/s, we want to know that when the object moves down a distance of 2 m, then at what speed is the pulley rotating? If the friction force on the pulley bearing produces a moment of resistance of 2 N-m 12 kg 0.3 marrow_forwardPROBLEM 4.6 With the aid of a string, a gyroscope is accelerated from rest to 38 rad/s in 0.5 s. What is its angular acceleration in rad/s²? c. 85 d. 95 6. а. 75 b. 65 7. How many revolutions does it go through in the process? а. 1.392 с. 1.492 b. 1.592 d. 1.692arrow_forwardA small grinding wheel is attached to the shaft of an electric motor which has a rated speed of 3600 rpm. When the power is turned on, the unit reaches its rated speed in 5 s, and when the power is turned off, the unit coasts to rest in 70 s. Assuming uniformly accelerated motion, determine the number of revolutions that the motor executes (a) in reaching its rated speed, (b) in coasting to rest.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY