
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
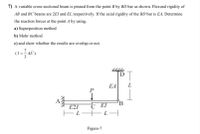
Transcribed Image Text:7) A variable cross-sectional beam is pinned from the point B by BD bar as shown. Flexural rigidity of
AB and BC beams are 2El and El, respectively. If the axial rigidity of the BD bar is EA, Determine
the reaction forces at the point A by using,
a) Superposition method
b) Mohr method
c) and show whether the results are overlap or not.
(1= E).
AL
D
EA
L
C EI
E21
L
Figure-7
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find the force in truss DE. T = 390 N, x = 1.8 m. (Note: if the force in the truss is in tension, please enter a positive value; if it is in compression, please enter a negative value.) A Farrow_forwardPart A and B pleasearrow_forwardThe rigid bar BDE is supported by two links AB and CD. Link AB is made of aluminum (E = 70 GPa) and has a cross-sectional area of 519 mm2; link CE is made of steel (E = 200 GPa) and has a cross-sectional area of 619 mm?. For the 41 kN force shown, determine the deflection of B (mm) *deflection should have a negative sign if compression and positive if tension. Also, your final answer should have two decimal places 04 m 0.3 m E 0.4 m 0.2 marrow_forward
- Q3 The truss ABC shown in the figure supports a horizontal load P-900 lb and a vertical load P2= 300 lb. Both bars have cross-sectional area A-2.4 in. and are made of steel with E-20 X 10 psi. (a) Determine the strain energy U, of the truss when the load P, acts alone (P2 -0). (b) Determine the strain energy U2 when the load P2 acts alone (P 0). (c) Determine the strain energy Uz when both loads act simultaneously. 30 B P =900 lb P2 300 lb 40 in.arrow_forwarda square box beam is made of two 30X120-mm planks and two 30X180-mm planks nailed together as shown. Knowing that the spacing between the nails is s=23 mm and that the vertical shear in the beam is V=1580N, determine (a) the shearing force in each nail, (b) the maximum shearing stress in the beam 30 mm 120 mm 30 mm 180 mmarrow_forwardThe rigid bar AB of negligible weight is supported by a pin at O. When the two steel rods are attached to the ends of the bar, there is a gap A = 4 mm between the lower end of the left rod and its pin support at C. %3D Compute the stress in the left rod after its lower end is attached to the support. The cross-sectional areas are 300 mm2 for rod AC and 250 mm? for rod BD. Use E = 200 GPa for steel. A В 0.75 m 1.5 m > 2 m Darrow_forward
- I need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forwardThe bar ABC shown below is loaded by a force P acting at the end C and by a force Q acting at the midpoint B. The bar has constant axial rigidity EA (20pts) 0) 0) Determine the strain energy Ul of the bar when the force Pacts alone (Q Determine the strain energy U2 of the bar when the force Q acts alone (P Determine the strain energy Us of the bar when the forces P and Q act simultaneously upon the bar. b. c. Use the following values to solve the problem: P=30kPa Q=75 kPa E = 130 GPa L=10 m Bar's cross section 450mm 450mmarrow_forward14. A pin-connected structure consists of a rigid beam ABCD and two supporting bars. Bar (1) is an aluminum alloy [E = 70 GPa] with a cross-sectional area of A₁ = 2,400 mm². Bar (2) is a bronze alloy [E = 100 GPa] with a cross-sectional area of A2 = 6,000 mm². All bars are unstressed before the load P is applied. If a load of P = 535 kN is applied at B, determine the normal force in bar (1). A) B) D) E) 2.9 m 0.8 m 391 kN 325 kN 301 kN 247 kN 181 kN B 1.5 m P = 535 KN (2) C 3.3 m 1.2 m F₁ K 0.8m D + 535 1.2marrow_forward
- A laminated plastic beam of square cross section is built up by gluing together three strips, each 20 mm x 60 mm in cross section (see figure). The beam has a total weight of 4.6 N and is simply supported with span length L = 460 mm. Considering the weight of the beam (q) calculate the maximum permissible CCW moment M that may be placed at the right support. (a) If the allowable shear stress in the glued joints is 0.4 MPa. Round to the nearest tenth. Mmax = __ N • m (b) If the allowable bending stress in the plastic is 8 MPa. Round to the nearest hundredth. Mmax = __ N • marrow_forwardA beam AB is fixed at both ends and carries a uniformly distributed load of intensity p per unit length run over its entire length. Due to some constructional defects, the end B is now reduced to a simple support. The percentage increase in bending moment at A isarrow_forwardA tapered bar AB of solid circular cross section and length L is supported at end B and subjected to a tensile load P at the free end A. The diameters of the bar at ends A and B are dA and de, respectively. Determine the elongation of the bar due to the load P, assuming that the angle of taper is small P da A B T dв 1 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning