
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Use the node-voltage method to find the V1, V2, and V3 for the circuit in figure (2). Upload your solution steps in blackboard assignment.
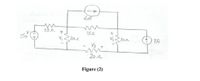
Transcribed Image Text:6A
152
201
7A
V3
20 r
Figure (2)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. In the circuit of Figure below is1 = Vs2=0, Vs1 = 9 V, İs2 = 12 A. For the four cases of (a) R = 0, (b) R=60,(c) R = 90 and (d) R = 10,0000 draw the simplified circuit and find IBA and VAC. Hint: A zero voltage source corresponds to a short-circuited element and a zero current source corresponds to an open-circuited element. İBA B A ww R VS₂ 3 Ω 6Ω U SVarrow_forwardResistor and RC Circuits Problem 12: Consider the circuit in the figure, with the current directions defined as shown. There are four resistors in this circuit (R1, R2, R3, and R4) and four batteries with emfs ℰ1 = 15.5 V, ℰ2 = 3.5 V, ℰ3 = 14 V, and ℰ4 = 27.3 V, each with internal resistance given by ri as marked in the figure. Part (a) Calculate the current I1 in amps. Part (b) Calculate the current I2 in amps. Part (c) Calculate the current I3 in amps.arrow_forwardUse the Principle of Superposition to determine the current i through R3 in the Figure. Let R1 = 100, R2 = 40, R3 = 20, R4 = 20, R5= 20, Vs 10 V, Is = 2A. ww VS R3 ww wwwarrow_forward
- PROBLEM 3: Consider the circuit shown below in which you are to assume that Vsi, Vs2, Is and the resistors are known. Use the node voltage method to compose the minimum set of equations sufficient to determine all of the labeled node voltages (i.e. A through F). Do not include redundant equations! Your equations should be in terms of ONLY the node voltages, Vsi, Vs2, Is, and the resistors. You do not need to arrange the equations in matrix form nor to simplify them algebraically. Vs₁ F + R₁ VD E R₂ www R4 A B + R3 C VS2 R5 Isarrow_forwardcan someone explain the concepts and show me how to do this problem step by steparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,