
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Gg.57.
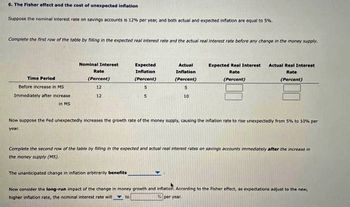
Transcribed Image Text:6. The Fisher effect and the cost of unexpected inflation
Suppose the nominal interest rate on savings accounts is 12% per year, and both actual and expected inflation are equal to 5%.
Complete the first row of the table by filling in the expected real interest rate and the actual real interest rate before any change in the money supply.
Time Period
Before increase in MS.
Immediately after increase
in MS
Nominal Interest
Rate
(Percent)
12
12
Expected
Inflation
(Percent)
5
5
Actual
Inflation
(Percent)
S
10
The unanticipated change in inflation arbitranly benefits
Expected Real Interest
Rate
(Percent)
Actual Real Interest
Rate
(Percent)
Now suppose the Fed unexpectedly increases the growth rate of the money supply, causing the inflation rate to rise unexpectedly from 5% to 10% per
year.
Complete the second row of the table by filling in the expected and actual real interest rates on savings accounts immediately after the increase
the money supply (MS).
Now consider the long-run impact of the change in money growth and inflation. According to the Fisher effect, as expectations adjust to the new,
higher inflation rate, the nominal interest rate will to
% per year.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 19 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. (40 points) In their 1999 Applied Economics Letters paper, Zakir and Wunnava proposed the following specification in identifying the factors affecting infant mortality rates (IMR): IMR₁ = B₁+ B₁FERTILITY, + ß₂LNGNP; +߸LABOUR; + ßLABOUR² + B₂LITERACY, + BHEALTH; +ε₁ Where i=1,2,..., 117 (i.e., based on a cross-section of 117 countries) IMR = infant mortality rate-number of deaths before age 1 per 1000 live births FERTILITY = number of births per woman LNGNP = the natural logarithm of per capita GNP (note that GNP is measured in '000 of $s) LABOUR = percentage of women in the labor force LITERACY = female literacy rate HEALTH = expenditure on health care as percentage of GNP Following are their estimated regression results along with sample means (based on a cross-section of industrialized and third world countries for 1993). Mean of IMR: 44.983 Variable name Estimated t-ratio Mean coefficient FERTILITY 10.812 7.848 3.5556 LNGNP -6.998 -3.134 8.2585 LABOUR 4.135 3.359 40.051 LABOUR²…arrow_forwardWhich of the following is counted in the GNP of the United States? A) the value of services that are produced by state and local governments in the United States B) the profit earned by a restaurant located in the United States but owned by a Guatemalan company C) the wage of a foreign citizen who works in the United States for a U.S. firm D) the interest earned by a Brazilian bank on loans to a business firm located in the United Statesarrow_forwardGg.220.arrow_forward
- Kk.263.arrow_forwardCan you please answer (Question.4) below?arrow_forwardAssume we have the following simple Quantity Dependent demand and supply system for steel: Demand: Supply: Qa = 120 - 2 P Qs=8 P-80 Where Qa is the quantity of the commodity demanded at price P and Q is the quantity of the commodity supplied at price P. A: Draw the supply and demand curves for the above commodity. Clearly identify each curve and the horizontal and vertical intercept values for the demand curve. Also identify the vertical intercept value for the supply curve. BÜÄ B: Solve for the market equilibrium price and quantity. C: Calculate the numerical values for the consumer surplus and the producer surplus. D: Identify the consumer and producer surplus on the figure you graphed and carefully define the concept of both consumer and producer surplus. Explain why in the absence of externality a extern competitive market maximizes the sum of consumer and producer surplus. E: F: Numerically calculate total producer cost at the equilibrium quantity. Carefully identify the area of…arrow_forward
- Find the coefficient of x2y3z3 in the expansion of(x + y + z)8.arrow_forwardThe marginal cost of producing one more unit at a given quantity can be inferred byarrow_forwardExports of goods and services 1,872 Imports of goods and services 2,375 Net unilateral transfers -99 Net Investment Income 170 Capital Account -7 Net US acquisition of financial assets 958 Net US incurrence of liabilities 1,391 Net financial derivatives -14 Based on table above, the statistical discrepancy is Group of answer choices 15 8 0. -8 -15arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education