
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
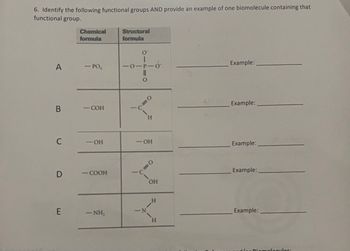
Transcribed Image Text:6. Identify the following functional groups AND provide an example of one biomolecule containing that
functional group.
A
B
C
D
E
Chemical
formula
- PO,
- COH
-OH
-COOH
-NH₂
Structural
formula
O
-O-P-0°
0=
0-
N
H
-OH
C=O
OH
H
H
Example:
Example:
Example:
Example:
Example:
Riomolecules:
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Introduction
Biomolecules are organic molecules that are found in living organisms and are essential for life. They include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), and various other types of smaller, organic molecules.
Biomolecules play important roles in the structural and functional organization of cells and tissues, and are involved in processes such as energy storage and transfer, communication between cells, and the regulation of metabolic pathways.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- H онн C-C-N -C C-N OH +H20 HH H. H N- C-N-C-C OH OH H. R R The chemical reaction illustrated in the accompanying figure H H C-N-C-C OH N- -C OH R R The chemical reaction illustrated in the accompanying figure O links two monomers to form a polymer separates two phospholipids in a bilayer breaks a peptide bond is a hydrolysis reaction in a polysaccharide A piece of DNA has the following sequence: 5' TCATGG 3'. What would be the sequence of the complementary strand? O 3'AGTACC 5' O S' AGTACC 3 O3 CCATGA 5 O s CCATGA 3 Refer to the accompanying figure. RNA at the beginning of the strands are shaded in lighter color. Identify th leading strand in this figure! O a O b HICIRarrow_forward3). reactions of the following alkyl iodide. Danny uses potassium tert-butoxide to promote the reaction while Claire uses water and high temperatures. One of their reactions has provided a single elimination isomer while the other has provided a mixture of elimination isomers. Organic chemistry students Danny and Claire are both performing elimination Me H20, heat Danny's Reaction Claire's Reaction H. Me a) Which student's reaction (Danny or Claire) has provided a single elimination isomer? b) Draw all the elimination isomers obtained from both students' reactions. c) Which of the dienes drawn (by you) in question 3b is the most stable? Circle that diene above.arrow_forwardThe structure of the dipeptide Gly-Asn is given by . The structures of the amino acids Gly and Asn are given below. NH2 H. ČH2 H3N-C-CO H. H3N-C-CO H. Asn Gly NH2 CH2 H H H2 C COO 2. H3N-C -C H. 1. H&N C C-NH C COO NH, NH2 CH2 H. H2 C C NH2 3. H3N-C C- -C COO 4. 0OC-C NH3" Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Ansuwers to save all answers. MacBook Air esc 吕0 DII DD F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 @ 2$ & 1 2 4 5 7 8 Q W E R Y | A S D F G K C V N M < CO # 3 HICHarrow_forward
- 30. The shown structure is a cyclic D-monosaccharide. Which of the following statements is true? HOCH₂ H OH H OH OH CH₂OH A. The chemical can react with methanol to form a hemiacetal in solution without forming an open chain structure B. The chemical needs to form an open chain structure to be able to react with methanol to produce a glycosidic linkage in solution C. Both A and B D. Neither A nor Barrow_forward6. b. Draw a box around the disulfide bridge in oxytocin, if present, or write "none". 7. Mark each peptide bond in oxytocin by making the corresponding line in the structure thicker or marking it with a different color. The first one is shown for you as an example (in dark orange). 8. Number the central carbon of each amino acid in oxytocin by pointing a small arrow to it or by circling the corresponding vertex in the image. Numbers 1 and 2 indicate the central carbons of the first and second amino acids of oxytocin, and are shown for you as an example. 9. Fill out the following table, listing amino acids that make up oxytocin in order, from the N terminus to the C terminus, characterizing each amino acid by the properties of its R group (side chains), and briefly indicating the reasoning for the characterization. You may consult amino acid groupings by category in the slides (or the textbook, p.49), but you must explain the reasoning for each in your own words. CO 1 AA# Abbre- Full…arrow_forwardF 9. In sugars that contain many chiral centers, only the chiral center that is most distant from the carbonyl carbon is designated as D (right) or L (left). Determine which of the structures below are D and L sugars. H-C-OH HIC OH H-C-OH I CH₂OH D-Ribose HO C-H H-C-OH H-C-OH I CH₂OH D-Arabinose H-C-OH HO-C-H H-C-OH H-C-OH T HO-C-H I H-C-OH I CH₂OH D-Xylose D-Aldoses Five carbons H-C-OH H-C-OH HO-C-H H-C-OH HO-C-H HO-C-H H-C-OH CH₂OH CH₂OH CH₂OH CH₂OH D-Ribose D-Arabinose D-Xylose D-Lyxose HO-C-H HO-C-H H- H-C-OH CHO IMPORTANT NOTE: most hexoses in living organism are D isomers. Thus, the D prefix is often omitted. DO NOT confuse this with amino acids. Remember that the most common amino acids in living organism are L isomers. L sugars are mirror images of D sugars. H-C-OH -OH 10. Sugars (monosaccharides) can be trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses, heptoses, etc., depending on the number of carbons they have. Determine the number of carbons in the structures above (#9) and determine…arrow_forward
- A Uracil B Adenine HN Cytosine Guanine 2 H₂N-C 6 3 N Which of the following nitrogenous bases is represented by this structure? 5 C C N 7 IZⓇ 8 CHarrow_forwardExplain these diagramsarrow_forwardMatch the following terms to the correct definition: disulfıde bonds V [ Choose ] molecular force between non-polar molecules resulting from temporary dipoles covalent bonds between two cysteines salt-bridges intermolecular interactions that occur between the R groups of positively and negatively charged residues bonds between R-groups, carbonyls and amides that are not used in forming the secondary structure van-der Waals forces [ Choose ] internal hydrogen bonds [ Choose ]arrow_forward
- Identify the functional groups in the following molecule as pointed by arrow A and B, then C and Darrow_forwardIdentify the names of the following molecules.arrow_forwardWhich of the following functional groups do NOT contain a carbonyl? Select all that apply. amide ketone O aldehyde etherarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education