
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
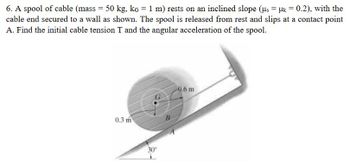
Transcribed Image Text:6. A spool of cable (mass = 50 kg, kg = 1 m) rests on an inclined slope (μs = μ = 0.2), with the
cable end secured to a wall as shown. The spool is released from rest and slips at a contact point
A. Find the initial cable tension T and the angular acceleration of the spool.
0.3 m
30°
B
-0.6 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The wheel is attached to the spring. The mass of the wheel is m=20 kg. The radius of the wheel is 0.6m. The radius of gyration KG=0.4 m. The spring's unstretched length is Lo=1.0 m. The stiffness coefficient of the spring is k=2.0 N/m. The wheel is released from rest at the state 1 when the angle between the spring and the vertical direction is 8-30°. The wheel rolls without slipping and passes the position at the state 2 when the angle is 8-0°. The spring's length at the state 2 is L2=4 m. (5) The stretched spring length of the spring at the state 2 is_ places) HULK ܪܐ TG नेता State 2 State 1 _(m) (two decimalarrow_forward4. A slender, rigid bar of mass m and length I is pinned to a massless collar as shown in the figure below. The collar and bar are initially stationary and slide on a frictionless rod. A force F is applied to the collar in the horizontal direction. Determine the acceleration of the collar at the instant that this force is applied. P Fightarrow_forwardThe figure shows a schematic of a simple Watt governor mechanism with the spindle 0102 rotating at an angular velocity w about a vertical axis. The balls at P and S have equal mass. Assume that there is no friction anywhere and all other components are massless and rigid. The vertical distance between the horizontal plane of rotation of the balls and the pivot O₁ is denoted by h. The value of h = 400 mm at a certain w. If w is doubled, the value of h will be mm. (0) g = 9.8 m/s₂ h Spindle O Q Sleeve (QR) Cylindrical Joint R Sarrow_forward
- A box with mass m = 2.75 kg rests on the top of a table. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the table is μs = 0.71 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is μk = 0.34. Write an expression for Fm the minimum force required to produce movement of the box on the top of the table. Solve numerically for the magnitude of the force Fm in Newtons. Write an expression for a, the box's acceleration, after it begins moving. (Assume the minimum force, Fm, continues to be applied.) Solve numerically for the acceleration, a in m/s2.arrow_forwardAn occupied cable car with a mass of 360 kg runs along the fixed overhead cable and is controlled by the attached cable at A with a tension of T = 1.8 kN. Force Pexerted on the wheel assembly by the cable. find the acceleration the cable car. wheel assembly O a. 0.45 ms 2 O b. 0.49 ms ² O c. 0.56 ms-² d. 0.53 ms 2 5 11 T GO W Tarrow_forwardProblem 1: The uniform drum shown weighs 80lb and has a radius of 0.5ft. Starting from rest, the cable wrapped around the drum is subjected to a vertical force P which resulted in a constant angular acceleration of 20 rad/s. Determine magnitude of P and the reaction at the support pin at O. Neglect the mass of the cable d = 20 80 - 2.48 32.2 r-0.5 %3Darrow_forward
- Problem: 15 (of 30) Do not round intermediate answers. Give your final answer(s) to three decimal places. Check your units. The uniform square steel plate has a mass of 12 kg and is resting on a smooth horizontal surface in the x-y plane. If a force P= 110 N is applied in the x-y plane to one corner in the direction shown, determine the magnitude of the initial acceleration of comer A. Hint: At the initial stage of motion when the plate begins to move, w= 0 because the plate is barely moving. a of A = 9 m/sec^2 A 500 mm P 500 mm 30° Check Answer for this Problem Closearrow_forwardThe wheel is attached to the spring. The mass of the wheel is m=20 kg. The radius of the wheel is 0.6m. The radius of gyration ke=0.4 m. The spring's unstretched length is Lo=1.0 m. The stiffness coefficient of the spring is k=2.0 N/m. The wheel is released from rest at the state 1 when the angle between the spring and the vertical direction is 8-30°. The wheel rolls without slipping and passes the position at the state 2 when the angle is 8=0°. The spring's length at the state 2 is L2=4 m. (3) The stretched spring length of the spring at the state 1 is_ places) 2₂ State 2 7717 State 1 _(m) (two decimalarrow_forwardthe cylinder with a mass m1=2kg and radius r=0,1m is placed at a plate with mass m2=4kg. We are applying force F at this plate. Find an acceleration of the plate, when the friction coefficient μ=0,2arrow_forward
- Problem 01 The thin plate ABCD has mass 20 kg and is held in the position shown by a wire BH and the two massless links AF and DE. What is the acceleration of the plate and the forces in each link immediately after the wire is cut? y = 30°. E F 0.3 m A D 0.5 m- H 9 B ↑ 0.25 m Carrow_forwardThe car shown in the figure has a mass of 2500 kgs and a center of mass at G. Determine the acceleration if the rear "driving" wheels are always slipping, whereas the front wheels are free to rotate. Neglect the mass of the wheels. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the wheels and the road is uk = 0.3. Determine also the normal forces on A and B.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY