
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Help please
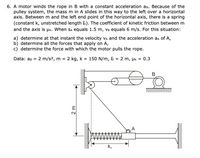
Transcribed Image Text:6. A motor winds the rope in B with a constant acceleration aB. Because of the
pulley system, the mass m in A slides in this way to the left over a horizontal
axis. Between m and the left end point of the horizontal axis, there is a spring
(constant k, unstretched length l). The coefficient of kinetic friction between m
and the axis is Pk. When Sa equals 1.5 m, VB equals 6 m/s. For this situation:
a) determine at that instant the velocity vA and the acceleration aa of A,
b) determine all the forces that apply on A,
c) determine the force with which the motor pulls the rope.
Data: ав 3
2 m/s2, m =
2 kg, k = 150 N/m, l
2 m, µk = 0.3
%D
В
SA
2m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A block of wood of mass 20 kg is supported as shown in the diagram. If the string suspending the 10 kg mass and connected to the 20 kg mass is light and inextensible and the coefficient of friction, u between the mass and the plane is 0.3 neglecting friction in the pulley (i) Compute the acceleration of the block. (ii) Determine the tension in the rope. 20 kg 10 kg 30°arrow_forwardI need help with part a, b, c, d.arrow_forwardFind the rato of masses m1/m2arrow_forward
- i asked this before but somone answered wrong and disnt explain. please answer again and explain thanks i will like.arrow_forwardblock C weighs 200lb is lifted by hoisting mechanism. the hoist is wrapped around compound drum B. drum b is rotating as a single unit and weighs 300 lbs. K(bar) is 4ft. a hoist tension (P) is rated 1.0 kips. And its power is being maintained by the power in Motor A. Determine the vertical acceleration of the block C and the resultant force on the bearing at O.arrow_forward15arrow_forward
- 1. Parcels are moved via conveyor with velocity vo down to a colinear incline that is static at point A where sliding begins. The parcels eventually fall off at point B, which is 7.0 m past A. If the coefficient of kinetic friction on the incline is 0.40, find the velocity of the conveyor belt, vo, such that the parcels have zero velocity at point B. 7m 15°arrow_forwardMary and her sister are playing with a cardboard box on the neighborhood hill. Mary climbs into the box, the total mass of the box with Mary in it is 115 kg. The box starts at rest at the beginning of the incline. The hill is at an incline of 28 degrees with respect to the horizontal.The static and kinectic friction between the box and hill is 0.4 and 0.2 respectively. Assume the box is sliding downhill. a. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the box? (same as Problem 3b)b. If the hill is 5m tall, what is the Mary's speed when she reaches the bottom?c. At the bottom of the hill, the ground becomes level, but the coefficients offriction do not change. How far will Mary slide before she comes to a stop?arrow_forwardThe 544g collar is free to slide on the smooth rod OA. The rod rotates about pin O at constant angular velocity, é. a =en + še, = a = RÔ?e, + RÖe, for a circular path, R = radius 2.1 Use N-T coordinates, draw a FBD and a kinetic diagram to determine the minimum value of é for which the collar will maintain contact with the stop at A throughout the rotation. 2.2 Would friction between the collar and the rod affect your result in 2.1?arrow_forward
- A 3.9-kg sphere S is being moved in a vertical plane by a robotic arm. When the angle 0 is 27°, the angular velocity of the arm about a horizontal axis through O is 52 deg/s clockwise and its angular acceleration is 179 deg/s² counterclockwise. In addition, the hydraulic element is being shortened at the constant rate of 600 mm/s. Determine the necessary minimum gripping force P if the coefficient of static friction between the sphere and the gripping surfaces is 0.46. Compare P with the minimum gripping force P required to hold the sphere in static equilibrium in the 27° position. 2.0 m Answers: P= Ps= i Z Z N Narrow_forward1.calculate the tension in each cable if the tension is in equilibrium 2.calculate the combined forces required by the 2 cables to lift the load with an acceleration of 0.2 per Square meters. 3.calculate the time needed to lift the load from the floor up to 9 meters givem that the acceleration upward is 0.2 per square meters.arrow_forward5. Three blocks are connected over two frictionless, massless pulleys by two inextensible, massless cords as shown in the figure. There is friction between block m and the horizontal surface of the table. If the block m, moves downward after being released from rest, then what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the blocks and the magnitude of the tension in the cords in terms of the masses of the blocks m, , and ms, the coefficient of kinetic friction between block my and the table, a. and the acceleration due to gravity, g. Include a force diagram or free-body diagram of the situation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L