
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285741550
Author: James Stewart
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
![**Problem 6: Prove the Trigonometric Identity**
Prove that:
\[ \cos^4 x - \sin^4 x = \cos 2x \]
This is a trigonometric identity that demonstrates the relationship between the fourth powers of sine and cosine functions and the double angle cosine. To prove this identity, utilize trigonometric identities and algebraic manipulation.
**Solution Outline:**
1. Start with the left side of the equation, \( \cos^4 x - \sin^4 x \).
2. Use the difference of squares identity:
\[ a^2 - b^2 = (a - b)(a + b) \]
Thus, express \( \cos^4 x - \sin^4 x \) as:
\[ (\cos^2 x - \sin^2 x)(\cos^2 x + \sin^2 x) \]
3. Recall the Pythagorean identity:
\[ \cos^2 x + \sin^2 x = 1 \]
Substitute this into the expression:
\[ (\cos^2 x - \sin^2 x)(1) = \cos^2 x - \sin^2 x \]
4. Use the double angle identity for cosine:
\[ \cos 2x = \cos^2 x - \sin^2 x \]
Conclude that:
\[ \cos^4 x - \sin^4 x = \cos 2x \]
This demonstrates the correctness of the identity through algebraic manipulation and application of known trigonometric identities.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/e708b20e-246d-43f9-aec0-b076b54d250e/93f55d8c-62ee-48df-8ea2-9c94d40447b8/xiscdc_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem 6: Prove the Trigonometric Identity**
Prove that:
\[ \cos^4 x - \sin^4 x = \cos 2x \]
This is a trigonometric identity that demonstrates the relationship between the fourth powers of sine and cosine functions and the double angle cosine. To prove this identity, utilize trigonometric identities and algebraic manipulation.
**Solution Outline:**
1. Start with the left side of the equation, \( \cos^4 x - \sin^4 x \).
2. Use the difference of squares identity:
\[ a^2 - b^2 = (a - b)(a + b) \]
Thus, express \( \cos^4 x - \sin^4 x \) as:
\[ (\cos^2 x - \sin^2 x)(\cos^2 x + \sin^2 x) \]
3. Recall the Pythagorean identity:
\[ \cos^2 x + \sin^2 x = 1 \]
Substitute this into the expression:
\[ (\cos^2 x - \sin^2 x)(1) = \cos^2 x - \sin^2 x \]
4. Use the double angle identity for cosine:
\[ \cos 2x = \cos^2 x - \sin^2 x \]
Conclude that:
\[ \cos^4 x - \sin^4 x = \cos 2x \]
This demonstrates the correctness of the identity through algebraic manipulation and application of known trigonometric identities.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
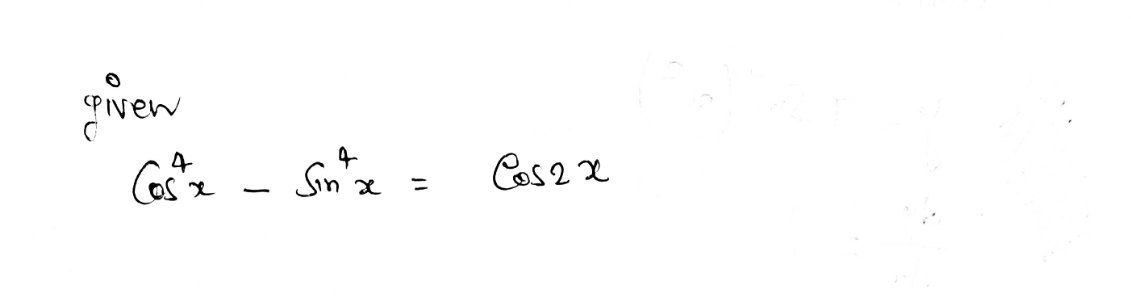
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134438986
Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134763644
Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781319050740
Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:9781337552516
Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:Cengage Learning