
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Can you please do 6
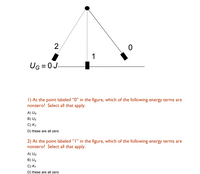
Transcribed Image Text:### Energy Terms in Pendulum Motion
#### Diagram Description:
The diagram depicts a simple pendulum in three different positions: 0, 1, and 2. The pendulum bob is shown hanging from a pivot point at the top, swinging to the left (position 2) and right (position 0) and as well as at the equilibrium position (position 1). The dotted lines represent the path of the pendulum as it swings back and forth. The gravitational potential energy at the equilibrium position (point 1) is marked as \( U_G = 0J \).
#### Questions:
1. **At the point labeled “0” in the figure, which of the following energy terms are nonzero? Select all that apply.**
- A) \( U_G \)
- B) \( U_S \)
- C) \( K_T \)
- D) these are all zero
2. **At the point labeled “1” in the figure, which of the following energy terms are nonzero? Select all that apply.**
- A) \( U_G \)
- B) \( U_S \)
- C) \( K_T \)
- D) these are all zero
#### Explanation:
- **\( U_G \)**: Gravitational potential energy.
- **\( U_S \)**: Spring potential energy (Note: This is not typically applicable in simple pendulum problems unless there is a spring involved, which is unusual).
- **\( K_T \)**: Kinetic energy.
#### Analysis of Pendulum Positions:
- At the point labeled "0" (maximum displacement to the right), the pendulum has maximum gravitational potential energy due to its height and zero kinetic energy if it comes momentarily to rest.
- At the point labeled "1" (equilibrium position), the gravitational potential energy is zero by definition, and the kinetic energy is maximal if there is no damping.
- At the point labeled "2" (maximum displacement to the left), similar to point "0", the pendulum has maximum gravitational potential energy and zero kinetic energy if it is momentarily at rest.
These aspects should be considered while selecting the appropriate answers for the questions provided.

Transcribed Image Text:### Energy Terms Problem Set
Below are questions related to energy terms at various points in a figure referred to, and during transitions between these points. Analyze each question to determine which energy terms are nonzero.
---
#### 3) At the point labeled “2” in the figure, which of the following energy terms are nonzero? Select all that apply.
A) \(U_g\)
B) \(U_s\)
C) \(K_T\)
D) These are all zero
---
#### 4) In moving from point “0” to point “1” in the figure, which of the following energy terms are nonzero? Select all that apply.
A) \(\Delta U_g\)
B) \(\Delta U_s\)
C) \(\Delta K_T\)
D) \(\Delta KE\)
E) \(\Delta PE\)
F) These are all zero
---
#### 5) In moving from point “0” to point “2” in the figure, which of the following energy terms are nonzero? Select all that apply.
A) \(\Delta U_g\)
B) \(\Delta U_s\)
C) \(\Delta K_T\)
D) \(\Delta KE\)
E) \(\Delta PE\)
F) These are all zero
---
#### 6) In moving from point “1” to point “2” in the figure, which of the following energy terms are nonzero? Select all that apply.
A) \(\Delta U_g\)
B) \(\Delta U_s\)
C) \(\Delta K_T\)
D) \(\Delta KE\)
E) \(\Delta PE\)
F) These are all zero
---
_Note to Educators: The accompanying figure referred to in the problem statements will provide the visual context needed to identify energy terms at specified points and transitions._
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON