
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Bookmarks Profiles Tab Window Help
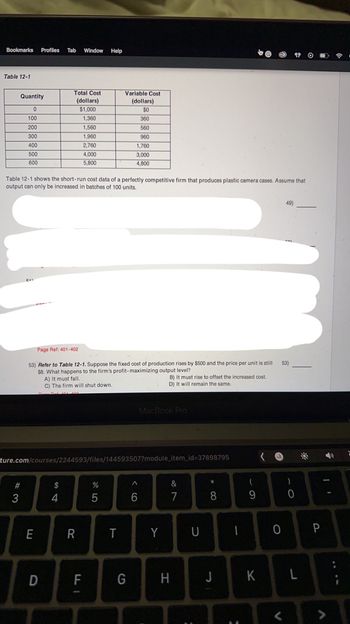
Table 12-1
Quantity
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
#3
Table 12-1 shows the short-run cost data of a perfectly competitive firm that produces plastic camera cases. Assume that
output can only be increased in batches of 100 units.
Total Cost
(dollars)
$1,000
1,360
1,560
1,960
2,760
E
Page Ref: 401-402
53) Refer to Table 12-1. Suppose the fixed cost of production rises by $500 and the price per unit is still
$8. What happens to the firm's profit-maximizing output level?
A) It must fall.
C) The firm will shut down.
101 100
D
$
4
4,000
5,800
ture.com/courses/2244593/files/144593507?module_item_id=37898795
R
FI
Variable Cost
(dollars)
$0
360
560
960
1,760
3,000
4,800
%
5
T
G
MacBook Pro
B) It must rise to offset the increased cost.
D) It will remain the same.
^
6
Y
87
&
H
U
*
8
J
-
(
9
K
O
V
49)
53)
)
0
L
P
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If the short-run marginal costs of producing a good are $30 for the first 500 units and $40 for each additional unit beyond 500, then in the short run, if the market price of output is $31, a profit-maximizing firm will produce as much output as possible since there are constant returns to scale. produce up to the point where average costs equal $31. produce exactly 500 units. not produce at all, since marginal costs are increasing. produce a level of output where its revenue equals marginal costs.arrow_forwardPROBLEM (4) The market for plastic toys is perfectly competitive, and it is composed of many identical firms, each with the total cost function TC(q) = ½ q² + 40q + 2,450 (a) What is the short run shut down price and the long run entry/exit price for this market? (b) Carefully draw the short run supply graph of an individual firm, and separately the long run aggregate (market) supply graph for this industry. (c) What is the optimal quantity to produce for the firm and the corresponding net profit, if the market price is (i) %3D $30? (ii) $70? Now, suppose in addition that the market demand is Q = 18,000 - 100p. (d) In the long run equilibrium, what is the market price and quantity? How many units does each firm in the market produce, and what is its net profit? How many firms are there in the long run equilibrium? (e) Suppose the government imposes a $14 per unit tax on plastic toys. Re-answer part (d) %3Darrow_forwardManagers of perfectly competitive firms must be cautious when deciding to permanently expand (or contract) the scale of production. What factors should go into the decision to expand the scale of production if the market price of your product increases? (select all that apply) A. Whether your product has a complement in consumption B. If the scale expansion is appropriate and not in excess C. If other firms are likely to enter the market D. Whether the price change is temporary or permanentarrow_forward
- Illustrate to the right, a graph showing a company being profitable in a competitive market in the Long Run selling its product at Market Price (MP*) based on its Average Variable Cost (AVC) and Average Total Cost (ATC) and Marginal Cost (MC). Identify each key point on the graph. Observe the Short - Run Loss information illustrated in the graph to the right. With respect to Price (P*"), Average Variable Cost (AVC), Average Total Cost (ATC), Marginal Revenue (MR), and Marginal Cost (MC), what assumption would you make if the firm was selling its product at P What would happen if this were to continue in the long run? Is there a Shut Down point? ** ? Notice that MR = Parrow_forwardAssume that the marginal revenue equals rising marginal cost at 100 units of output. At this output level, a profit-maximizing firm's total fixed cost is $700 and its average variable costs are $5. If the price of the product is $4 per unit and the firm produces the profit-maximizing level of output, How much profit firm will earn ?arrow_forwardUse the following statements to answer this question: 1) The firm’s decision to produce zero output when the price is less than the average variable cost of production is known as the shutdown rule 2)The firm’s supply decision is to generate zero output for all prices below the minimum AVC. A) 1 and 2 are true b)1 is true and 2 is false c)2 is true and 1 is false d) 1 and 2 are falsearrow_forward
- Question 23 A competitive firm has a total cost function in dollars of the form C(q)= 100–4q + q^2, where q is output. Suppose the market price is $10 per unit of output. What is the firm’s short run point elasticity of supply? a) 20/7 b) 5/7 c) 10/7 d) 0.5 e) 2arrow_forwardConsider a kettle firm A in a perfectly competitive market. Table 1 shows the quantity produced per hour (Q) and the total cost (TC) in the short run. Quantity 0 12345C70 2 6 8 Total cost 17 30 40 55 75 100 130 165 210 Fixed cost 17 17 17 17 17 17 17 17arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education