
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Redox is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the substrate change. Electrons will move from the right electrode to the left. Describe the role/what happens to copper and silver in the redox process. Copper is in the left beaker and silver is in the right.
Example attached

Transcribed Image Text:A voltaic cell is a device that converts the chemical energy of a spontaneous redox reaction into
electrical energy. Let's consider Zinc and copper, copper is in the left beaker and zinc is in the right
beaker. The anode is an electrode where oxidation occurs. The cathode is an electrode where reduction
occurs. The zinc electrode is located in the anode and the cu electrode is located in the cathode.
In a redox reaction, the reducing agent loses electrons and the oxidizing agent gains electrons. In this
case, Zinc metal is the reducing agent because it loses electrons. In this case, zinc metal is the reducing
agent because it loses electrons and gets oxidized to the Zn2+ ion. Cu2+ ion is an oxidizing agent
because it gains electrons and gets reduced to Cu metal. Elemental zinc has an oxidation state of zero
and loses two electrons which raises its oxidation state to +2. Cu2+ ion has an oxidation state of +2, and
gains electrons from zinc, which reduces its oxidation state to zero. As zinc loses two of its electrons, it
becomes ionized +2, and its ions move into the solution. At the same time, because the copper ions gain
two electrons, they become neutral copper metal, which is deposited on the surface of the zinc. Zinc
metal dissolves the electrolyte during the reaction and the Zn sheet thins. Oxidation half-reactions are
represented as follows: Zn0 ➜ Zn+2+2e- (reducing agent). The reduction half-reaction is represented as
follows: Cu+2+2e-→ Cu (oxidizing agent).
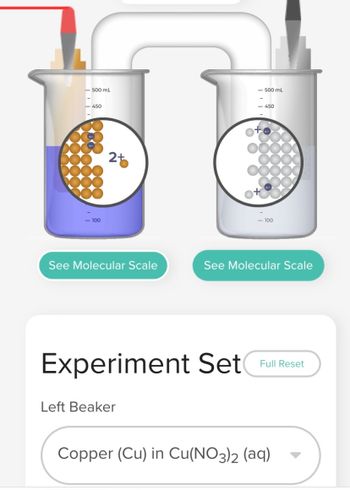
Transcribed Image Text:- 500 mL
450
- 100
25
See Molecular Scale
- 500 mL
Left Beaker
<-450
- 100
See Molecular Scale
Experiment Set Full Reset
Copper (Cu) in Cu(NO3)2 (aq)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which statement is NOT true? During the corrosion, metal cations transform into metal atoms. During the corrosion, metal atoms oxidized. The corroding metal surface is called the anode. During the corrosion, metal atoms lose electrons.arrow_forward232. Subject :- Chemistryarrow_forward12. Which of the following statements is not correct regarding the following redox reaction? MnO2 + 4HCI –→ MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O Manganese(IV) oxide is the oxidizing agent. b. Chloride is oxidized. a. The oxidation number of Mn changes from +4 to +2. d. The oxidation number of Cl changes from -1 to 0. One electron is transferred from manganese to each chloride. с. е.arrow_forward
- what is the oxidation number of carbon in each of the following compounds or ions? 1.)CO 2.)CO2 3.)CCL4 4.)Na2CO2arrow_forwardIdentify the species oxidized, the species reduced, the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent in the following electron-transfer reaction.2Cl-(aq) + F2(g) Cl2(g) + 2F-(aq) species oxidized species reduced oxidizing agent reducing agent As the reaction proceeds, electrons are transferred from to .arrow_forwardIn the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, sodium is reduced sodium is oxidized sodium is both oxidized and reduced chloride is reducedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY