
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
can sameone solve this thanks
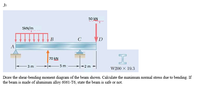
Transcribed Image Text:2:
50 KN
5kN/m
В
C
D
A
I
70 kN
- 3 m
5 m
-2 m
W200 x 19.3
Draw the shear-bending moment diagram of the beam shown. Calculate the maximum normal stress due to bending. If
the beam is made of aluminum alloy 6061-T6, state the beam is safe or not.
H
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please by using this formula Thanks..arrow_forwardhow did you know k=2.3? where did th evalue of 2.3 come from?arrow_forwardQuestions T 40 mm TABLE 3.1. Coefficients for Rectangular Bars in Torsion a/b C₁ C₂ 1.0 0.208 0.1406 1.2 0.219 0.1661 60 mm 1.5 0.231 0.1958 2.0 0.246 0.229 2.5 0.258 0.249 3.0 0.267 0.263 4.0 0.282 0.281 5.0 0.291 0.291 N 10.0 0.312 0.312 0.333 0.333 1. Determine the largest torque T which may be applied to end of the solid bar which is shown in the diagram above, knowing that the maximum allowable shear stress = 107 MPa and G = 40 GPa. Provide the answer in kNm with precision to two decimal points. 2. The same solid bar is subjected to a torque of 1.5 kNm. Its total length, denoted as z, is 601 mm. What will be the angle of twist? Provide the answer in degrees with precision to two decimal points.arrow_forward
- Rigid bar ABCD is loaded and supported as shown. Steel [E = 28800 ksi] bars (1) and (2) are unstressed before the load P is applied. Bar (1) has a cross-sectional area of 0.62 in.2 and bar (2) has a cross-sectional area of 0.3 in.2. After load P is applied, the strain in bar (1) is found to be 610 μe. Assume L₁=59 in., L2=98 in., a=39 in., b=26 in., and c=24 in. Determine: (a) the stresses in bars (1) and (2). (b) the vertical deflection VD of point D on the rigid bar. (c) the load P. W (2) (1) L₁ a B L2 b C D Parrow_forwardProblem 2: Given are matrices A, B, C and D. 21 -4 -26 7 -1 -2 2 -2 10 -8 A B = -1 3 -13 25 -11 -1 -1 21 -2 25 -18 1 -26 1/3 C =| -16 8. -7 D 10 -100 10y 7 -10 13 -98 1/2 22 Solve for: a) A + D b) 2C – 3A + B – 10D c) B +D - 2C + 3A d) В + D e) С - Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning