
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
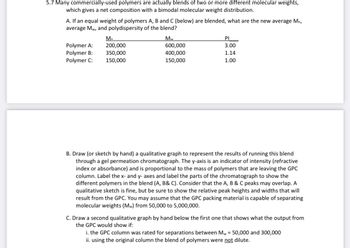
Transcribed Image Text:5.7 Many commercially-used polymers are actually blends of two or more different molecular weights,
which gives a net composition with a bimodal molecular weight distribution.
A. If an equal weight of polymers A, B and C (below) are blended, what are the new average Mn,
average Mw, and polydispersity of the blend?
Polymer A:
Polymer B:
Polymer C:
M₂
200,000
350,000
150,000
Mw
600,000
400,000
150,000
PI
3.00
1.14
1.00
B. Draw (or sketch by hand) a qualitative graph to represent the results of running this blend
through a gel permeation chromatograph. The y-axis is an indicator of intensity (refractive
index or absorbance) and is proportional to the mass of polymers that are leaving the GPC
column. Label the x- and y- axes and label the parts of the chromatograph to show the
different polymers in the blend (A, B& C). Consider that the A, B & C peaks may overlap. A
qualitative sketch is fine, but be sure to show the relative peak heights and widths that will
result from the GPC. You may assume that the GPC packing material is capable of separating
molecular weights (Mw) from 50,000 to 5,000,000.
C. Draw a second qualitative graph by hand below the first one that shows what the output from
the GPC would show if:
i. the GPC column was rated for separations between Mw = 50,000 and 300,000
ii. using the original column the blend of polymers were not dilute.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 25 1. T The specific heat of water is 4.18 J-g-¹ K-¹. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 500 g of water from 20 °C to the boiling point (100 °C)? What is the molar heat capacity of water? Specific heat of 11₂0= 4₁185.5-1-14-1 motor mass of waver: 18,001g/mol mas of water = 5003 a. 5 D HRAMCAT Hear = 500g (thit 3). 2014 Initial Temp: 20%= 2931 molar hear capacity & spresse head capacting of w Anal Temp: 100% = 3731 Hear =? Molar heat coperty? Hent = 1672003 Hear = 167.23 = 4.182 * 75,23/10.19 2. In studying the energy generated by a person, you may view the person roughly as a constant pressure calorimeter using sugar (i.e., sucrose, C12H22O11) to generate power. The reaction of table sugar in a calorimeter is given by C. Q b. Calculate the enthalpy of combustion per mole of sugar utilization. Does the result of your calculation make sense? C12H22O11(s)+120₂(g) →12CO₂(g)+11H₂O+heat. →give the magnitudo (no sign is recessure) What is the heat released by consuming one…arrow_forwardShow the work.arrow_forward4 attempts left Check my work Enter your answer in the provided box. Report probi Water gas, a mixthře of H, and CO,, is a fuel made by reacting steam with red-hot coke (a by product of coal distillation): Hint Solution H,O(g) +C(s) S CO(g) +H;(g) Guided Soluti Using a table of thermodynamic data, estimate the temperature at which the reaction begins to favor the formation of products. °Carrow_forward
- 4) You are stranded and have two plastic jugs, you decide to burn one of the jugs to to send smoke signals and to keep yourself warm, and you decide to save the other jug to carry and store water. One jug is made out of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and one is made out of polypropylene (PP). Which jug do you choose to burn and why? Combustion of PVC Combustion of PP AHFPVC = 29.6 kJ/mole C₂H3Cl(g) + O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + H₂O(g) + HCl(g) C3H6(g) + O2(g) → CO₂(g) + H₂O(g) AHFPP = 20.6 kJ/molearrow_forwardCengage Learning OWLv2 | Online teaching and b Cengage Learning OWLv2 | O ☑ Inbox (4,532) - erica.e.2022@ × + C prod03-cnow-owl.cengagenow.com/ilrn/takeAssignment/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator-assignment-take CH 18 Thermodynamics [Review Topics] [References] 1. Compare Absolute Entropies 2 pt Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. For the reaction 2. Standard Entropy of Reaction (Enh...2 pt (M) N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3 (9) 3. AS surroundings: Calculate (Enhan... 2 pt 1req ΔΗ = - - 92.2 kJ and AS° = - 199 J/K 4. AG° = AH-TAS° (Enhanced) 2 pt (M) 5. AG: Predict Signs 2 pt (M) The equilibrium constant for this reaction at 273.0 K is Assume that AH° and AS° are independent of temperature. 6. AG: Enthalpy, Entropy and Tempera..2 pt (M) Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 3 more group attempts remaining 7. AG from Free Energies of Formatio...2 pt 8. Calculate K from AG° 2 pt 1req 9. Calculate K from AH° and AS° (E... 2 pt 1req Question Question O ☑ Question…arrow_forwardAluminum-Lithium alloys have been developed by aircraft industry to reduce the weight and improve the performance of an aircraft. A commercial aircraft skin material having a density of 2.47g/cm? is desired. What is the Li wt% that is required on that material alloy? Density of lithium = 0.534g/cm? Density of aluminum = 2.7g/cm a. 12.28 wt% b. 9.7 wt% c. 4.51 wt% d. 2.3 wt%arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY