
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305081550
Author: Braja M. Das
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
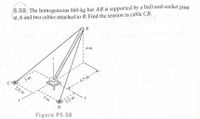
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem 5.58**
The homogeneous 860-kg bar \( AB \) is supported by a ball-and-socket joint at \( A \) and two cables attached to \( B \). Find the tension in cable \( CB \).
**Diagram Description (Figure P5.58):**
The diagram illustrates a three-dimensional setup where a bar \( AB \) is supported by a joint at point \( A \) and two cables extending from point \( B \).
- The bar \( AB \) is leaning upwards and away from the coordinate plane, attached at the bottom by a ball-and-socket joint located at point \( A \).
- Point \( B \) is situated above and slightly forward of the joint, at a height of 4 meters along the \( z \)-axis.
- The base coordinates measure distances from \( A \) as follows:
- \( B \) is located 4.5 meters along the \( y \)-axis.
- Two additional points, \( C \) and \( D \), serve as anchoring positions for the cables:
- Point \( C \) is 3 meters along the \( x \)-axis and 2.6 meters along the \( y \)-axis.
- Point \( D \) is 3 meters along the \( x \)-axis and 2.2 meters along the \( y \)-axis.
This configuration shows the spatial relationship and measurement points necessary to calculate the tension in cable \( CB \).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Refer to Figure P6.4. A strip load of q = 900 lb/ft2 is applied over a width B = 36 ft. Determine the increase in vertical stress at point A located z = 15 ft below the surface. Given: x = 27 ft. Figure P6.4arrow_forwardFor the beam shown: (a) determine the distance a for which the maximum positive and negative bending moments in the beam are equal; and (b) draw the corresponding shear and bending moment diagrams for the beam.arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305084766
Author:Saeed Moaveni
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781111988609
Author:Charles Gilmore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning