
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Even when the head is held erect, as shown in the figure, its center of mass is not directly over the principal point of support (the atlanto-occipital joint). The muscles at the back of the neck should therefore exert a force to keep the head erect. That is why your head falls forward when you fall asleep in class.
Part (a) If the head has a weight of 48.3 N, calculate the force in units of newtons exerted by these muscles using the information in the figure.
Part (b) What is the force in newtons exerted by the pivot on the head?
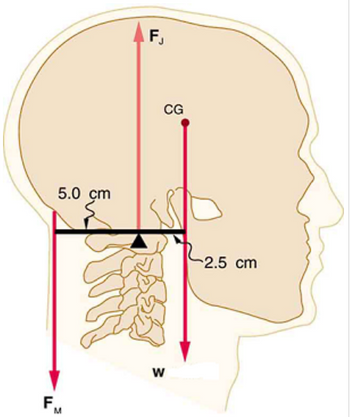
Transcribed Image Text:5.0 cm
F.
M
FJ
CG
W
2.5 cm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a method for measuring the mass of a person’s arm in anatomical studies. The subject lies on her back, extends her relaxed arm to the side and two scales are placed below the arm. One is placed under the elbow and the other under the back of her hand. Construct a problem in which you calculate the mass of the arm and find its center of mass based on the scale readings and the distances of the scales from the shoulder joint. You must include a free body diagram of the arm to direct the analysis. Consider changing the position of the scale under the hand to provide more information, if needed. You may wish to consult references to obtain reasonable mass values.arrow_forwardWhen you bend your knee, the quadriceps muscle is stretched. This increases the tension in the quadriceps tendon attached to your kneecap (patella), which, in turn, increases the tension in the patella tendon that attaches your kneecap to your lower leg bone (tibia). Simultaneously, the end of your upper leg bone (femur) pushes outward on the patella. Shown is how these parts of a knee joint are arranged. What size force does the femur exert on the kneecap if the tendons are oriented as in the figure and the tension in each tendon is 60 N?arrow_forwardSuppose a 905-kg car is on the bridge in the figure with its center of mass halfway between the hinges and the cable attachment. (The bridge is supported by the cable and hinges only.) The mass of the bridge is 2500 kg. Find the tension, in newtons, in the cable.arrow_forward
- For a meter stick of mass 147.89 g, it is found that its weight can be balanced by hanging a 183.99 g mass at the 95.00 cm mark. Where does the center of the weight of the meter stick locate on the meter stick? Enter the number in cm unit.arrow_forwardA taho vendor carries a 1.5 m long light plank over his shoulder. At the ends of the plank are two buckets weighing 40 N and 60 N respectively. (a) Find the value of force F exerted by his shoulder. Neglect the weight of the plank. ( b) Where should he support the plank for it to be balanced horizontallyarrow_forwardA new art exhibit featuring mobile works is going up in the Holland, MI, area. One piece is shown in the figure. The 140-N uniform beam is pinned to the ground by a pivot. The beam is supported by a cable (attached to the center of the beam) to allow for each of the shoes to hang freely. Each individual shoe has a weight of 9.5-N. 1.If one shoe is attached two-fifths of the way up the beam and another shoe is attached and three-fifths of the way up the beam, with θc = 19.5° and θb = 33.5° as shown in the figure, what is the tension in the cable, in newtons?arrow_forward
- Two children push on opposite sides of a door during play. Both push horizontally and perpendicular to the door. One child pushes with a force of 12.5 N at a distance of 0.750 m from the hinges, and the second child pushes at a distance of 0.550 m. What force must the second child exert to keep the door from moving? (assume friction is negligible)arrow_forwardA 68 kg man is in the prone position while during pushups. His feet and hands are 95 cm and 42 cm away respectively from his center of mass. What is the normal force exerted by on each (a) hand and (b) foot?arrow_forwardThe forearm shown below is positioned at an angle with respect to the upper arm, and a 5.6 kg mass is held in the hand. The total mass of the forearm and hand is 2.1 kg, and their center of mass is 16.1 cm from the elbow. (Assume the biceps muscle exerts a force on the forearm that acts vertically.) 5.6 kg B 37.5 cm 4.0 cm (a) What is the magnitude of the force (in N) that the biceps muscle exerts on the forearm for 0-60%7 N (b) What is the magnitude of the force on the elbow joint (in N) for the same angle? N (c) How do these forces depend on the angle 07 The force that the biceps muscle exerts increases and the force on the elbow joint decreases as increases. They both decrease as @ increases. They both increase as increases. They do not depend on 0. The force that the biceps muscle exerts decreases and the force on the elbow joint increases as increases.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON