
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
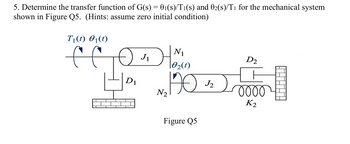
Transcribed Image Text:5. Determine the transfer function of G(s) = 01(s)/T₁(s) and 02(s)/T₁ for the mechanical system
shown in Figure Q5. (Hints: assume zero initial condition)
T₁(t) 01(t)
102(1)
Ол
N1
D1
D2
No. 1790220000
N2
Figure Q5
K2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Solve the following without the use of AI. Show all steps. Thank You!arrow_forwarda) Suspension system of a car. Finding the transfer function F₁(s) = Y(s)/R(t) and F₂ (s) = Q(s)/R(t), consider the initial conditions equal to zero. car chassis www K₂ M₂ 1 Tire M₁ K₁ B₁ y(t)= output q(t) r(t)= input Where [r, q, y] are positions, [k1, k2] are spring constants. [B₁] coefficient of viscous friction, [M₁, M₂] masses. b) Find the answer in time q(t) of the previous system. With the following Ns values: M₁ = 1 kg, M₂ = 0 kg, k₁ = 4 N/m, k₂ = 0 N/m, B₁. = 1 Ns/m, considered m a unit step input, that is, U(s) = 1/sarrow_forwardAll values equal to 1arrow_forward
- Do not give answer in image and hand writingarrow_forwardPlease Help with this question. Show clear steps and highlight the answers.arrow_forwarda) Find the transfer function F₁(s) = 01(s)/T(s) of the rotational system. Consider the initial conditions equal to zero. Goth G browse, T(t) B J₁ B. , B3 = 05 B₂ = K₁ Where [k₁, k₂] spring constant, [B₂] coefficients of viscous friction, [B₂, B3] are coefficients of dry friction, U₁] moment of inertia, [0₁] angular position, T(t) torque or mechanical torque of entrance. 1₁=kg m², B₁ = 3 ms 10 rad consider a unit step input, that is, T(s) = 1/s b) Find the answer at time 0₁ (t) of the previous system with the following values: Nm 1 Nms 2 rad Nms 1 rad , K₂ = 45 rad' Ba Nm rad my E K₂ ,K₁₂ = 1;arrow_forward
- A velocity of a vehicle is required to be controlled and maintained constant even if there are disturbances because of wind, or road surface variations. The forces that are applied on the vehicle are the engine force (u), damping/resistive force (b*v) that opposing the motion, and inertial force (m*a). A simplified model is shown in the free body diagram below. From the free body diagram, the ordinary differential equation of the vehicle is: m * dv(t)/ dt + bv(t) = u (t) Where: v (m/s) is the velocity of the vehicle, b [Ns/m] is the damping coefficient, m [kg] is the vehicle mass, u [N] is the engine force. Question: Assume that the vehicle initially starts from zero velocity and zero acceleration. Then, (Note that the velocity (v) is the output and the force (w) is the input to the system): A. Use Laplace transform of the differential equation to determine the transfer function of the system.arrow_forward02(s). T(s) Find the transfer function G(s) Tt) 1 N-m/rad 1 N-m/rad I kg-m? 1 N-m-s/rad 1 N-m-s/rad Figure: Rotational mechanical system.arrow_forwardQ5: Given the rotational system shown in below, find the transfer function G(s)= 01(s)/T(s) D K2 Please help ASAP. Pls show all steps and calculations. Make sure to find theta1(s)/T(s)arrow_forward
- A velocity of a vehicle is required to be controlled and maintained constant even if there are disturbances because of wind, or road surface variations. The forces that are applied on the vehicle are the engine force (u), damping/resistive force (b*v) that opposing the motion, and inertial force (m*a). A simplified model is shown in the free body diagram below. From the free body diagram, the ordinary differential equation of the vehicle is: m * dv(t)/ dt + bv(t) = u (t) Where: v (m/s) is the velocity of the vehicle, b [Ns/m] is the damping coefficient, m [kg] is the vehicle mass, u [N] is the engine force. Question: Assume that the vehicle initially starts from zero velocity and zero acceleration. Then, (Note that the velocity (v) is the output and the force (w) is the input to the system): 1. What is the order of this system?arrow_forwardRotational Mechanical System: Find the transfer function for each rotational mechanicalnetwork shown belowarrow_forwardPlease solve the following question. Note that the second picture is the solution of the question from the book, I just want to know the steps to reach it.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY