
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
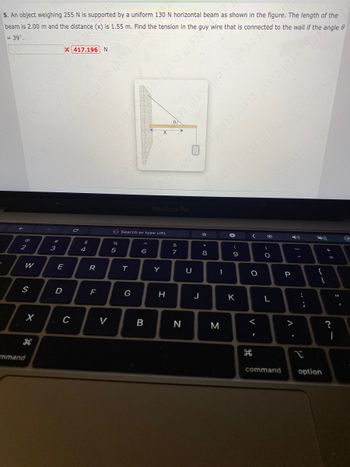
Transcribed Image Text:P
5. An object weighing 255 N is supported by a uniform 130 N horizontal beam as shown in the figure. The length of the
beam is 2.00 m and the distance (x) is 1.55 m. Find the tension in the guy wire that is connected to the wall if the angle
= 39⁰.
@
2
W
S
X
mmand
#
w =
3
E
D
X417.196 N
C
C
$
4
R
F
V
G Search or type URL
on se
%
5
T
G
6
B
MacBook Pro
Y
0
H
&
7
N
U
1332 jj1332
J
32 jj1332 jil332 jj1332 jj1332 jjl332
☆ * 00
M
-
→
- O
9
K
32 jjl332 jj1332 jj1332 j
H
<
O
<
)
O
L
command
P
..
€
-
....
{
+ 11
[
option
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Item 22 A uniform ladder of mass m and length l, leans at an angle against a wall, see the figure. (Figure 1) The coefficients of static friction between ladder-ground and ladder-wall are μc and μw, respectively. The ladder will be on the verge of slipping when both the static friction forces due to the ground and due to the wall take on their maximum values. Figure HG l mg "w 1 of 1 Part B emin = Submit "Leaning ladder problems" are often analyzed under the seemingly unrealistic assumption that the wall is frictionless. You wish to investigate the magnitude of error introduced by modeling the wall as frictionless, if in reality it is frictional. Using the relation found in part A, calculate the true value of min for a frictional wall, taking uc = μw = 0.50. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Part C Omin = Submit μA Part D Value Request Answer Determine the approximate value of min for the "frictionless wall" model by taking μ = 0.50 and…arrow_forwardA UNIFORM ROD OF LENGTH 3M AND WEIGHT 100N, WITH ENDS A ANDB RESTING ON TWO BRACKETS, BEARS 5ØN WEIGHT 0.5M FROM END A AND 150N WEIGHT 2M FROM FIRST WEIGHT. FIND THE REACTION FORCES AT B AND A. FB FA Aarrow_forwardPlease asaparrow_forward
- A uniform ladder 10.o m long weighing 50.0 N rests against a smooth wall (no frictional force between ladder and wall). If the coefficient of static friction is .360 and makes a 60 degree angle with respect to the horizontal, what is the frictional force and how far along the ladder can a 70.0 kg painter climb before ladder begins to slip?arrow_forwardA 6.0 m long ladder AB leans against a smooth wall making an angle of 60º with the floor (Figure 3). The ladder is uniform and has a mass of 20.0 kg.(a) Determine the forces exerted on the ladder by the floor and the wall (i.e. at A and B, respectively).(b) Determine the minimum value of the coefficient of static friction to prevent the ladder from slipping.arrow_forward2. A 3.0-m-long ladder leans against a wall at an angle of 60° with respect to the floor. What is the minimum value of us, the coefficient of static friction with the ground, that will prevent the ladder from slipping? Assume that friction between the ladder and the wall is negligible. Center of gravity 19 TULO L 60⁰ Weight acts at the center of gravity. Known L-30 m Find Me Contro <= 0 about this point. Static friction prevents slipping.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON