Question
Please be very sure of the answer you upload as I got multiple answers from your platform for this question. Also please write the answer on paper as it becomes really hard to understand the solution if its typed .
Transcribed Image Text:1:11 > M
@ l 94%i
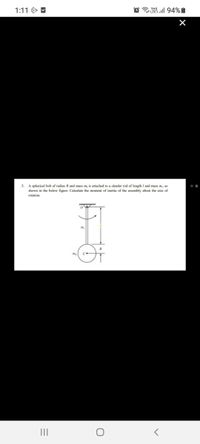
A spherical bob of radius R and mass m, is attached to a slender rod of length / and mass m, as
shown in the below figure. Calculate the moment of inertia of the assembly about the axis of
rotation
II
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In the process of using the scientific method, a researcher: O Directly tests both the null and alternative hypotheses. O Directly tests only the alternative hypothesis because this is the hypothesis of interest. O Directly tests only the null hypothesis because this is the hypothesis of interest. O Directly tests only the null hypothesis because the null hypothesis leads to a specific prediction that can be compared with data. O Can not directly test either hypothesis.arrow_forwardA Block-Spring System A block of mass 1.0 kg is attached to horizontal spring that has a force constant of 2,000 N/m as shown in figure (a). The spring is compressed 3.0 cm and then released from rest as in figure (b). (a) A block attached to a spring is pushed inward from an initial position x -0 by an external agent. (b) At position x, the block is released from rest and the spring pushes it to the right. x = 0 (For the following, when entering a mathematical expression, do not substitute numerical values; use variables only.) (a) Calculate the speed of the block as it passes through the equilibrium positio x = 0 if the surface is frictionle SOLUTION Conceptualize This situation has been discussed before, and it is easy to visualize the block being pushed to the right by the spring and moving with some speed at x = 0. Categorize We identify the system as the block and model the block as [--Select-- Vsystem. Analyze In this situation, the block starts with v, = 0 at x, = -3.0 cm, and…arrow_forwardPlease please solve accurate and exact answer please sir it's very importantarrow_forward
- I would like a step by step process with formulas used and drawings, along with therefore statementsarrow_forwarduse guess method as mention below if you cant use it dont do the question at all please do it in guss method no other way Solving problems in Physics, we must always use GUESS method.Guess stands for: Guess: G Here you write down what is given in the questionUnknown: U Here you list what you have to calculate, to solve for.Equations: E here you list all the formulas you need to use to solve the problemSubstitution: S This first letter S in the word, you will just substitute what is given in theformula. You do not calculate anything. The calculations will occur at the second S: Solve. Whatis very important here is to carry with you the units of measure in the formula. Not only thenumbers. This is very important, once again.Solve: S The last step, second S, you will solve what you plugged in the first S for Substitution.Very important here is to manipulate the units of measure such that the final units of measureto be proved by your work. This part is very important, since you will…arrow_forwardActivity 3: Circles and Pi Collect 10 things that are circular shaped. For example, an old CD, a Bike tire, cups or plates, basketball, flower pots, a quarter, hula hoop, soup can, poker chip, barrel or frisbee. The LARGER range in diameters the items are, the better your results will be. Indicate the items used in your data table. Measure the diameter of each circular shape and record this information in Data Table 2. Measure the circumference of cach circular shape. It may be casier to roll it or to wrap a piece of string or a paper strip around the circle, marking the distance around. Then you can straighten the string or paper strip on a ruler to determine the total circumference. NOTE: If you are measuring something which is tapered, such as some drinking glasses, ensure you measure the circumference at exactly the same position you measure the diameter (e.g, at the rim or at the base). Data Table 2: Measurements of Circles Item Description Diameter D (mm) Circumference C (mm) 1 2…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios