
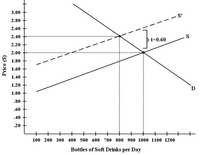
5) There have been proposals that a tax be imposed on sugar-laden soft drinks in an attempt to reduce their consumption. Assume for simplicity that all bottled soft drinks are the same size. Suppose the initial
a) Refer to Figure 2. Suppose the government imposes a tax of $0.60 per soft drink purchased. The
b) Refer to Figure 2. Suppose the government imposes a tax of $0.60 per soft drink purchased. The after-tax price received by the seller becomes =
c) Refer to Figure 2. Suppose the government imposes a tax of $0.60 per soft drink purchased. The government total tax revenue from sales of soft drinks is =
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- D(x) is the price, in dollars per unit, that consumers are willing to pay for x units of an item, and S(x) is the price, in dollars per unit, that producers are willing to accept for x units. Find (a) the equilibrium point, (b) the consumer surplus at the equilibrium point, and (c) the producer surplus at the equilibrium point. D(x)=(x−9)^2, S(x)=x^2+6x+57arrow_forwardThe demand and supply functions for three (03) goods are given as follows: Dx = 100-3Px+Py+3Pz Dy = 80+Px-2Py-Pz Dz = 120+3Px-Py-4Pz Sx = -10+Px Sy = -20+3Py Sz = -30+2Pz The equilibrium prices and quantities of all three goods are? The government decides to: a) Impose a 25% Tax on X? b) Impose a 5 Rs /unit Tax on Y? c) Give a 10% subsidy on good z? Analyze the impact of each of these policies separately on equilibrium prices and quantities? Analyze the impact of each of these policies separately on equilibrium prices and quantities? Provide theoretical justification (using diagrams) of all results obtained?arrow_forwardFind the consumer surplus at the equilibrium 13) D(x)= 5 – 3x; x = 1 A $1.50 B) $6arrow_forward
- 110 The demand for a particular item is given by the function D(x) Find the consumer's surplus if the %3D x + 3 equilibrium price of a unit $5. The consumer's surplus is $arrow_forwardThe demand for tomatoes is Q = 40-4P and the supply of tomatoes is Q = P +10. Answer the following questions. (a) Suppose that $1 per unit tax is levied on the consumers. Who bears the economic incidence of this tax? (b) Calculate the deadweight loss (c) Suppose that stores will pay $1 per unit tax directly. What will happen to the "sticker price" on tomatoes? How will the size of the consumer tax burden change? (d) Suppose that tax is increased to $2 per unit on the consumers. Calculate the deadweight loss. Compare the size of the deadweight loss with (b).arrow_forwardConsumer surplus is a measure of the difference between: a) The price which a consumer has to pay and the cost of producing the good (in a diagram, the area between the market price, and the supply curve). b) The consumer’s willingness to pay, and the cost of production (the area between the demand curve and the supply curve). c) The value which a consumer places on a unit of the good, and the market price (the area between the demand curve and the market price line). d) The marginal revenue from sales and the marginal cost of sales (the area between the marginal revenue and the marginal cost curves).arrow_forward
- please help me with this questionarrow_forwardRefer to the figure entitled "Market for Cola". Suppose DO denotes the original demand curve and D1 denotes the demand curve after a per-unit tax is imposed on the buyers. What is the change in equilibrium price due to the tax? Price (per six pack) 10 1 4 10 Market for Cola D₂ 20 30 40 Quantity (# of six packs) Da 50 1) $1 2) $2 3) $3 4) $4 5) None of the above.arrow_forwardQ4) Assume a market of a specific good. The demand and supply equation is as shown below: Pp = 70 – 3QD Ps = 5 + 20s The demand price elasticities is inelastic. From the firms' perspective, the revenue would be higher if price increases. Let's assume that the market is currently not at the equilibrium with the market price being higher by 2 units than the equilibrium price. 1. Find the market quantity 2. Find the new Consumer Surplus 3. Find the new Producer Surplusarrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





