
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
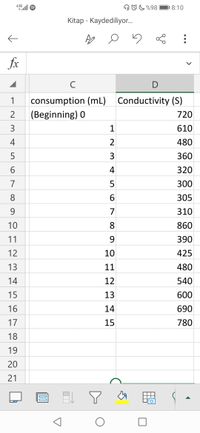
5 mL of HCl and 5 mL of CH3COOH solutions are titrated with a pipette in a glass bottle and 150 mL of distilled water is added. The initial conductivity (720) of this diluted mixture is measured and recorded in the table. Then, one ml of M/10 NaOH solution is added and their conductivity is measured and recorded in the table. Find the concentration of HCl and CH3COOH.
Transcribed Image Text:C%98
4.5G
1 8:10
Kitap - Kaydediliyor.
G
fx
C
1
consumption (mL) Conductivity (S)
2
(Beginning) 0
720
3
1
610
4
2
480
360
4
320
7
5
300
8
305
9.
7
310
10
8
860
11
9.
390
12
10
425
13
11
480
14
12
540
15
13
600
16
14
690
17
15
780
18
19
20
21
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Help with the following question Round the answer to 2 sig figsarrow_forwardExplain how acidification or neutralization can impact the solubility of a compound (for example, compare the solubility of sodium salicylate in water to the solubility of salicylic acid.) How can this be used to purify a mixture using liquid/liquid extraction?arrow_forward(CH), the freezing point of the solution is measured to be 3.5 °C. Calculate If you need any additional information on benzene, use only what you find in the ALEKS Data resource. Also, be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and is rounded to 2 significant digits. 0 When 11.5 g of a certain molecular compound X are dissolved in 45. g of benzene the molar mass of X. ロ・ロ X 0x1.2arrow_forward
- A water contains 180 mg/l Ca, 75 mg/I Mg, 160 mg/l HCO3', and 150 mg/l CO2, all expressed as CaCO3. Assume that water is to be softened to a final Ca-hardness of 60 mg/l as CaCO3, and a final Mg- hardness of 30 mg/l as CaCO3. Also, assume that the excess lime equals 1 meq/l. MW Ca 40 Mg 24 HCO3 61 CO2 44 CaCO3 100 Calculate the required amount of lime (in mg/l): Calculate the required amount of lime (in mg/l):arrow_forwardPlease show steps and answer accordingly. Thanks!arrow_forwardWhich of the following is false about exothermic dissolutions? Select one: PLEASE EXPLAIN WHY IT IS TRUE AND WHY IT IS FALSE. Exothermic dissolutions will always result in an increase in the solution temperature Decreasing the temperature will increase solubility Exothermic dissolutions occur when solute-solvent interactions are weaker than solute-solute and solvent-solvent interactions Cooling a solution of Ca(OH)2will result in better dissolutionarrow_forward
- Describe how to prepare 100.0 mL of 0.0600 mol/L copper(II) sulfate solution from a 0.304 mol/L stock solution of copper(1I) sulfate. Include the necessary calculations and references to the appropriate equipment.arrow_forwardA boric acid stock solution was prepared by dissolving 19 g boric acid in a small amount of purified water USP and then adding sufficient volume of purified water USP to make up the volume to 1000 ml. Calculate the volume of this solution needed to prepare 25 ml of 0.95% boric acid solution in purified water. A solution of sodium chloride contains 77 mEq/L. Calculate its osmolar strength in terms of milliosmoles per liter. Assume complete dissociation.arrow_forwardThe conductivity values of ch3cooh solutions at different concentrations were measured. Using these values, the conductivity values given in the table were calculated. Using these values, calculate the α values for each ch3cooh solution and find out what this constant is.arrow_forward
- synthetic ion exchange resins. These resins are organic polymeric networks that contain functional groups that are permanently attached to the resin. One such functional group is sulfonic acid, -SO3H. When placed in water, the resin (being a large organic molecule) will not dissolve. However, the ionic functional groups become hydrated and the resin will swell as it takes up waters of hydration. The resin may then be thought of as a solid solution mixture with the functional groups being "dissolved" but the polymer remaining as a solid. The hydronium ion (H3O+) associated with acidic functional groups like sulfonic acid will dissociate just as it would if the acid were free of the resin. If other cations such as Cu2+ or Na+ are added to the resin, an ion-exchange reaction can occur: . Note that one H+ is released for each positive charge bound to the resin. Since the resin exchanges a hydrogen ion for a sodium ion in this reaction, sulfonic acid resins are called cation-exchange…arrow_forwardFind the freezing point of a solution obtained by dissolving 4.71 g of the aminoacid alanine (a molecular compound with molecular formula C3H7NO2 and molar mass = 89.09 g/mol) in 174 g of benzene. The melting point of pure benzene is 5.5 °C and the freezing point depression constant of benzene is 5.12 °C/m. Give the answer with 2 or more significant figures.arrow_forwardThe freezing point of a liquid will change when a solute is added. Explain how the addition of salt impacts the boiling point of water. Calculate the freezing point change for a given concentration. Given that water’s freezing point is 0.00ºC and the freezing point depression constant (Kf) is 1.86 ºC・kg/mol, calculate the freezing point depression for a 4.35 molal solution (moles/kg) of NaCl in water. Assume ideal behavior of the ions.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY