
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
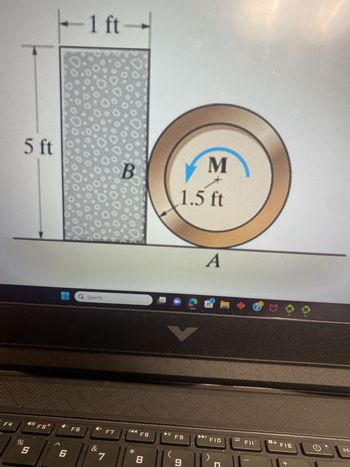
The uniform concrete block in (Figure 1) has a weight of 300 lb. The coefficients of static friction are μA= 0.2, μB = 0.3, and between the concrete block and the floor, μ = 0.4.
a) Determine the smallest couple moment that can be applied to the 130-lb wheel that will cause impending motion. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Transcribed Image Text:F4
5 ft
do
437
10 F5
5
-1 ft--
^
6
Q Search
F6
4+
-0
F7
&
7
B
144 FB
*
8
▶11
(
M
1.5 ft
F9
9
A
FIO
C
10
G
FIL
□
F12
+
G
DE
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A block of mass, m = 20 kg, rests on the inclined plane shown. What is the minimum force, P, required to maintain equilibrium of the block? The static coefficient of friction is 0.2 and the kinetic coeficcient of friction is 0.15 M 25° P 80⁰ Solve the problem and answer the questions that follow.arrow_forwardWe are experimenting with a brake system. Bar AC rests on the spool at B. Find the force P that can be applied to the cord that is wrapped around the smaller radius of the spool. The spool is frictionless. Only consider friction occurring at point B. The coefficient of static friction at B is 0.37. A 250 lb 1211+ -2 ft- -211--111-1 Radius=9 in.. B P C Radius= 15 in.arrow_forwardIn the figure, a climber with a weight of 390 N is held by a belay rope connected to her climbing harness and belay device; the force of the rope on her has a line of action through her center of mass. The indicated angles are 0 = 45° and p = 30°. If her feet are on the verge of sliding on the vertical wall, what is the coefficient of static friction between her climbing shoes and the wall? %3D %3D Hs =Number i Uarrow_forward
- Each problem requires a proper FBD and separate kinematic diagram. 1. The wheel has a weight of 20 lb and a radius of gyration of kg = 0.75 ft. If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the wheel and the surface are 4 = 0.5 and 4 = 0.35, find the greatest angle, 0 , that the slope can have without the wheel slipping. 1.25 ft-arrow_forwardCalculate the maximum force P that can be applied without causing any motion for the given coefficients of static friction. The weight of block A is 20 lb. and that of B is 10 lb. MB = 0.4 2 ft. B A 3 ft. MA=0.5 P MD=0.3 D Pc=0.35 Carrow_forwardThe uniform concrete block in (Figure 1) has a weight of 300 lb. The coefficients of static friction are μA = 0.2, μB = 0.3, and between the concrete block and the floor, μ = 0.4. A) Determine the smallest couple moment that can be applied to the 180-lb wheel that will cause impending motion. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forward
- Need only a handwritten solution only (not a typed one).arrow_forwardSubmit correct and complete solutions. Please provide Explanation. Provide step-by-step detailed explanations.arrow_forwardConsider (Figure 1). The cord is attached to the 36-lb block, and the coefficients of static friction are HB = 0.2 and μp = 0.3. Figure M 1.5 ft B 3 ft -1.5 ft- D C < 1 of 1 Part A Determine the smallest couple moment which can be applied to the 24-lb wheel that will cause impending motion. Express your answer in pound-feet to three significant figures. VAΣo↓↑ vec M = Submit Provide Feedback Request Answer A ? lb-ftarrow_forward
- B4arrow_forwardSolve each of the following problems indicated below. Present your complete-detail solution including the free- body diagrams. Box your only final answer.arrow_forwardA 250-lb block rests on a horizontal surface, as shown. The coefficient of static friction is 0.25. Calculate the maximum value of the horizontal force P so that neither sliding nor tipping will occur. 2'-0" W = 250 lb P. 4' 6" 3'-0"arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY