
Economics (MindTap Course List)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9781337617383
Author: Roger A. Arnold
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
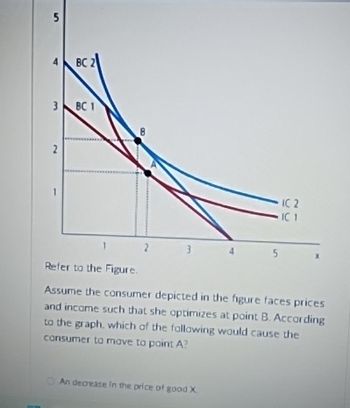
Transcribed Image Text:5
4
BC 2
3
BC 1
B
2
1
2
3
5
IC 2
IC 1
Refer to the Figure.
Assume the consumer depicted in the figure faces prices
and income such that she optimizes at point B. According
to the graph, which of the following would cause the
consumer to move to point A?
An decrease in the price of good X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What are the assumptions of the consumer equilibrium??arrow_forwardThe following table presents information on Angel's marginal utility and price paid for the consumption of Pomegranates and Oranges, which are the only two goods that he consumes. Angel OYes ONO ONot enough information What should Angel do? Pomegranates Price $4 Based on the utility maximizing rule, Is Angel maximizing their utility? OPurchase more Pomegranates and less Oranges OPurchase less Pomegranates and more Oranges OMake no changes Marginal Utility MacBook Air 7 Oranges Price $12 Marginal Utility 31arrow_forwardDemonstrate how a consumer’s equilibrium changes if the price of a product changesaccording to marginal utility theory. Include in your answer a discussion of the derivation of the demand curve according to marginal utility theory. Please provide a detailed answer with a graph if possible.arrow_forward
- KAMVA 489 Time Remaining: 02:54:13 Hide Time Remaining A Suppose the weighted marginal utility for two goods, x and y, at a position of consumer equilibrium is 70. If the price of good x is R10 and the relevant marginal utility for y is 140, what is the price of good y and the relevant marginal utility for good x? A. The price of y = R70; the marginal utility for x = 70 %3D B. The price of y = R2; the marginal utility for x = 700 C. The price of y = R10; the marginal utility for x = 700 D. The price of y = R2; the marginal utility for x = 140 E. The price of y = R140; the marginal utility for x = 70 Reset Selection |54 IIarrow_forwardCan you help me answer this macroeconomics theory questionarrow_forwardFor normal goodsA) the substitution effect of a price decrease will decrease the quantity of the good demanded while theincome effect of a price decrease will increase the quantity of the good demanded.B) the substitution and income effects of a price decrease will both increase the quantity of the gooddemanded.C) the substitution and income effects of a price decrease will both decrease the quantity of the gooddemanded.D) the substitution effect of a price decrease will increase the quantity of the good demanded while theincome effect of a price decrease will decrease the quantity of the good demanded.arrow_forward
- Why does a change in income cause a parallel shift in the budget constraint?arrow_forwardRecent research confirms that the demand for cigarettes is not only inelastic, but it also indicates that smokers with incomes in the lower half of all incomes respond to a given price increase by reducing their purchases by amounts that are more than four times as large as the purchase reductions made by smokers in the upper half of all incomes. How can the income and substitution effects of a price change help explain this finding?arrow_forward. If average income increases, ceteris paribus, then there will be: A) a shift of the demand curve B) a movement along and a shift in the demand curve c) a movement along the demand curve D) no effect on the demand curve, because income is not a ceteris paribus conditionarrow_forward
- Please explain in detail, in relation to microearrow_forwardNot sure where to plot market demandarrow_forwardProblem 6 Consider the following diagram that shows the effects of a decrease in the price of beer on a consumer's choice of consumption of beer and pretzels: Ber 19 17 ICI Pretzds a.) What is the value of the income effect on beer consumption of the price change? b.) Are beer and pretzels complements or substitutes?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506893
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506725
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...
Economics
ISBN:9781285165875
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning