
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
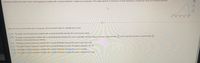
Transcribed Image Text:Determine whether the graph shown could represent a variable with a normal distribution. Explain your reasoning. If the graph appears to represent a normal distribution, estimate the mean and standard deviation.
47
50
53
56
59
Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice.
O A. The graph could not represent a variable with a normal distribution because the curve has two modes.
approximately
and its standard deviation is approximately
B. The graph could represent a variable with a normal distribution because the curve is symmetric and bell-shaped. Its mean
(Round to one decimal place as needed.)
O C. The graph could not represent a variable with a normal distribution because the curve crosses the x-axis.
O D. The graph could not represent a variable with a normal distribution because the graph is skewed to the left.
O E. The graph could not represent a variable with a normal distribution because the curve is constant.
O F. The graph could not represent a variable with a normal distribution because the graph is skewed to the right.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- One graph in the figure represents a normal distribution with mean µ = 6 and standard deviation o=3. The other graph represents a normal distribution with mean µ = 16 and standard deviation o = 3. Determine which graph is which and explain how you know. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Graph A has a mean of µ = 6 and graph B has a mean of μ = 16 because a larger mean shifts the graph to the right. B. Graph A has a mean of μ = 6 and graph B has a mean of µ = 16 because a larger mean shifts the graph to the left. C. Graph A has a mean of µ = 16 and graph B has a mean of μ = 6 because a larger mean shifts the graph to the left. D. Graph A has a mean of μ = 16 and graph B has a mean of µ = 6 because a larger mean shifts the graph to the right. A B s 6 16arrow_forwardOne graph in the figure represents a normal distribution with mean u = 9 and standard deviationo = 3. The other graph represents a normal distribution with mean u = 15 and standard deviation o = 3. Determine which graph is which and explain how you know. 9 15 Choose the correct answer below. O A. Graph A has a mean of u = 15 and graph B has a mean of u = 9 because a larger mean shifts the graph to the left. O B. Graph A has a mean of u =9 and graph B has a mean of u = 15 because a larger mean shifts the graph to the left. O C. Graph A has a mean of u =9 and graph B has a mean of p = 15 because a larger mean shifts the graph to the right. O D. Graph A has a mean of u = 15 and graph B has a mean of u = 9 because a larger mean shifts the graph to the right.arrow_forwardD Applet Exercise 2.3 Use the applet Mean versus Median to study the effect that an extreme value has on the difference between the mean and median. Begin by setting appropriate limits and plotting the following data on the number line provided in the applet: 0 6 7 7 8 88 99 10 a. Describe the shape of the distribution and record the value of the mean and median. On the basis of the shape of the distribution, do the mean and median have the relationship that you would expect? just do "by hand", no appletarrow_forward
- The data in the table represent the ages of the winners of an award for the past five years. Use the data to answer questions (a) through (c). 25 30 61 48 42 a. Determine the population mean age, μ, of the five winners. μ=________________ (Type an integer or a decimal.) b. Consider samples of size 3 without replacement. Find the mean of the variable x. Ages x Ages x Full data set 25, 30, 61 38.67 25, 48, 42 38.33 25, 30, 48 34.33 30, 61, 48 46.33 25, 30, 42 32.33 30, 61, 42 44.33 25, 61, 48 44.67 30, 48, 42 40.00 25, 61, 42 42.67 61, 48, 42 50.33 The mean of the variable x is ______________. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) c. Find μx, using only the result of part (a). μx=_________________ (Type an integer or a decimal.)arrow_forwardq3- For categorical data: Select one or more: a. We can't apply boxplot to show its distribution b. We can apply aggregate functions. c. We can't use histogram to show its distribution. d. The interval between units is the same.arrow_forwardShaded diagram.. 3. The random variable X has a normal distribution with mean 80 and standard deviation 6. Choose random samples of size 40 from this distribution. Let X be the random variable of sample means. (5) a. What is the distribution of X ? (5) b. What is the mean of X ? yarrow_forward
- 10. The following dot plot shoes the test scores for 10 students on a unit exam. Which shape most accurately describes these data? A. Skewed left B. Skewed right C. Normal Distribution Test Resuits D. Constant + 50 60 70 80 100 Test Score LEGO xx+8 XXxx-arrow_forwardThe accompanying data represent the wait time (in minutes) for a random sample of 40 visitors to a popular attraction in a large amusement park. Use the sample data to complete parts (a) through (d). Click the icon to view the data for wait times. (a) Construct a relative frequency histogram of the data. Comment on the shape of the distribution. Choose the correct graph below. O A. ARelative Freq. 0.6- 0+ 60 Wait Time (min.) What is the shape of the distribution? O O E A. Q 60 B. No A. Yes, there is(are) B. A Relative Freq. 0.6 outlier(s). 07 0 60 Wait Time (min.) O A. The distribution is bell-shaped and roughly symmetric about its peak between 25 and 30 minutes. B. The distribution is right-skewed because the peak is between 0 and 5 minutes and the right tail is much longer than the left tail. C. The distribution is left-skewed because the peak is between 55 and 60 minutes and the left tail is much longer than the right tail. D. The distribution is right-skewed because the peak is…arrow_forwardFind the mean for the data items in the given frequency distribution. 6. 8. Score, x Frequency, f 3 1 The mean IS Round to 3 decimal places as needed.) 55 4/3 3/5 26 1.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman