
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Apply a force of 40 N to a box with a mass of 10 kg and a homogeneous force to slide. If the coefficient of friction between the box and the floor is 0.2, what is the maximum height x that can cause the box to slide without falling over? answers: option 3
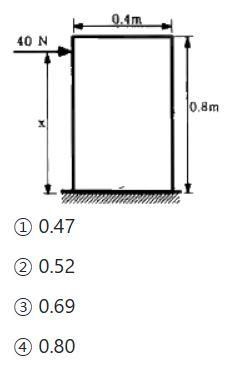
Transcribed Image Text:40 N
1 0.47
2 0.52
3 0.69
4 0.80
0.4m
0.8m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Need help please round answers to 3 sig figs. Thanksarrow_forwardQuestion 4 If the coefficient of friction between surfaces is 0.47, calculate the smallest force P required to keep the block from falling down .arrow_forwardA 250 lb refrigerator is being pushed. You do not know what force P should be applied. The coefficient of static friction between the refrigerator and floor is lg = 0.4. The center of gravity of the refrigerator is at point G. - d2 -- d2 F1 d3 d1 d4 Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value di 4.5 ft d2 1.5 ft d3 2.5 d4 3.5 a. Determine the force P that is needed to overcome friction. b. Determine the location of the normal force r measured from the center of the refrigerator if the force P from part a is applied. c. Determine the minimum force P that is required to tip the refrigerator. d. Will the refrigerator slip or tip first? Round your final answers to 3 significant digits/figures. P= lb ft Pip = lb Will the refrigerator slip or tip first? tip O sliparrow_forward
- 2. The coefficient of static friction between all contacting surfaces is μ = 0.4. The weight of each box is the same, W, and the center of gravity of each box is at its geometric center. a) Determine the minimum horizontal force P needed for the top box to be on the verge of sliding across the top of the lower box (be sure to provide a free body diagram). Is this situation physically possible? b) Determine the minimum horizontal force P needed for both boxes to tip together (be sure to provide a free body diagram). Is this situation physically possible? c) Based on your solutions to parts 'a' and 'b' (no new analysis required), if the magnitude of P is slowly increased from a value of zero, which of these two situations will be realized? 1 m 1 m 0.5 m- [ 1.5 marrow_forwardDetermine the force P for impending sliding motion and the friction forces on all the surfaces.arrow_forwardExample 1 Suppose a block with a mass of 2.50 kg is resting on a ramp. If the coefficient of static friction between block and ramp is 0.350, what maximum angle can the ramp make with the ng sin 8 mg cos 8e the horizontal before the mg block starts to slip down? Dr. Hazem Falah Sakeek www.hazemsakeck.net & www.physicsacademy.org 11arrow_forward
- Box A weighs 1000N and has a height of H1=3m and width W1=2m. Box B weighs 800N. the static friction coefficient between the boxes is uA=0.7 and the static friction coefficient between box B and the ramp is uB=0.5. Find the max allowable angle for the following instances where no motion occurs, box A and B remain stationary. 1) Box A slides, Box B remains stationary 2) Box A tips, Box B remains stationary 3) Box B slides, Box A remains stationary on block Barrow_forwardAnswers typed in are incorrect. Tried them many times and they are not right. Please dont give me the same wrong answers marked with a red Xarrow_forwardA heavy cask (full of wine!) sits on an inclined plane. It is held in place by a rope that is attached to the cask and to a hook further up the inclined plane (at A). The rope comes off of the cask tangent to the cask. The mass of the cask is 40 kg, and the coefficient of static friction between the inclined plane and the cask is 0.25. What is the maximum value of 0 just before the cask begins to slip? Also, what is the tension in the rope when slipping is impending? Finally, if the inclined plane became icy, and the rope didn't break as the cask slipped, what would be remarkable about the lines of action of the W, N and T force vectors once equilibrium was re-established? 0.70 m 40arrow_forward
- Question 5 If the coefficient of static friction at contact points A and B is 0.46 calculate the maximum force P that can be used without causing the 196 kg spool to move. (X,XX,XXX represents the last digits number pf your IC) 0.6 m 0.9marrow_forwardA wedge assembly, composed of wedges X and Y, is designed to lift crate W whose weight is 1CDE N, as shown in the figure below. What will be the maximum force P that can be applied before movement begins if the coefficient of friction for all surfaces of contact is 0.0875? Draw all necessary free-body diagrams and indicate the direction of impending motion. This is not your it in any way property so do not use were your own. 1CDE N W This is not your own property so do not use it in any way as if it were your own. 1C P property sol The not it in any way if your ow Parameters 1℃° 1D ° 1E ° 1CDE N 13° 14° 15° 1345 N 1Dº of use 1Eºarrow_forwardQuestion 3(a) The non uniform XYZ bar which weighs 155 kg has its centre of gravity G at a distance 4 m from X. This bar rests on a homogeneous crate P. The static coefficient of friction between the bar and the crate is 0.31 while the same between the crate and the floor is 0.22. Determine the mass of the lightest crate P (in kilograms) that can be used to support this non uniform bar in the position shown in Figure 3. The height of the crate is 4.32 m and the length of the bar is 8.59 m. 4 m 3 m - 1 m - Figure 3 Question 3(b) Take an example from everyday life where you can identify the application of the concepts we learn in the "Dry friction" module. Sketch this example and discuss about the effect of friction on that particular scenario. Sketch does not have to be drawn to a scale. (Description should be 250 words or less).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY