
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I believe I use the equations in the second picture to find the pressure of the isobaric.

Transcribed Image Text:4.5 x 104 J of heat are delivered to 18 moles of an monatomic ideal gas at 4.3 x 10° Pa at 355°C. If the gas
expands isobarically from 3.1 x 103 m³ to 7 x 10 m³, what is the final temperature of the gas in °C?
Tfinal =
°C
%3D
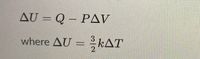
Transcribed Image Text:AU = Q – PAV
3
where AU = kAT
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- can you please find solution for part b?arrow_forwardGauge pressure is the pressure read by a pressure gauge. The gauge pressure will be zero if the pressure is the same as the general atmospheric pressure, because the gauge measures only the excess above atmospheric pressure. The actual pressure will thus be atmospheric pressure plus gauge pressure. Atmospheric pressure is about 14 pounds per square inch. The Rankine temperature scale is the Fahrenheit verson of the absolute temperature, and absolute zero in Rankine is about -460 F. Now, imagine a football has been stored in a warm locker room at a temperature of 71 F, and has a gauge pressure of 12.5 pounds per square inch. Next, it is taken outside and cooled to 40 F. What will the gauge pressure be after this is done?arrow_forwardFor the flow nozzle shown, estimate the rate of flow of water through the venturi meter shown. Assume the temperature of water is 10°C. 1.2 m -1m- Air Diameter = 10 cm Diameter = 30 cm I 30°arrow_forward
- Please do part d only Knudsen number variationA space capsule is 15.6 feet in diameter and weighs 22 metric tons at Earth sea level.(a) Calculate the Knudsen number for the capsule at Earth sea level. Assume a molarmass of 28.9 ×10−3 kg/mol, a molecular diameter of 0.36 nm, and a density of1.225 kg/m3.(b) Calculate the Knudsen number for the capsule as it is approaching the Interna-tional Space Station in low Earth orbit (LEO), 300 km above sea level during a pe-riod of extremely high solar activity. Assume a molar mass of 18.1 ×10−3kg/mol,a molecular diameter of 0.34 nm, and a density of 1.7 × 10−11 kg/m3.(c) Calculate the particle number density at LEO.(d) Classify the flow around the capsule at sea level and in low earth orbit as con-tinuum, transitional or free molecular based on the Knudsen number. Explain inwords why this classification is important to understanding the fluid dynamics.arrow_forward12 of 20 Provide Feedback P Pearson MacBook Proarrow_forwardSolvearrow_forward
- Assume that a raindrop has a volume of 0.05 cm^3 and you need an Avogadro's number of raindrops to fill up the cubic water tank. What is the length of the edge of the tank?arrow_forwardCan you please solve the below problem, showing step by step: A balloon contains mostly helium and a little nitrogen. The pressure of the helium is 425 mm Hg. What is the partial pressure of the nitrogen if the total pressure of the balloon is 67.98 kPa?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON