
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
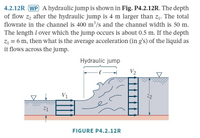
Transcribed Image Text:4.2.12R WP A hydraulic jump is shown in Fig. P4.2.12R. The depth
of flow z2 after the hydraulic jump is 4 m larger than z1. The total
flowrate in the channel is 400 m³/s and the channel width is 50 m.
The length l over which the jump occurs is about 0.5 m. If the depth
Z1 = 6 m, then what is the average acceleration (in g's) of the liquid as
it flows across the jump.
Hydraulic jump
V2
V1
7.2
Z1
FIGURE P4.2.12R
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A dam releases water into a spillway, and then some distance downstream a hydraulic jump occurs. The dam height is 25 m, the initial depth in the spillway is 1 m, and the hydraulic jump leads to a region of depth 15 m. Upstream of the dam may be considered a reservoir. Determine the average velocity before the jump and whether the jump will occur. If there will be a jump, determine the velocity after the hydraulic jump, neglecting any friction losses.arrow_forwardQ: Water is flowing through an inclined aquifer (a=15°) as shown in the following figure. The depth of aquifer is H₁-3m. Two observation wells are constructed at 55m apart (S-55m) to reach the top of the aquifer. It is found that the head difference between the points, observation wells were constructed, is h=3m. (i) Find the flow rate in m³/s/m length (at right angles to the cross section shown) if k-0.05 cm/s. (ii) Find the percentage rate of change in flow rate if the head difference is increased to 4m (h-5m). H Impervious layerPermeable layer Direction of flowarrow_forwardProblem 4. A 2-mm-diameter tube is used to siphon water at 20° C from a tank. When the tube length is 1 m, is there a value for H that exceeds the limit for laminar flow? If the maximum H = 75 cm, what would be the maximum flow rate? Neglect losses due to curvature and entrance effects. L=1m,d=2mm Water at 20°C Harrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning