
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
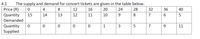
4.1.4. The functions underlying the example in the table are linear and can be presented as P = 18+2Q (supply) and
P = 60−4Q (
Transcribed Image Text:4.1
The supply and demand for concert tickets are given in the table below.
Price (R)
4
8
12
16
20
24
28
32
36
40
Quantity
15
14
13
12
11
10
7
6
5
Demanded
Quantity
1
5
7
11
Supplied
00
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Q.2. Suppose the demand of a particular product is represented by the following linear demand function Demand for Product Y = 200- 4P Calculate the quantity demand at the market prices $10, $20, $30, $40, and $50. Construct a demand schedule in a table and plot the demand curve for this demand function.arrow_forwardConsider two markets: the market for waffles and the market for pancakes. The initial equilibrium for both markets is the same, the equilibrium price is $6.50, and the equilibrium quantity is 35.0. When the price is $9.75, the quantity supplied of waffles is 57.0 and the quantity supplied of pancakes is 101.0. For simplicity of analysis, the demand for both goods is the same. Using the midpoint formula, calculate the elasticity of supply for pancakes. Please round to two decimal places. Supply in the market for waffles isarrow_forwardRead the instructions carefully. Show the complete solutionarrow_forward
- Let the supply and demand functions for raspberry-flavored licorice be given by p = S(q) = q and p = D(q) = 90 - q ,where p is the price in dollars and q is the number of batches. Graph these functions on the same axes (graph the supply function as a dashed line and the demand function as a solid line). Also, find the equilibrium quantity and the equilibrium price.arrow_forwardif there is any diagram can you add it. Given the following demand and supply equations: QD = 10 - 0.8P + 5Y + A QS = -10 + P where Q = quantity (million units per month), P = price (€ per unit). Y = average monthly income (€000) and A monthly advertising expenditure (€000). Suppose average monthly income is €4,000 and monthly advertising expenditure is €50,000: (a) Find the market equilibrium price and quantity. (b) Find total welfare when the market is in equilibrium. (c) Find the price elasticity and income elasticities of demand and price elasticity of supply at equilibrium. Interpret your results. (d) What would be the effect of a price ceiling of €60? Explain. (e) Suppose a tax of €8 per unit is introduced: (i) What is the effect on market price and quantity? Explain. (ii) What is the impact of the tax on total welfare? Explain. (iii) How is the incidence of the tax shared between the consumer and the supplier? Explainarrow_forwardConsider the demand for shrimp shown in Figure 2. Suppose the current demand for shrimp is D (in black), the current price of a pound of shrimp is $10, and the current quantity demand for shrimp is 200K. Which of the following correctly describes the effect of a decrease in the price of a pound of shrimp? A) The price of a pound of shrimp falls to $3, the demand curve shifts left to D'' (red), and the quantity demand for shrimp remains at 200K pounds. B) The price of a pound of shrimp falls to $3, the demand curve remains at D (black), and the quantity demand for shrimp decreases to 150K pounds. C) The price of a pound of shrimp falls to $3, the demand curve shifts right to D' (blue), and the quantity demand for shrimp increases to 270K pounds. D) The price of a pound of shrimp falls to $3, the demand curve remains at D (black), and the quantity demand for shrimp increases to 270K.arrow_forward
- In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X. An increase in the price of a product that is a close substitute for X willarrow_forwardQXd = 14 - 0.5PX and QXs = 0.25PX - 1 a. Determine the equilibrium price and quantity. Show the equilibrium graphically. b. Suppose a $12 excise tax is imposed on the good. Determine the new equilibrium price and quantity (see video on inverse functions).arrow_forwardFind the market equilibrium point for the following demand and supply functions. Demand: 2p= -q+45 Supply: 3p-q=20arrow_forward
- Suppose the equation for demand can be expressed as P = 40 – 2Q. The equation for supply can be expressed as P = Q. Find the equilibrium price and quantity. Be able to draw the graph that illustrates your answer.arrow_forwardThe weekly demand for wine in the United States is described by the following equation: Qd = 45,000,000 - 1,500,000P where Qd is the weekly quatity demanded in bottles and P is the price per bottle in dollars. The weekly supply of wine in the United States is described by the following equation: Qs = -5,000,000 + 1,000,000P where Qs is the weekly quantity supplied in bottles and P is the price per bottle in dollars. a. What is the equilibrium price and quantity for wine in the US? Intense lobbying efforts result in the United States government establishing a $5 per bottle excise tax by wine producers. b. What would be the new equilibirum price and quantity after the imposition of the per bottle excise tax? c. Determine the total amount of the consumer surplus assuming the market for wine is in equilibrium after the imposition of the excise tax.arrow_forwardThe market equilibrium point for a product is reached when 6000 units are produced and sold at $21 per unit. The manufacturer will not produce any units at the price of $5, and the customers will not buy any at the price of $69. Find the supply and demand equations, assuming they are linear. The equations should express price p in terms of quantity q. a. Supply equation P= b. Demand equation P=arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education