
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
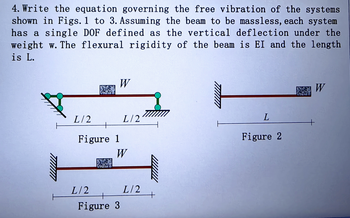
Transcribed Image Text:4. Write the equation governing the free vibration of the systems
shown in Figs. 1 to 3. Assuming the beam to be massless, each system
has a single DOF defined as the vertical deflection under the
weight w. The flexural rigidity of the beam is EI and the length
is L.
L/2
W
Figure 1
L/2
L/2
W
Figure 3
L/2
L
Figure 2
PW
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: State the given data
VIEW Step 2: Express the deflection for a simply supported beam and determining the system's free vibration
VIEW Step 3: Express the deflection for a simply supported beam and determining the governing the system's vibrat
VIEW Step 4: Express the deflection for the fixed beam and determining the system's free vibration
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Derive a formula for the strain energy U of the cantilever bar shown in the figure. The bar has circular cross sections and length L. It is subjected to a distributed torque of intensity t per unit distance. The intensity varies linearly from t = 0 at the free end to a maximum value t = to at the support. Express your answer in terms of maximum value zo , length L, shear modulus G and polar moment of inertia Ip . U =arrow_forward4. The truss shown in figure Q4.1 is constructed out of square steel bars, all of which are of 25mm x 25mm cross-section. The value of Young's Modulus for steel should be taken as 200 GPa. Calculate the horizontal deflection of point A when the truss is subjected to the loading shown. B 0.5m 5kN A с 10kN 2m D 1marrow_forward6...arrow_forward
- B.2. Elementary beam theory predicts that the axial bending stress ox in a prismatic beam is given by: σ, X (M.1, M,1,)y+ (M, I. - M.1,-) z (1,1.-1²-) where My and M₂ are bending moments applied to a cross-section, and where ly, Iz and lyz are second moments of area in the usual notation (Oxyz is a Cartesian coordinate system in which the x axis corresponds to the centroidal axis of the beam). (i) What assumptions have been made in the derivation of the above expression? (ii) Indicate by means of a sketch the directions in which positive values of the bending moments My and M₂ act on a cut plane facing in the positive x direction.arrow_forwardRigid bar ABC is supported by bronze rod (1) and stainless steel rod (2) as shown in the figure. A concentrated load of P = 24 kips is applied to the free end of bronze rod (3). Determine the magnitude of the deflection of rod end D after the temperature of all rods has increased by 115 Fo. Use the following dimensions and properties: a = 3.5 ft, b = 7.5 ft. Rod (1): d 1= 1.10 in.,L 1= 12 ft , E 1= 15,200 ksi , a 1= 12.20 × 10 - 6 /Fo. Rod (2): d 2 = 0.65 in. , L 2 = 10 ft , E 2 = 28,000 ksi, a 2 = 9.60 x 10 - 6/Fo. Rod (3): d 3 = 1.15 in. , L 3 = 6 ft, E3 = 15,200 ksi , a 3 = 12.20 x 10 - 6/Fo. (1) L (2) b L2 a Rigid bar A (3) L3 vD = i in.arrow_forwardDo not copy.arrow_forward
- = 29,000 For the structure and loading shown below, find the lateral deflection at the top. Use E ksi and I = 250 in4 for all members. Note that in frames, we neglect axial deformation, so you can calculate the deflection at either of the upper corners; the answer will be the same. t. 201 8K 10! 1. What is the deflection at the top in inches (two decimal places) otarrow_forwardDerive a formula for the strain energy U of the cantilever bar shown in the figure. The bar has circular cross sections and length R. It is subjected to a distributed torque of intensity z per unit distance. The intensity varies linearly from z = 0 at the free end to a maximum value z = zo at the support. Express your answer in terms of maximum value zo , length R, shear modulus G and polar moment of inertia Ip . U =arrow_forwardPlease Calculate the bearing reaction of a beam structure in the figure. Assume that the value of EI is constant throughout the beamarrow_forward
- Please solve part Aarrow_forwardPROBLEM2: The displacement amplitude u, of an SDF system due to harmonic force is known for two excitation frequencies. At w=wn, up = 15 cm; at w=5w, u, = 0.06 cm. Estimate the damping ratio of the system. @= PROBLEM3: Find the response of the rigid bar shown in Figure 2 when the end P of the spring PQ is subjected to the displacement, x(t) = xoSin10t. Data: k 500, 1 = 1 m, m = 10 kg, xo = 1 cm. N = m 00000 Uniform bar, mass m - Li+ Figure 2-Rigid bar undergoing rotational motionarrow_forwardNon uniform beam Flexural Rigidity that is _y(x) = fixed support on left Simple support 07 right P 2.26 meters long 141702000 6441 + 100x Find the deflection of the bean if it is uniform distributed load of under a 92 N/m TPE Nm²arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning