
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
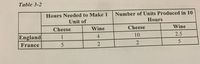
Transcribed Image Text:Table 3-2
Hours Needed to Make 1
Unit of
Number of Units Produced in 10
Hours
Wine
Cheese
Wine
Cheese
England
4
10
2.5
1
5
France
2

Transcribed Image Text:4. Refer to Table 3-2. Assume that England and France each has 10 labor hours available. If each country divides its time
equally between the production of cheese and wine, then total production is
a. 10 units of cheese and 6 units of wine.
b. 6 units of cheese and 3.75 units of wine.
c. 10 units of cheese and 3.75 units of wine.
d. 6 units of cheese and 10 units of wine.
mparative
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given:
Total hours available with each country=10 hours
Production of: Cheese and Wine
To find: Total production
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Suppose that the country of Greece has only one factor of production, labour, and can produce at most 1500 units of olives and at most 6000 units of cheese. (a) Draw the PPF of Greece, with cheese on the vertical axis. What is the oppor- tunity cost of producing cheese? What must be the relative price of olives for Greece to specialise in producing olives? To produce both goods? Pcarrow_forwardTable 2-1 Production Possibilities Tennis Rackets Tennis Balls 100 200 300 8,000 6,500 ? Refer to Table 2-1. If the production possibilities frontier is bowed outward, then which of the following could be the maximum number of tennis balls produced when 300 tennis rackets are produced? O a. 6,000. b. 5,500. O c. 5,000. O d. 4,500.arrow_forward7. Which of the above figures represents economic growth caused by an improvement in the technology of producing product of both X and Y? a) FIG A b) FIG B c) FIG C d) FIG Darrow_forward
- 2. Comparative and absolute advantage David and Morgan are farmers. Each one owns an 18-acre plot of land. The following table shows the amount of zucchini and watermelon each farmer can produce per year on a given acre. Each farmer chooses whether to devote all acres to producing zucchini or watermelon or to produce zucchini on some of the land and watermelon on the rest. David Morgan WATERMELON (Pounds) 180 162 On the following graph, use the blue line (circle symbol) to plot David's production possibilities frontier (PPF), and use the purple line (diamond symbol) to plot Morgan's PPF. 144 126 108 90 72 54 36 1.8 0 Zucchini (Pounds per acre) 28 0 zucchini. 18 90 180 Watermelon (Pounds per acre) 7 6 270 360 450 540 630 720 810 900 ZUCCHINI (Pounds) David's opportunity cost of producing 1 pound of watermelon is pound of watermelon is David's PPF Morgan's PPF has an absolute advantage in the production of zucchini, and has an absolute advantage in the production of watermelon. pounds of…arrow_forwardRefer to the production possibility frontiers for two friends Frodo and Sam who can both produce Ice creams and Jelly beans. Frodo's maximum production of Ice creams is 500 with no Jelly beans, or 2,000 Jelly beans with no Ice creams. Sam's maximum production of Ice creams is 600 with no Jelly beans, or 1,200 Jelly beans with no Ice creams. ICE CREAMS ICE CREAMS 600 500 1200 JELLY BEANS 2000 JELLY BEANS Frodo' PPF Sam's PPF Answer briefly these TWO questions in the box space provided below. Part A: Assuming efficient production without trade, derive the maximum amount of Jelly beans that can be produced by Sam along with 300 Ice creams. Describe your steps in detail. Part B: Assume that Frodo and Sam agree to specialize in production and trade between themselves. Frodo offers 1,000 Jelly beans to Sam in exchange for 300 lce creams. Would Sam agree to this trade?arrow_forward25. Assuming labor is the only resource and England has 60 man-hours (mhrs) and Portugal 180 mhrs of labor resource available for production, which country has the comparative advantage in wine? a) Portugal b) England c) Both d) Neither e) Cannot tellarrow_forward
- Question 4 There is now also another country, Foreign, there is a labor force of 800. Foreign's unit labor requirement in watermelon production is 5, while in kiwi production it is 1. a) how many units of watermelon can be produced? when the labor in Foreign country only produce watermelon. b) how many units of kiwi can be produced? When all the labor in Foreign country only produce kiwi. c) What is the opportunity cost of watermelon in terms of kiwi in Foreign country? d) Describe the pattern of trade. Home country should produce? Foreign country should produce? Why? e) Show that how both Home and Foreign country gain from trade.arrow_forward11arrow_forwardSuppose there exist two imaginary countries, Everglades and Yosemite. Their labor forces are each capable of supplying four million hours per day that can be used to produce chinos, pistachios, or some combination of the two. The following table shows the amount of chinos or pistachios that can be produced by one hour of labor. Country Everglades Yosemite Chinos Pistachios (Pairs per hour of labor) (Pounds per hour of labor) 4 6 16 12 Suppose that initially Yosemite uses 1 million hours of labor per day to produce chinos and 3 million hours per day to produce pistachios, while Everglades uses 3 million hours of labor per day to produce chinos and 1 million-hours per day to produce pistachios. As a result, Everglades produces 12 million pairs of chinos and 16 million pounds of pistachios, and Yosemite produces 6 million pairs of chinos and 36 million pounds of pistachios. Assume there are no other countries willing to engage in trade, so, in the absence of trade between these two…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education