
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781337614085
Author: Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Match each image to the correct scale factor if a dilation exists.
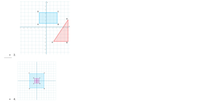
Transcribed Image Text:### Image 3:
The image contains a coordinate grid with two geometric shapes:
1. **Blue Rectangle**:
- Located in the first quadrant.
- Vertices are labeled as A, B, C, and D.
- A is at the origin (0,0).
- B is directly to the right of A along the x-axis.
- D is directly above A along the y-axis.
- C is diagonally opposite to A and located at the farthest top-right corner of the rectangle.
2. **Red Triangle**:
- Located mostly in the first quadrant, with a small part extending into the fourth quadrant.
- Vertices are labeled as P, Q, and R.
- P is at (4,0) on the x-axis.
- Q looks to be at (6,0), slightly to the right of P.
- R is above P at a point higher on the y-axis than Q on the x-axis, giving it a vertical alignment above the x-axis line between P and Q.
### Image 4:
The image contains a coordinate grid with two geometric shapes:
1. **Purple Square**:
- Centered at the origin (0,0).
- Vertices are labeled as A, B, C, and D.
- Surrounds the origin symmetrically, with equal distance extending into all four quadrants.
2. **Blue Square**:
- Surrounds the purple square.
- Larger in size and aligned with the grid.
- Vertices are labeled as E, F, G, and H.
- Each vertex is located at a point that is farther from the origin compared to the corresponding vertex of the purple square.
The diagram illustrates the concept of similar geometric shapes and their positions relative to the coordinate axes.
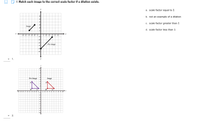
Transcribed Image Text:**Worksheet: Understanding Dilations**
**Instruction 4:** Match each image to the correct scale factor if a dilation exists.
---
### Image 1: Line Segment Dilation
- **Description:** The coordinate plane shows two line segments. The "Pre-image" is a larger, diagonal line segment located in Quadrant IV. The "Image" is a smaller, diagonal line segment positioned in Quadrant II, appearing to be a scaled-down version of the pre-image.
### Image 2: Triangle Dilation
- **Description:** The coordinate plane depicts two triangles. The "Pre-image," a larger purple triangle labeled A, B, and C, is located in Quadrant II. The "Image," a smaller red triangle labeled A', B', and C', is in Quadrant I, appearing to be a scaled-down version of the pre-image.
---
**Answer Choices:**
a. scale factor equal to 1
b. not an example of a dilation
c. scale factor greater than 1
d. scale factor less than 1
*End of Worksheet*
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Find the area of the indicated region. We suggest you graph the curves to check whether one is above the other or whether they cross, and that you use technology to check your answer. Enclosed by y = x3 and y = x4arrow_forwardA surveyor measured the length of a piece of land at 100-ft intervals (x), as shown in the table. Use Simpson's Rule to estimate the area of the piece of land in square feet. Give the value of n on line 1. the Area on line 2. x Length (ft) 0 40 100 50 200 70 300 45 400 40arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:9781285195698
Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:Cengage Learning