
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
4.For the beam with built-in ends, determine (a) all the support reactions; and(b) the displacement at the midpoint C. (Hint: Use symmetry.)
5.The beam ABC has a built-in support at A and roller supports at B and C. Find all the support reactions.
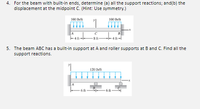
Transcribed Image Text:4. For the beam with built-in ends, determine (a) all the support reactions; and(b) the
displacement at the midpoint C. (Hint: Use symmetry.)
100 Ibit
100 h/t
8 ft
5. The beam ABC has a built-in support at A and roller supports at B and C. Find all the
support reactions.
120 Ib/ft
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 5: Determine the support reactions at A and E if F = 750 N. 80 mm A VB E D -170 mm 1 125 mm 75 mmarrow_forward1) The truss (containing 12 pin joints, A, B, C, ... L) shown in the figure is simply supported at points H and L that are 4 meters apart. Angles A between different truss members are either 90° or 45° and the member lengths are either 1 m or m. H a) Compute the support reactions when P = 4 kN b) Draw a free body diagram from which internal forces in AB, EJ and IJ can be obtained. c) From the free body diagram of part b obtain forces in members AB, EJ and IJ (indicate if the internal forces are tension or compression) d) List all zero force members that carry no load. (a) (b) 3 (c) 3 (d) 2 RH = FAB = RL = FEJ = Fj =arrow_forwardSolve for internal forces at the "TOP" of member BC.arrow_forward
- Find the resultant force from the force reactions found at B in problem 1. (Provide size and direction with the angle to the +x axis.) (ps. I have already solved question #1. I did not realize there was a "part b" to it)arrow_forward1. 1 For the beam shown below, (a) Draw the V-Diagram (b) Draw the M-Diagram (c) Find the largest value of o, and give the (x,y,z) coordinates of its location. (d) Find the largest value of 7y and give the (x,y,z) coordinates of its location. List of beam properties List of displacements List of forces of single-point constraints (these are the reactions at the supports) List of forces in beam elements List of stresses in beam elements S = 0.05" Si = 0.04" 30" Cross section Aluminum 50.000 in.lb E- l0xIo psi V=0. 3 60"arrow_forward1. Given: A structure shown below Find: (1) Determine the magnitudes and locations of the two distributed loadings. In other words, determine the magnitude and location of the loading between A and C, and those of the loading between D and B. (2) For the member DEB, (a) take the moment at B and find the reaction at E and (b) then find By by either Fy= 0, or EMp = 0. (Recall that support conditions at B and E are rollers, so there are no reactions in x-direction.) (3) For the whole structure, 3 unknown forces and moment at A (Ax, Ay and Ma) are the only unknowns. Determine those 3 unknowns at A. 900 N/m 900 N/m B A C D 2E - 3 m 3 m - 4 m - 3 m3 m-arrow_forward
- Static of rigid bodies Show FBDarrow_forwardThe construction features of a cantilever truss bridge are shown in Fig. Here it can be seen that the center truss CD is suspended by the cantilever arms ABC and DEF. C and D are pins. Determine the vertical reactions at the supports A, B, E, and F if a 15-k load is applied to the center truss.arrow_forwardThe asymmetric simple truss is loaded as shown. Determine the reactions at A and D. Neglect the weight of the structure compared with the applied loads. Is the knowledge of the size of the structure necessary? 1L 60° Answers: Ay = i Dy= Dx= i i B 3L 60° 60° E y 1 1L L L L 30° x 4L Darrow_forward
- Please solve all steps properlyarrow_forwardFrom the following armor, determine the following: Reactions in A and F. The internal forces at node C. (Indicate whether the forces are in compression or tension.) The internal forces in the elements CH, CD and HI. (Indicate if the forces are in compression (C) or tension (T)). Draw the respective free-body diagrams. Consider the following: A and F are supports. the angles a, B, y are angles of 90, 60 and 30 ° respectively (Check image pr2 for the image of the armor) (Check image pr2.2 for the values to be used)arrow_forwardGiven the support reaction is 9.5KN SOLVE FOR THE MEMBER FORCED CD AND CGarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning