
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Question 4

Transcribed Image Text:price of lemonade falls, it is as
LO7.4
a. Increases.
b. Decreases.
C. Stays the same
. Suppose that Omar's marginal utility for cups of coffee is con-
the other hand, his marginal utility per doughnut is 10 for the first
doughnut he eats, 9 for the second he eats, 8 for the third he eats,
and so on (that is, declining by 1 util per additional doughnut). In
addition, suppose that coffee costs $1 per cup, doughnuts cost $1
each, and Omar has a budget that he can spend only on dough-
nuts, coffee, or both. How big would that budget have to be before
he would spend a dollar buying a first cup of coffee? LO7.2
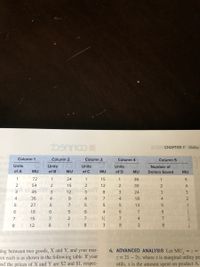
4. Columns 1 through 4 in the following table show the marginal
utility, measured in utils, that Ricardo would get by purchasing
various amounts of products A, B, C, and D. Column 5 shows
the marginal utility Ricardo gets from saving. Assume that the
prices of A, B, C, and D are, respectively, $18, $6, $4, and $24
and that Ricardo has an income of $106. L07.2
a. What quantities of A, B, C, and D will Ricardo purchase in
maximizing his utility?
b. How many dollars will Ricardo choose to save?
c. Check your answers by substituting them into the algebraic
statement of the utility-maximizing rule.
Transcribed Image Text:KIOVCHAPTER 7 Utility
COUUGCE
Column 1
Column 2
Column 3
Column 4
Column 5
Units
Units
Units
Units
Number of
of A
MU
of B
MU
of C
MU
of D
MU
Dollars Saved
MU
1
72
1
24
1
15
1
36
1
2
54
2
15
12
30
4
45
12
8
3
24
3.
3.
4
36
4
9
4
7
4
18
4
27
7 5 sO
13
6
18
4
6.
7
7
7
4
8.
12
8.
1 bs 82 21 3
8.
8.
sing between two goods, X and Y, and your mar-
om each is as shown in the following table. If your
nd the prices of X and Y are $2 and $1, respec-
6. ADVANCED ANALYSIS Let MU, = z =
z = 21 - 2y, where z is marginal utility pe
utils, x is the amount spent on product A,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please pass question on to someone with more knowledge. I do not like using up my questions for wrong answers.arrow_forward8 Write an email (120-150 words) to ask for • information about an activity that you would like to do. Use an idea from the list or your own idea. Follow the content checklist and remember to use indirect questions. a course at a college or with a one-to-one tutor a sport / activity at a gym joining a volunteering group Checklist • how you heard about the course / activity/group ⚫ the days and times ⚫ the cost if you need any experience / skills • if you need any equipmentarrow_forwardPlease answer question Darrow_forward
- Trying to figure out?arrow_forwardMany people believe that businesses that commit fraud cannot last long because (a) the government will shut them down (b)their competition will sue them (c)word will spread and they will lose their customers (d) they will be apprehended and put in jail.arrow_forwardAnswer this questionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education