
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
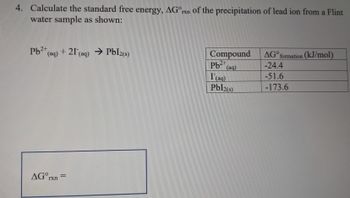
Transcribed Image Text:4. Calculate the standard free energy, AGºrxn of the precipitation of lead ion from a Flint
water sample as shown:
Pb2+ (aq) + 21 (aq) → Pbl2(s)
AGOrxn=
Compound
Pb (aq)
2+
I (aq)
Pbl2(s)
AGO formation (kJ/mol)
-24.4
-51.6
-173.6
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chemist fills a reaction vessel with 0.855 g silver chromate (Ag₂ CrO4) solid, 0.779 M silver (Ag*) aqueous solution, and 0.830 M chromate (Cro₂²-) aqueous solution at a temperature of 25.0°C. Under these conditions, calculate the reaction free energy AG for the following chemical reaction: 2- Ag₂ CrO4(s) ⇒ 2Ag+ (aq) + CrO² (aq) Use the thermodynamic information in the ALEKS Data tab. Round your answer to the nearest kilojoule. KJ Xarrow_forwardA chemist fills a reaction vessel with 0.537 g aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) solid, 0.392 M aluminum (A1³+) aqueous solution, and 0.621 M hydroxide (OH) aqueous solution at a temperature of 25.0°C. Under these conditions, calculate the reaction free energy AG for the following chemical reaction: Al(OH)₂ (s) → A1³+ (aq) + 3OH(aq) Use the thermodynamic information in the ALEKS Data tab. Round your answer to the nearest kilojoule. KJ X Ś ? ▷ olo Ar Barrow_forwardA chemist fills a reaction vessel with 0.493 g aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) solid, 0.356 M aluminum (A1³T) aqueous solution, and 0.237 M hydroxide (OH) aqueous solution at a temperature of 25.0°C. Under these conditions, calculate the reaction free energy AG for the following chemical reaction: Al(OH)3 (s) → Al³+ (aq) + 3OH¯(aq) Use the thermodynamic information in the ALEKS Data tab. Round your answer to the nearest kilojoule. KJ xarrow_forward
- The standard reaction free energy AG = 890. kJ for this reaction: ALO3(s) + 3H₂(g) 2 Al(s) + 3H₂O(g) Use this information to complete the table below. Round each of your answers to the nearest kJ. reaction — Al(s) + H₂O(g) → = ALO, (-) – È F¹₂ (3) –Al₂O; (3) + H₂(g) — — Al(s) – H₂O(g) 2Al(s) + 3H₂O(g) → ALO₂ (s) + 3H₂(g) 4 AG 0 OKJ Xarrow_forward@ た曲8 [Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Consider the following reaction at 298 K. Cr³+ (aq) + Fe2+ (aq) → Cr²+ (aq) + Fe³+ (aq) Which of the following statements are correct? Choose all that apply. On =1 mol electrons OK>1 U The reaction is reactant-favored. OAG° <0 cellarrow_forward(H2 ) →(12 ) +( 2HI) (AS = 82.4 J/K ),(AH = 25.9 KJ/K ) %3D %3D Calculate AG for this reaction at 25 C°arrow_forward
- What is the spontaneity of the chemical system? Cu(s) + H+(aq) -> Cu2+(aq, 1M) + H2(g) standard statearrow_forwardaqueous solution, and 0.545 g lead (II) bromide A chemist fills a reaction vessel with 0.390 M lead (II) (Pb2+) aqueous solution, 0.591 M bromide (Br) ad (PbBr2) solid at a temperature of 25.0°C. Under these conditions, calculate the reaction free energy AG for the following chemical reaction: Pb2+(aq) + 2Br (aq) = PbBr₂ (s) Use the thermodynamic information in the ALEKS Data tab. Round your answer to the nearest kilojoule. pla 18 Ararrow_forwardA chemist fills a reaction vessel with 0.273 M lead (II) (Pb²") aqueous solution, 0.961 M bromide (Br) aqueous solution, and 0.448 g lead (II) bromide (PbBr.) solid at a temperature of 25.0°C. Under these conditions, calculate the reaction free energy AG for the following chemical reaction: Pb (aq) + 2Br (aq) PbBr₂(s) 1 Use the thermodynamic information in the ALEKS Data tab. Round your answer to the nearest kilojoule.arrow_forward
- The solubility product, Ksp, for the following solubility equilibrium at 25oC is 1.1 x 10-10. BaSO4(s)<--> Ba+2(aq) + SO4-2(aq) Calculate the standard free energy change for this equilibrium at this temperature. Group of answer choices 0.470 kJ/mol 56.8 kJ/mol 5.61 kJ/mol 4.77 kJ/molarrow_forwardThe standard reaction free energy AGO= == -910. kJ for this reaction: 6 C(s) + 6H₂(g) + 3O₂(g) →C6H12O6(s) Use this information to complete the table below. Round each of your answers to the nearest kJ. AGⓇ reaction x10 1 C₂H₁2O6 (s) → 2C (s) + 2H₂ (g) + O₂ (g) kJ 3 C6H₁2O6 (s). 6C (s) + 6H₂(g) + 30₂ (g) kJ 12 3 1 3C (s) + 3H₂(g) + - 12/0₂ (8) → — C₂H₁2 06 (8) kJ 6 12 X ?arrow_forwardA chemist fills a reaction vessel with 0.137 g calcium phosphate (Ca, (PO,) solid, 0.349 M calcium (Ca ) aqueous solution, and 0.240 M phosphate (Po,") 3- POA aqueous solution at a temperature of 25.0°C. Under these conditions, calculate the reaction free energy AG for the following chemical reaction: Ca3 (PO4),(s) → 3Ca (aq) + 2PO, (aq) 4. Use the thermodynamic information in the ALEKS Data tab. Round your answer to the nearest kilojoule. kJarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY