Question
please answer d only
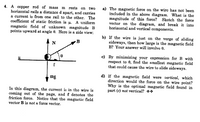
Transcribed Image Text:4. A copper rod of mass m rests on two
horizontal rails a distance d apart, and carries
a current io from one rail to the other. The
coefficient of static friction is u. A uniform
magnetic field of unknown magnitude B
points upward at angle 0. Here is a side view:
a) The magnetic force on the wire has not been
included in the above diagram. What is the
magnitude of this force? Sketch the force
vector on the diagram, and break it into
horizontal and vertical components.
b) If the wire is just on the verge of aliding
sideways, then how large is the magnetic field
B? Your answer will involve 0.
N
c) By minimizing your expression for B with
respect to 0, find the smallest magnetic field
that could cause the wire to slide sideways.
d) If the magnetic field were vertical, which
direction would the force on the wire poin
Why is the optimal magnetic field found in
part (c) not vertical?
mg
In this diagram, the current in in the wire is
coming out of the page, and f denotes the
friction force. Notice that the magnetic field
vector B is not a force vector.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios