
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
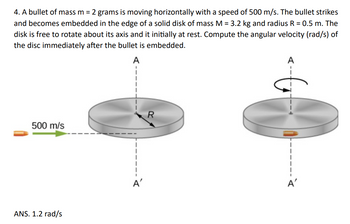
Transcribed Image Text:4. A bullet of mass m = 2 grams is moving horizontally with a speed of 500 m/s. The bullet strikes
and becomes embedded in the edge of a solid disk of mass M = 3.2 kg and radius R = 0.5 m. The
disk is free to rotate about its axis and it initially at rest. Compute the angular velocity (rad/s) of
the disc immediately after the bullet is embedded.
A
R
500 m/s
ANS. 1.2 rad/s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Two children A and B, each having a mass 30kg, sit at the edge of the merry-go-round which is rotating with angular velocity @ = 2 rad/s. Excluding the children, the merry-go-round has a mass 180 kg and a radius of gyration k₂ = 0.8m. Determine the angular velocity of the merry-go-round if A jumps off horizontally in the -n direction (away from the merry-go-gound) with a speed of 3 m/s, measured with respect to the merry-go-round. After A jumps off, B then jumps off horizontally in the +t direction with a speed of 3 m/s, measured with respect to the merry-go-round - what is the merry-go-round's angular velocity now? Neglect friction and the size of each child. 1m 1m B w = 2 rad/sarrow_forwardPart A A horizontal uniform circular disk has a mass 2m. The disk is free to rotate about the z axis and initially at rest. A man having mass m begins to run along the edge in a circular path whose radius is approximated to be R. If he maintains a speed of vo relative to the disk, what is the angular velocity of the disk? Neglect friction. ○ VOR O 3 /(2R) ○ 2 vo/(3R) ○ vo/(3R) 0 Rarrow_forwardHello! Can I have the solution to this question, when the mass of m is 218kg. Both parts please.arrow_forward
- A thin rod of mass 100m and length L is suspended vertically and initially at rest when it is struck at its center point by a bullet of mass m flying at speed vB as shown below. The bullet is then lodged in the rod after impact. What is the angular velocity of the rod/bullet system immediately after impact? L/2 L/2 100m VB m ←arrow_forwardA slender 6-kg rod can rotate in a plane about a pivot at B. A spring of k = 600 N/m (unstretched length 0.225m) is attached the rod as shown. The rod is released from rest in the position shown. Determine its angular velocity after it has rotated 90 degrees CCW. Use energy methods.arrow_forward9. 1) The target is a thin 5.3-kg circular disk of radius r= 318 mm that can rotate freely about the z axis. Initially it is at rest. A 23-g bullet, traveling at v = 570 m/s, strikes the target at A and becomes embedded in it. The dimensions are di = 189 mm and d2 = 99 mm. Determine the magnitude of the angular velocity (in rad/s) of the target after the impact. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². V Your Answer: Answerarrow_forward
- 8. 2) Rods AB and BC are linked at Band have weights of 18 lb and 37 lb, respectively. The 8-lb collar C, which is connected to BC and the spring, slides freely along the smooth vertical guide. The lengths of the rods are 4 = 1.4 ft and 2 = 2.9 ft. If the system is released from rest when 0 = 0°, determine the magnitude of the angular velocity (in rad/s) of rod BC when 0 = 90°. The attached spring has spring constant k = 20 Ib/ft, and is unstretched when 0 = 0°. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g= 32.2 ft/s2. k CO Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardThe pendulum consists of a 12-kg uniform disk and a 3-kg uniform slender rod. It is released from rest in the position shown. Suppose that L = 2.5 m 08 m *M= 30N - m L. Part A Determine its angular velocity, measured clockwise, when it rotates clockwise 90°. Express your answer using three significant figures. Enter positive value if the angular velocity is clockwise and negative value if the angular velocity is counterclockwise. ANSWER: rad/s %3=arrow_forwardGiven a projectile with a m= 0.025 kg with a velocity of v = 400 m/s which impacts a rod with a mrod = 3.3 kg and L=0.8m, determine the angular velocity of the rod immediately after impact, which can be assumed to be perfectly plastic. Note: h= 0.6 m and plastic impact results in the projectile embedding into the rod. O harrow_forward
- Find Part D and Earrow_forwardQuestion 3 3.1. The 10 kg disk shown below is pin supported at its center. Determine the number of revolutions it must make to attain a speed of 150 rpm starting from rest. It is acted upon by the constant force F = 10 N, which is applied to the cord wrapped around its periphery, and a constant couple moment T = 5 Nm. Neglect the mass of the cord in the calculations. T= 3 Nm. 0.2 m F= 10N 3.2. The same disk is suddenly unbalanced and its axis passing through its mass center G. If it is released from rest, determine the horizontal and vertical components of reaction at the pin O as shown below. 100 0, 10 kgarrow_forwardThe arms of a Porter governor are each 250 mm long and pivoted on the governor axis. The mass of each ball is 5 kg and the mass of the central sleeve is 30 kg. The radius of rotation of the balls is 150 mm when the sleeve begins to rise and reaches to certain radius at maximum speed. The governor has radius that is 175 mm at mid position. The speed range of the governor is 38 rpm, and the increment in speeds is constant in the three positions. Find : (1) the friction of the load which existed at the sleeve, and (2) the governor radius at maximum speed. The friction is ignore in mid position only.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY