
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
45)
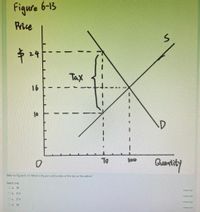
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 6-13
Pice
24
Tax
16
10
TO
Quertity
l00
Refer to Figure 6-13. What is the per-unit burden of the tax on the sellers?
Select one:
O a. $6
cross out
O b. $16
cross out
O c. $14
cross out
O d. $8
cross out
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (Q1) Many software companies, after years of providing unlimited free telephone technical support for their products, began to charge for these services (typically after an initial start-up period of 90 days). Most companies offer two pricing plans. For instance, Lotus Development offers users of their spreadsheet software the option of paying either (i) $2.00 per minute for telephone support or (ii) a $129 flat charge for a year of unlimited toll-free calls. Question 1: Consider a customer with a yearly (expected) demand for service support of P = 11 – 0.1Q, where P is the price per minute and Q is the number of minutes of calls made per year. How many calls would this customer make under plan (i)? Why? How many calls would he or she make under plan (ii)? What would be the annual cost to this customer under each plan? Explain your answer. Question 2: Which plan would this customer choose? Explain your answer.arrow_forward(8) The consumer price index using a __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ to calculate the index value.arrow_forward19. (Use this information to answer qustion 19 - 23) Suppose there is one firm solving the following profit maximization problem. Note that the output price is normalized as 1. max AL¹-a {L} wL where A = 2 and a = 0.6. How much is the aggregate labor demand when the wage is 1? (a) 0.242 (b) 0.435 (c) 0.689 (d) 0.923arrow_forward
- 6. Who should pay the tax? The following graph gives the labor market for laboratory aides in the imaginary country of Episteme. The equilibrium hourly wage is $10, and the equilibrium number of laboratory aides is 150. Suppose the federal government of Episteme has decided to institute an hourly payroll tax of $4 on laboratory aides and wants to determine whether the tax should be levied on the workers, the employers, or both (in such a way that half the tax is collected from each party). Use the graph input tool to evaluate these three proposals. Entering a number into the Tax Levied on Employers field (initially set at zero dollars per hour) shifts the demand curve down by the amount you enter, and entering a number into the Tax Levied on Workers field (initially set at zero dollars per hour) shifts the supply curve up by the amount you enter. To determine the before-tax wage for each tax proposal, adjust the amount in the Wage field until the quantity of labor supplied equals the…arrow_forwardEach term (3 months) the current group of economics students completed a questionnaire as to how much they would spend on new purchases compared to how much they would save/pay off bills, if they suddenly and unexpectedly received a check for $1,000. The average MPC is shown in the table below. Month in which student poll was taken Average of students’ responses as MPC March 0.41 June 0.30 September 0.22 December 0.56 What do these MPC’s imply about the students’ thinking over the course of the year? (Enter response here.) What is likely happening in the economy during the same period of time?arrow_forwardNote:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
- The Law Firm of Smith and Jones of Barrie, Ontario has 3 new civil cases and 5 lawyers available for assignments. Based upon the type of case and the qualifications of each lawyer, the managing partners have determined the profits (in $1000’s) that the law firm would make if each particular lawyer was assigned to each particular case. Their analysis produced the following profits: Profits (1000’s) Case Lawyer A B C Lui 36 53 101 Pathak 39 54 105 Owens 43 50 103 Rosen 42 54 104 Millier 45 57 101 To keep lawyers available for future cases, Smith and Jones’ policy is to assign at most 1 lawyer to each specific case. To better serve its clients, Smith and Jones’ policy is to assign each specific lawyer to at most one case at a time. Using xij’s as your decision variables, formulate a linear programming model so that Smith and Jones’s can determine which…arrow_forwardThe following graph gives the labor market for laboratory aides in the imaginary country of Episteme. The equilibrium hourly wage is $10, and the equilibrium number of laboratory aides is 150. Suppose the federal government of Episteme has decided to institute an hourly payroll tax of $4 on laboratory aides and wants to determine whether the tax should be levied on the workers, the employers, or both (in such a way that half the tax is collected from each party). Use the graph input tool to evaluate these three proposals. Entering a number into the Tax Levied on Employers field (initially set at zero dollars per hour) shifts the demand curve down by the amount you enter, and entering a number into the Tax Levied on Workers field (initially set at zero dollars per hour) shifts the supply curve up by the amount you enter. To determine the before-tax wage for each tax proposal, adjust the amount in the Wage field until the quantity of labor supplied equals the quantity of labor demanded.…arrow_forward40.) What was one negative consequence of the development of factories? a. People migrated to cities for factory jobs b. the first textile factory was built in England c. Diseases spread quickly through cramped factory neighborhoodsarrow_forward
- 2. (a) Derive and carefully explain the wage- and price-setting model.arrow_forward3. Mercantilism Mercantilism is an economic system which developed after manorialism (from the 15th to the 18th centuries – time period) and is associated with colonial types of government. Some countries that practiced mercantilism included Great Britain, Portugal and Spain (society). Mercantilism is when a country believes that the more wealth it stores up, the greater their government should be. So, mercantilist countries build up their nation's wealth by exporting (selling) more goods than they import (buy from other countries). Countries needed to find places to sell their goods as well as to find places where to get natural resources. For this reason, they found and conquered colonies. Colonies supplied their Mother countries with the raw materials that were used to produce finished goods and then send those goods back to their colonies. Generally, merchants controlled what resources were to be produced and how they were to be used, sold or traded. However, monarchs (kings or…arrow_forwardFor each of the proposals, use the previous graph to determine the new number of research assistants hired. Then compute the after-tax amount paid by employers (that is, the wage paid to workers plus any taxes collected from the employers) and the after-tax amount earned by research assistants (that is, the wage received by workers minus any taxes collected from the workers). Levied on Employers (Dollars per hour) 4 Tax Proposal 0 2 Levied on Workers (Dollars per hour) 0 4 2 Quantity Hired (Number of workers) After-Tax Wage Paid by Employers (Dollars per hour) O The proposal in which the entire tax is collected from workers O The proposal in which the tax is collected from each side evenly O The proposal in which the tax is collected from employers O None of the proposals is better than the others After-Tax Wage Received by Workers (Dollars per hour) Suppose the government doesn't want to discourage employers from hiring research assistants and, therefore, wants to minimize the share…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education