
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Chap
More
Prac
C Simp
Inval
For e
Prac
User
All s
O MSc
(9) CZ Unit
SCI
b Ansv
logi Logi
Offic
Prac
Setti
Man
Ims.auis.edu.krd/pluginfile.php/79387/mod_resource/content/0/SCI%20102%20_%20Chapter%202.pdf
Update :
Chapter 2 Motion
35 / 52
87%
+ | 0 O
EXERCISE
A motorboat starting from rest travels in a straight line on a lake.
(ajif the boat achieves a speed of 8.0 m/s in 10s, what is the boat's average
acceleration?
(bIThen, in 5.0 more seconds, the boat's speed is 12 m/s. What
is the boat's average acceleration for the total time?
34
8
ee Ciee le tovlity h
W de e =2
W tee mn t1
35
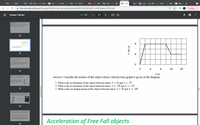
Acceleration of Free Fall objects
> Objects in motion solely under the influence of gravity
are said to be in free fall.
The acceleration due to gravity at the Earth's surface is
directed downward and is denoted by the letter g. Its
magnitude in SI units is
g- 9.81 m/s?
* Frictional effects (such as air resistance) are negligible.
4
8
12
16
36
t (s)
ruestion: Consider the motion of the object whose velocity-time graph is given in the diagram.
Acceleration of Free Fall objects
Consider a constant acceleration of 9.8 m/s2,
Because the velocity increases, the
displacement traveled by the falling
object each second also increases, but
not uniformly
1. What is the acceleration of the object between times t = 0 and t = 2?
2. What is the acceleration of the object between times t = 10 and t =
12?
3. What is the net displacement of the object between times t = 0 and t = 16?
37
* The velocity of a freely falling object on the Earth increases 9.80
m/s each second but the distance covered is not uniform because
the object speeds up. This distance con be found using
d =
g t2
38
* Air resistance is the result of a moving object colliding with air
molecules. Therefore, air resistance (considered a type of
friction) depends on an object's size and shape, as well as on its
speed.
* The larger the object (or the more downward area exposed)
the more collisions and the more air resistance there will be.
* The velocity of a freely falling object on the Earth increases 9.80
m/s each second but the distance covered is not uniform becouse
the object speeds up. This distance can be found using
Acceleration of Free Fall objects
39
(s/u) a
II
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- r (ms) 4. Consider the following v vs. t graph a. What is the acceleration at: i. t= 11 s? ii. t= 15 s? b. How far, and in which direction, did the object travel: i. ii. from t = 13 to t = 18 s? c. During what time intervals is the object speeding up? slowing down? d. During what time intervals is the acceleration positive? Negative? Zero? from t = 4 to t = 11 s? e (sec) iparrow_forwardA toy car can move to the right or left along a horizontal line (the positive portion of the distance axis). The positive direction is to the right. 0 + Choose the correct velocity-time graph (A - H) for each of the following questions. You may use a graph more than once or not at all. If you think that none is correct, answer choice J. A B D V e e 1 e + 0 0 0 e 0 1 0 Time Time Time Time E G H V 1 V + 0 e 0 1 0 0 None of these graphs is correct. Time Time Time Time Which velocity graph shows the car moving toward the left (toward the origin) at a steady (constant) velocity?arrow_forwardA body moves on a coordinate line such that it has a position s = f(t) = t2 - 7t+6 on the interval 0 ≤t≤8, with s in meters and t in seconds. a. Find the body's displacement and average velocity for the given time interval. b. Find the body's speed and acceleration at the endpoints of the interval. c. When, if ever, during the interval does the body change direction? The body's displacement for the given time interval is m. (Type an integer or a simplified fraction.) E The body's average velocity for the given time interval is m/s. (Type an integer or a simplified fraction.) The body's speeds at the left and right endpoints of the interval are (Type integers or simplified fractions.) 3 The body's accelerations at the left and right endpoints of the interval are m/s² and m/s², respectively. (Type integers or simplified fractions.) When, if ever, during the interval does the body change direction? Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes within your choice. OA. The…arrow_forward
- An object's position in a given coordinate system is described by the vector r = t2 i - (3t + 3) j. Assume the object moves without air resistance. a. what is the displacement between times t1=1s & t2=3s? Write your answer in component form.b. what is the object's velocity at t3 = 2 seconds? Write your answer in component form.c. What is the object's acceleration at t4 = 5 seconds? Write your answer in component form.arrow_forwarda.Members of the froghopper family of insects (family Cercopoidea) can accelerate from rest to 0.84 m/s in 5.80 ms. What is the acceleration (in m/s2)? Enter the numerical part of your answer, rounded to three significant figures. b.A western honey bee (Apis mellifera) flies 3.51 m north and then 6.31 m east. What is its displacement from the starting position? Enter only the numerical part of your answer (in m) to the nearest integer.arrow_forward1. Consider the following v-t graph. a. At what time(s) is the object moving fastest? What is its speed at that time(s)? b. c. Draw a matching d-t graph. d. How far did the object move during the first 5 seconds? e. How far did the object move during the first 10 seconds? √(5) O 0 IT N + 6 4 1 T 00 O IN 2 IT -lot *LD O • [] 4 20 t(o)arrow_forward
- a. enter a symbolic expression for the average acceleration vector of the car during the given time period in terms of the problem and standard unit vectors.b. What is the magnitude, in meters per squared second, of the car's acceleration during the given time period.arrow_forwardQ. The diagram below shows the speed-time graph for an object. E 30 25 20 velocity (m/s) 5 9 i B D 10 20 30 40 time(s) Which of the following region has the most acceleration? a) The region from A to B c) The region from C to D b) The region from B to C d) The region from D to Earrow_forwardA cheetah sees a gazelle running at a constant speed of 12.4 m/s. The gazelle is 15 m ahead of the cheetah. The cheetah starts from rest to chase (with constant acceleration) the gazelle. After 4.2 s the cheetah catches the gazelle. a.)Determine the distance that cheetah traveled before it catches the gazelle. b.) What is the acceleration of the cheetah? c.) What is the cheetah's speed when it catches the gazelle?arrow_forward
- Suppose a rock is launched from the ground straight upward (use up as the positive direction) and reaches its maximum height in a time of 3.0 s. Then the rock descends back to the ground. (To simplify your numbers, you may use |g| = 10 m/s².) Find the following: a. The maximum height reached above the ground. b. The velocity of the rock at the time t = 4.5 s.arrow_forwardAt time t, the position of a body moving along the s-axis is s=−t^3+12t^2−36t m. a. Find the body's acceleration each time the velocity is zero. b. Find the body's speed each time the acceleration is zero. c. Find the total distance traveled by the body from t=0 to t=3.arrow_forwardA motorcycle begins at rest at t0 = 0 seconds. The motorcycle starts moving, and eventually covers a distance d = 840 m, in a time tf = 189 s. In a coordinate system with north being the positive x-direction, the motorcycle's motion is in the northern direction (see figure). 1. What was the motorcycle's average velocity in in the northern direction vavg,N, in this period in meters per second? 2. If the motorcycle's final velocity at tf was 12 m/s, what was the motorcycle's average acceleration in the northern direction, aavg,N, during this period in m/s2?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON