
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:4)) 50%
Sun 10:50 AM Q
session.masteringchemistry.com
Consider summer class...
Inbox (13) - thesym1@g...
Class Schedule Listing
Schedule 111.009 & 111....
Ellucian Degree Works...
Pearson's MyLab & Mas...
ALEKS - Sofia Simmons...
MasteringChemistry: H.
<Homework 5
Electrolytic Properties and Molarity
7 of 24
<>
I Review I Constants I Periodic Table
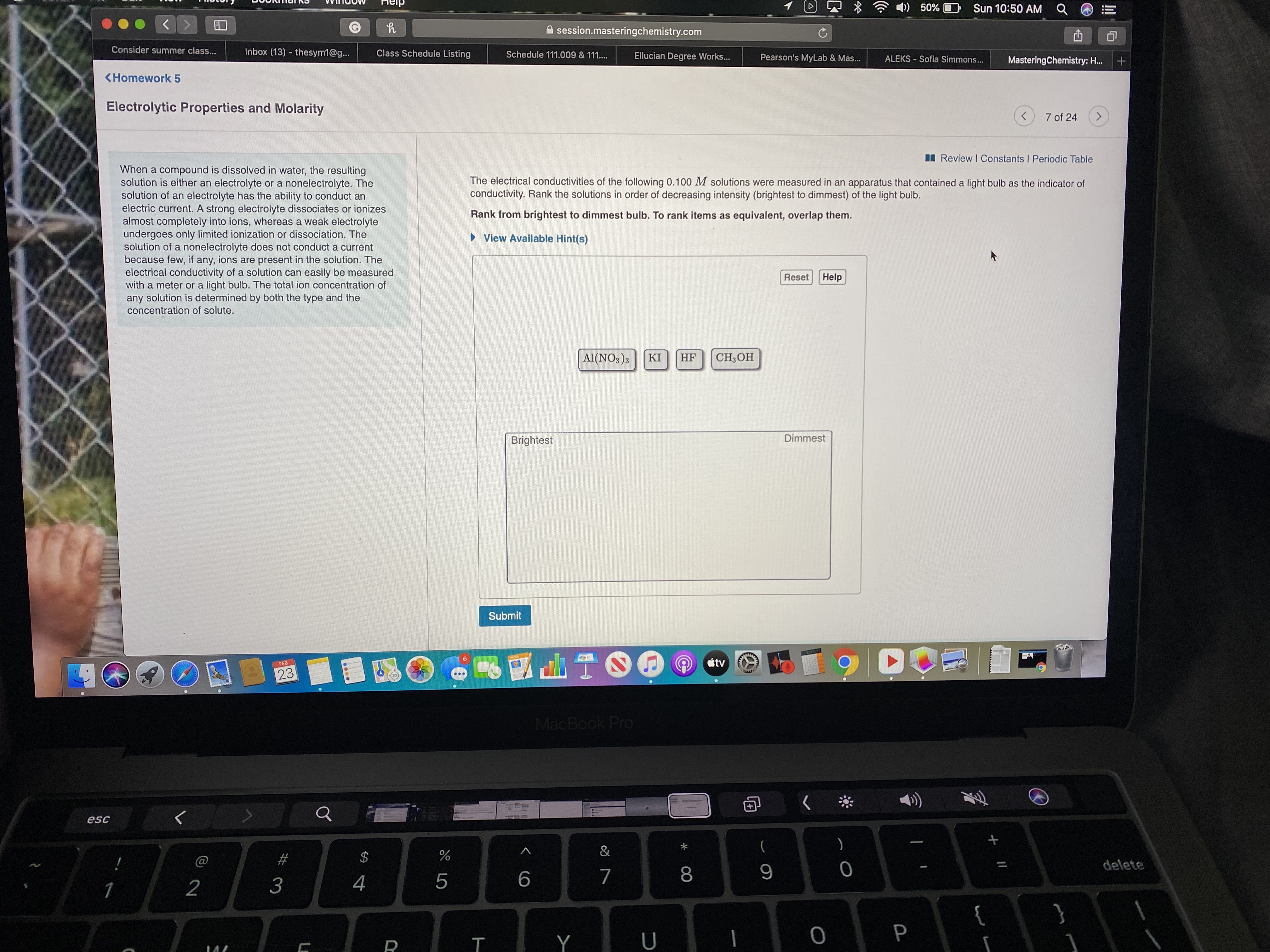
When a compound is dissolved in water, the resulting
solution is either an electrolyte or a nonelectrolyte. The
solution of an electrolyte has the ability to conduct an
electric current. A strong electrolyte dissociates or ionizes
almost completely into ions, whereas a weak electrolyte
undergoes only limited ionization or dissociation. The
solution of a nonelectrolyte does not conduct a current
because few, if any, ions are present in the solution. The
electrical conductivity of a solution can easily be measured
with a meter or a light bulb. The total ion concentration of
any solution is determined by both the type and the
concentration of solute.
The electrical conductivities of the following 0.100 M solutions were measured in an apparatus that contained a light bulb as the indicator of
conductivity. Rank the solutions in order of decreasing intensity (brightest to dimmest) of the light bulb.
Rank from brightest to dimmest bulb. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.
• View Available Hint(s)
Reset
Help
Al(NO3)3
KI
HF
CH;OH
Brightest
Dimmest
Submit
tv
FEB
23
MacBook Pro
esc
&
(
@
23
24
delete
8
1
2
3
4
{
}
Transcribed Image Text:Safari
File
Edit
View History Bookmarks
Window
Help
)) 50%
Sun 10:51 AM
session.masteringchemistry.com
Consider summer class...
Inbox (13) - thesym1@g...
Class Schedule Listing
Schedule 111.009 & 111..
Ellucian Degree Works...
Pearson's MyLab & Mas...
ALEKS - Sofia Simmons...
<Homework 5
MasteringChemistry: H.
Electrolytic Properties and Molarity
7 of 24
When a compound is dissolved in water, the resulting solution is either
an electrolyte or a nonelectrolyte. The solution of an electrolyte has the
ability to conduct an electric current. A strong electrolyte dissociates or
ionizes almost completely into ions, whereas a weak electrolyte
undergoes only limited ionization or dissociation. The solution of a
nonelectrolyte does not conduct a current because few, if any, ions are
present in the solution. The electrical conductivity of a solution can
easily be measured with a meter or a light bulb. The total ion
concentration of any solution is determined by both the type and the
concentration of solute.
I Review I Constants I Periodic Table
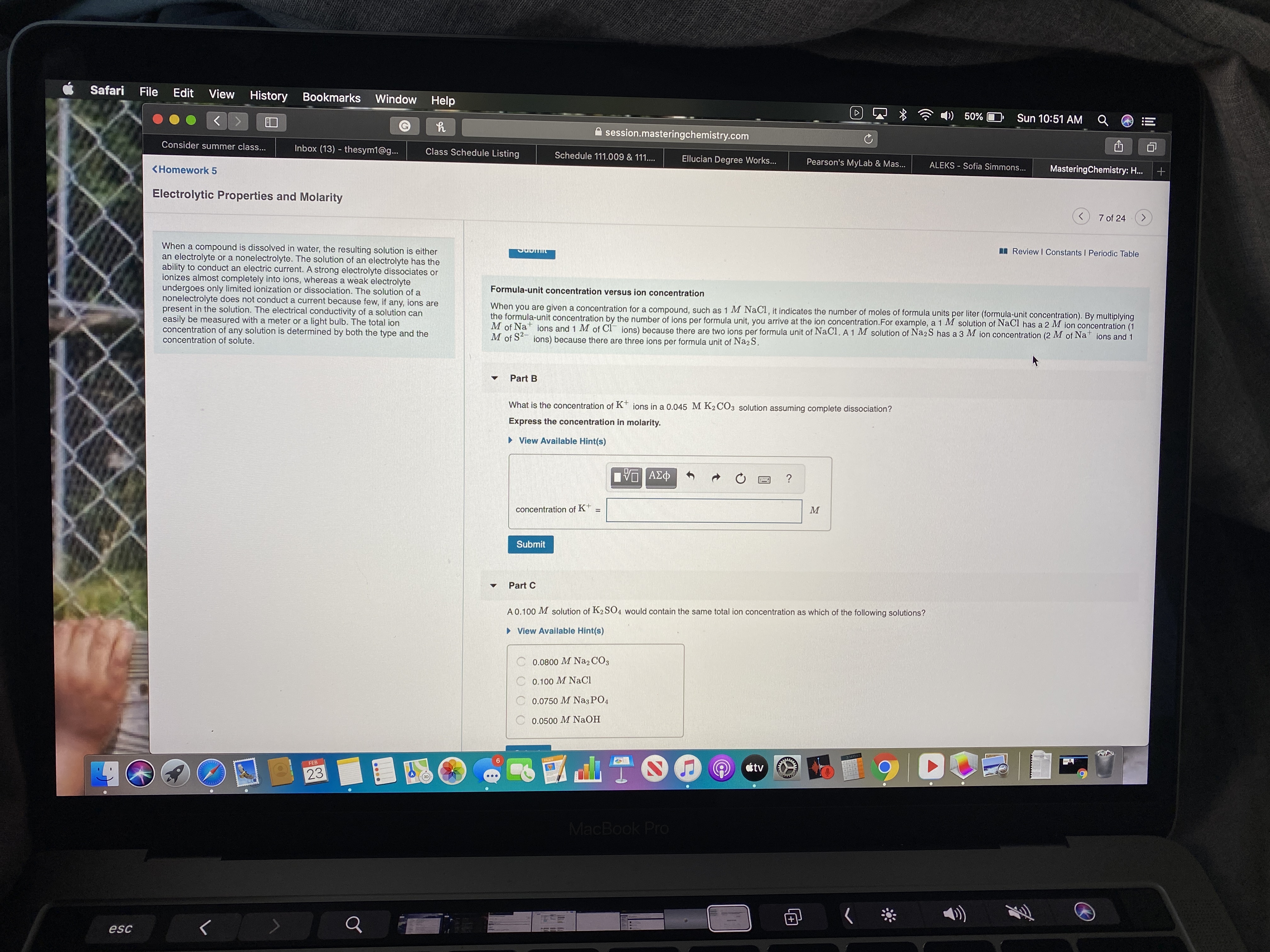
Formula-unit concentration versus ion concentration
When you are given a concentration for a compound, such as 1 M NaCI, it indicates the number of moles of formula units per liter (formula-unit concentration). By multiplying
the formula-unit concentration by the number of ions per formula unit, you arrive at the ion concentration.For example, a 1 M solution of NaCl has a 2 M jon concentration (1
M of Na ions and 1 M of CI ions) because there are two ions per formula unit of NaCl. A 1 M solution of Na2 S has a 3 M ion concentration (2 M of Na
M of S ions) because there are three ions per formula unit of Na2S.
ions and 1
Part B
What is the concentration of K* ions in a 0.045 M K2 CO3 solution assuming complete dissociation?
Express the concentration in molarity.
> View Available Hint(s)
νο ΑΣφ
concentration of K+
Submit
Part C
A 0.100 M solution of K2SO4 would contain the same total ion concentration as which of the following solutions?
> View Available Hint(s)
0.0800 M Na2 CỐ3
C 0.100 M NaCl
0.0750 M NazPO4
0.0500 M NaOH
FEB
tv
23
MacBook Pro
esc
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 13 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Safari File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help ) 47% Sun 11:00 AM Q A session.masteringchemistry.com Consider summer class... Inbox (13) - thesym1@g... Class Schedule Listing Schedule 111.009 & 111... Ellucian Degree Works... Pearson's MyLab & Mas... ALEKS - Sofia Simmons... MasteringChemistry: H.. I Review I Constants I Periodic Table To solve stoichiometry problems, you must always calculate numbers of moles. Recall that molarity, M , is equal to the concentration in moles per liter: M = mol/L. When solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chloride are mixed, silver chloride precipitates out of solution according to the equation AGNO3 (aq) + NaCI(aq)→AgCl(s) + NaNO3 (aq) Part A What mass of silver chloride can be produced from 1.19 L of a 0.232 M solution of silver nitrate? Express your answer with the appropriate units. > View Available Hint(s) mass of AgCl = Value Units Submit Part B The reaction described in Part A required 3.31 L of sodium chloride. What is the concentration…arrow_forward+ www-awu.aleks.com Mail - Stovall, Anniston Marie -... Week 6 Objectives and Notes:. b My Questions | bartleby A ALEKS - Anniston Stovall - Learn G atomic mass of water - Google... STEM Lab Schedule: MS: ULC:.. O CHEMICAL REACTIONS Anniston V Theoretical yield of chemical reactions 1/5 Gaseous ethane (CH,CH,) reacts with gaseous oxygen gas (O2) to produce gaseous carbon dioxide (CO,) and gaseous water (H,O). What is the theoretical yield of water formed from the reaction of 9.32 g of ethane and 52.4 g of oxygen gas? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits in it. ol. Ar Explanation Check © 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardI don't know how to fill out those boxesarrow_forward
- 12: Mastery - Kinetics X com/ilm/takeAssignment/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator=assignment-take juju_ ncepts " Q Search OWLv2 | Online teaching and le Free Online Survey... [CO] = [Cl₂] = [COCI₂] = Submit Answer Home - Academia... PRO Modules Create Your Rubric-... [Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. The equilibrium constant, K, for the following reaction is 77.5 at 600 K. CO(g) + Cl₂(g) CoCl₂(g) Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactant and products when 0.474 moles of CO and 0.474 moles of Cl₂ are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 600 K. Retry Entire Group IL & M M M X + hp 4+ 7 more group attempts remaining 8 19 ( 9 110 The Utility Experts ... m 4 12 = insert » | ← 12/1 baarrow_forwardSafari File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help 4)) 51% O Sun 10:43 AM session.masteringchemistry.com Consider summer class... Inbox (13) - thesym1@g... Class Schedule Listing Schedule 111.009 & 111... Ellucian Degree Works... Pearson's MyLab & Mas... ALEKS - Sofia Simmons... MasteringChemistry: H...arrow_forwardEsc B II. Brightspace Aktiv Chemistry C D Q A Z + @ 2 S Alt W app.101edu.co Walmart - Hiring Ce... What volume in mL of 0.220 M HBr solution is required to produce 0.0145 moles of HBr? X O F3 - X # 3 11. Unit 12: Late Adulthood - Devel X E D F4 с 14 $ 4 F5 刀 LL F % 5 V F6 T G F7 A 6 Simulation play - Labster B Y F8 & 7 H Question 4 of 9 DELL U N F9 X D * 8 2 F10 1 Walmart - Hiring Center ( M 9 K F11 ဆုံး O O F12 L Alt P X + 4 7 +/- PrtScr W Garrow_forwardEnow-owl.cengagenow.com/ilrn/takeAssignment/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator o-dos- HR Portal a GPS, Finders & Acc... e answers will not be recorded For the following reaction: k H₂CO3 + 2 NaOH → Na₂CO3 + 2 H₂O Submit Answer Home - Workday Calculate the normality of a solution that contains 2.39 grams of H₂CO3 in 707 mL of solution. Try Another Version myQ- myQ Serv 10 item attempts remaining Use the Rearrow_forwardNeed help asap chemarrow_forwardSafari File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help () 48% Sun 10:56 AM A session.masteringchemistry.com Consider summer class... Inbox (13) - thesym1@g... Class Schedule Listing Schedule 111.009 & 111.. Ellucian Degree Works... Pearson's MyLab & Mas... ALEKS - Sofia Simmons... MasteringChemistry: H-arrow_forwardn Course: CHEM262-SEC01 Org. x O OWL Exam O Noor Abid - 32843659 S x b Answered: Place the following x G how to take a screenshot on m + A owl.umass.edu/owlj/servlet/Student Update : M Gmail O YouTube e Google Keep n UMass Amherst M.. C Write The Comple.. O SPIRE Logon A Swank Movies O Discovering Nutrit. 26 UMass Amherst -. t. Minitab >> .CO2H heat `CO2H ОН H. + CO2 + CO2 A В + CO2 +H2Oarrow_forward) - O + 88 www-awu.aleks.com Files Lecture 16 - The Punic... Rhetorical Analysis Essa... Journal Assignment: Pre... Document3.docx ALEKS - Anniston Stovall... b Answered: One way the... O CHEMICAL REACTIONS Anniston V Solving for a reactant in solution 1/5 One way in which the useful metal copper is produced is by dissolving the mineral azurite, which contains copper(II) carbonate, in concentrated sulfuric acid. The sulfuric acid reacts with the copper(II) carbonate to produce a blue solution of copper(II) sulfate. Scrap iron is then added to this solution, and pure copper metal precipitates out because of the following chemical reaction: Fe(s) + CUSO 4(aq) Cu(s) + FeSO4(aq) Suppose an industrial quality-control chemist analyzes a sample from a copper processing plant in the following way. He adds powdered iron to a 100. mL copper(II) sulfate sample from the plant until no more copper will precipitate. He then washes, dries, and weighs the precipitate, and finds that it has a mass of…arrow_forwardB pleasearrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY