
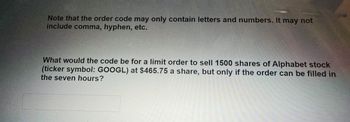
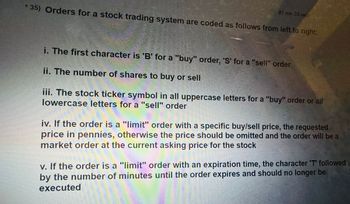
35) Orders for a stock trading system are coded as follows from left to right:
i. The first character is 'B' for a "buy" order, 'S' for a "sell" order
ii. The number of shares to buy or sell
iii. The stock ticker symbol in all uppercase letters for a "buy" order or alf lowercase letters for a "sell" order
iv. If the order is a "limit" order with a specific buy/sell price, the requested price in pennies, otherwise the price should be omitted and the order will be a market order at the current asking price for the stock
v. If the order is a "limit" order with an expiration time, the character 'T' followed by the number of minutes until the order expires and should no longer be executed
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- Flora Co sells bunches of fresh flowers which have a limited shelf life so forecasting sales demand is extremely important for maximising profits. Quarter 1 Quarter 1 contains a national holiday and as a result sales of a particular red flower are usually very high. Sales of the red flower will depend on market conditions. After the national holiday there will be no demand for the red flowers and they will be thrown away. Flora Co must decide whether to purchase 250 bunches, 400 bunches or 500 bunches of the red flowers from its supplier for re-sale to its customers. The following payoff table has been produced: Market conditions Poor Good Excellent Expected value Probability 0.20 0.25 0.55 Number of bunches to be bought from supplier 400 $900 $3,900 $3,900 250 $2,400 $2,400 $2,400 $2,400 $3,300 500 ($100) $2,900 $4,900 $3,400arrow_forwardA business introduces e-purchasing and is able to process the same number of orders with lesser buyers. As a result of this: purchase quantity should be reduced inventory holding cost must be reduced O purchase lead time should be reduced inventory pooling must be initiatedarrow_forwardThe following table contains figures on the monthly volume and unit costs for a random sample of 16 items from a list of 2,000 inventory items at a health care facility: Item Unit Cost Usage Item Unit Cost Usage K34 $10 200 F99 20 60 K35 25 600 D45 10 550 K36 36 150 D48 12 110 M10 16 25 D52 15 110 M20 20 80 D57 40 120 Z45 80 200 N08 30 40 F14 20 300 P05 16 500 F95 30 800 P09 10 30 Determine the percentage of items in each category and the annual dollar value for each category for part barrow_forward
- Dart is a product of the Digby company. Digby's sales forecast for Dart is 2067 units. Digby wants to have an extra 10% of units on hand above and beyond their forecast in case sales are better than expected. (They would risk the possibility of excess inventory carrying charges rather than risk lost profits on a stock out.) Taking current inventory into account, what will Dart's Production After Adjustment have to be in order to have a 10% reserve of units available for sale? a. 2053 units b. 2274 units c. 2260 units d. 2067 unitsarrow_forwardProducts A,B, and C are sold door-to-door. A costs $ 3 per unit, take 10 minutes to sell (on the average) and costs $0.50 to deliver to customer. B costs $ 5, takes 15 minutes to sell, and is left with the customer at the time of sale. C costs $ 4, takes 12 minutes to sell, and costs $ 1 to deliver. During any week, a salesperson is allowed to draw up to $ 500 worth of A,B,C (at cost) and is allowed delivery expenses not to exceeds $ 75. If a salesperson’s selling time is not expected to exceed 30 hours (1,800 minutes) in a week, and if the salesperson profit (net after all expenses) is $ 1 each on a unit of A and B and $ 2 on a unit of C, what combination of sales of A, B, and C will lead to maximum profit, and what is the maximum profIt?arrow_forwardWith a probabilistic model, increasing the service level A. will decrease the level of safety stock level. B. will increase the cost of the inventory holding. C. will have no impact on the cost of the inventory policy. D. will reduce the cost of the inventory holding.arrow_forward
- North Dakota Electric Company estimates its demand trend line (in millions of kilowatt hours) to be: D = 77.0 +0.43Q, where Q refers to the sequential quarter number and Q = 1 for winter of Year 1. In addition, the multiplicative seasonal factors are as follows: Quarter Winter Spring Summer Fall In year 26 (quarters 101-104), the energy use for each of the quarters beginning with winter is (round your response to one decimal place): Quarter Winter Factor (Index) 0.80 1.20 1.40 0.60 Spring Summer Fall Energy Usearrow_forwardSelect the appropriate description of the distribution 10 | 0, 0, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 8 12 | 0, 3, 4, 5, 8 13 | 0, 4, 6 14 | 1, 3 Legend 11 | 0 represents 100 Uniforms Bell shaped Skewed right Skewed leftarrow_forwardAn automotive warehouse stocks a variety of parts that are sold at neighborhood stores. One particular part, a popular brand of oil filter, is purchased by the warehouse for $1.50 each. It is estimated that the cost of order processing and receipt is $100 per order. The company uses an inventory carrying charge based on a 28 percent annual interest rate. The monthly demand for the filter follows a normal distribution with mean 280 and standard deviation 77. Order lead time is assumed to be five months. Assume that if a filter is demanded when the warehouse is out of stock, then the demand is back-ordered, and the cost assessed for each back-ordered demand is $12.80. Determine the following quantities: The optimal values of the order quantity and the reorder level. The average annual cost of holding, setup, and stock-out associated with this item assuming that an optimal policy is used. Evaluate the cost of uncertainty for this process. That is, compare the average annual cost you…arrow_forward
- Give typed answer onlyarrow_forwardInventory can be very expensive for firms to hold and manage. One measure of how effective a firm is at managing their inventory is the inventory sales ratio (inventory/sales). Assume a firm has quarterly sales of 1 million and inventory is normally distributed with a mean of $500k and a standard deviation of $100k. simulate the expected inventory to sales ratio for 10,000 iterations. What is the expected mean inventory to sales ratio? What is the probability that the inventory sales ratio is less than 0.5?arrow_forwardYou are the president of XYZ Manufacturing company. You have recently learned about the following issue: A month ago, the company’s general manager (GM) told one of the line managers to produce an extra 15,000 units of a product so that there would be inventory in stock for the next time the item is ordered. Last week, the GM scolded the line manager for having 15,000 units of the item in stock. The GM told the line manager that producing excess inventory costs the company money and should never be done. The GM then puts the line manager on a performance plan. This is not the first time you have heard about the GM telling an employee to do one thing only to criticize him or her for doing it later. This employee feels very frustrated by this, but does not want to make a formal complaint because she has seen other employees lose their jobs or get demoted for questioning the GM. Create an outline that proposes a leadership solution to this issue. The outline should address the following:…arrow_forward
 Principles Of MarketingMarketingISBN:9780134492513Author:Kotler, Philip, Armstrong, Gary (gary M.)Publisher:Pearson Higher Education,
Principles Of MarketingMarketingISBN:9780134492513Author:Kotler, Philip, Armstrong, Gary (gary M.)Publisher:Pearson Higher Education, MarketingMarketingISBN:9781259924040Author:Roger A. Kerin, Steven W. HartleyPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
MarketingMarketingISBN:9781259924040Author:Roger A. Kerin, Steven W. HartleyPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Foundations of Business (MindTap Course List)MarketingISBN:9781337386920Author:William M. Pride, Robert J. Hughes, Jack R. KapoorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Business (MindTap Course List)MarketingISBN:9781337386920Author:William M. Pride, Robert J. Hughes, Jack R. KapoorPublisher:Cengage Learning Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)MarketingISBN:9780134149530Author:Gary Armstrong, Philip KotlerPublisher:PEARSON
Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)MarketingISBN:9780134149530Author:Gary Armstrong, Philip KotlerPublisher:PEARSON
 Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning





