
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Hi could you fill out the blanks for me?

Transcribed Image Text:32
11
17
7
6.
y
167
37
132
127
69
53
In this setting we have Ex = 74, Ey = 585, Ex? = 1520, Ey? = 70,381, and Exy = 9793.
(a) Find x, y, b, and the equation of the least-squares line. (Round your answers for x two decimal places. Round your least-squares estimates to four decimal
and y to
places.)
y =
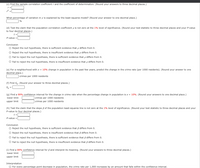
Transcribed Image Text:(c) Find the sample correlation coefficient r and the coefficient of determination. (Round your answers to three decimal places.)
What percentage of variation in y is explained by the least-squares model? (Round your answer to one decimal place.)
%
(d) Test the claim that the population correlation coefficient p is not zero at the 1% level of significance. (Round your test statistic to three decimal places and your P-value
to four decimal places.)
P-value -
Conclusion
O Reject the null hypothesis, there is sufficient evidence that p differs from 0.
O Reject the null hypothesis, there is insufficient evidence that p differs from 0.
O Fall to reject the null hypothesis, there is sufficient evidence that p differs from 0.
O Fail to reject the null hypothesis, there is insufficient evidence that p differs from 0.
(e) For a neighborhood with x = 10% change in population in the past few years, predict the change in the crime rate (per 1000 residents). (Round your answer to one
decimal place.)
crimes per 1000 residents
(f) Find S.. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
S.-
(9) Find a 99% confidence interval for the change in crime rate when the percentage change in population is x = 10%. (Round your answers to one decimal place.)
lower limit
| crimes per 1000 residents
upper limit
crimes per 1000 residents
(h) Test the claim that the slope B of the population least-squares line is not zero at the 1% level of significance. (Round your test statistic to three decimal places and your
P-value to four decimal places.)
P-value =
Conclusion
O Reject the null hypothesis, there is sufficient evidence that 8 differs from 0.
O Reject the null hypothesis, there is insufficient evidence that 8 differs from 0.
O Fall to reject the null hypothesis, there is sufficient evidence that p differs from 0.
O Fall to reject the null hypothesis, there is insufficient evidence that 8 differs from 0.
(1) Find a 99% confidence interval for ß and interpret its meaning. (Round your answers to three decimal places.)
lower limit
upper limit
Interpretation
O For every percentage point decrease in population, the crime rate per 1,000 increases by an amount that falls within the confidence interval.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman