
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
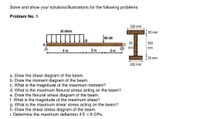
Transcribed Image Text:Solve and show your solutions/illustrations for the following problems:
Problem No. 1
300 mm
30 kN/m
50 mm
40 KN
B
50
350
Ic
mm
A
mm
4 m
2 m
2 m
50 mm
200 mm
a. Draw the shear diagram of the beam.
b. Draw the moment diagram of the beam.
c. What is the magnitude of the maximum moment?
d. What is the maximum flexural stress acting on the beam?
e. Draw the flexural stress diagram of the beam.
f. What is the magnitude of the maximum shear?
g. What is the maximum shear stress acting on the beam?
h. Draw the shear stress diagram of the beam.
i. Determine the maximum deflection if E = 8 GPa.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The solid shaft shown in the figure below is fixed at one end and has a lever at the other. The shaft is supported by two bearings. A force F of 790 N is applied at the end of the lever, a distance b of 75 mm from the centre line of the shaft. The shaft has an outer diameter of 12 mm. Find the bending stress at point A, on the outer surface of the shaft, a distance a of 80 mm along the shaft from the lever. Give your answer in N/mm² to 3 significant figures. Fixed end Bearing Shaft A a Lever b Farrow_forwardQuestion 2) In the system given in the figure, a distributed load of w=36 kN/m acts on the rod AB of L=4 m length. The angle θ that the bar BC makes with the horizontal is θ=48°. The allowable normal stress for bar BC is σm= 221 MPa, and the allowable shear stress for pins at points A and B is τm=68 MPa. Bar BC has a rectangular section and the side length a of the section is given as a=34 mm. According to this;Question 2-A) Find the smallest b side length required for the bar section BC. (Write your result in mm.)Question 2-B) The connection type at point B is given in the figure next to it. Accordingly, find the smallest diameter required for pin B. (Write your result in mm.)arrow_forwardThe internal shear force V at a certain section of an aluminum beam is 40 kN. The beam's centroid is located 54.40 mm above the bottom surface of the beam, and the moment of inertia is l₂ = 398,300 mm4. Determine the shear stress at point H, which is located 30 mm above the bottom surface of the beam. 30 mm 75 mm y H 5 mm 5 mm 75 mmarrow_forward
- A vertical force P of magnitude 15 kN is applied at point C located on the axis of symmetry of the cross-section of a short column. Knowing C = 80 mm, d, e, f and g are 70, 30, 40 and 70 mm, respectively. P y d B B g ежеж a) Determine (a) the stress at point A. Use negative sign to indicates the compressive stress. A = MPa b) Determine the stress at point B. Use negative – sign to indicates the compressive stress. B= __MPa c) Determine the location of the neutral axis where the stress is equal to zero from point A (in mm)arrow_forwardH.W 2 A steel tee shape is used to support the loads shown on the beam in Figure 2 a. dimensions of the shape are shown in Figure 2b. determine: The Consider the entire 24-ft length of the beam and (a) the maximum tension bending stress at any location along the beam, and (b) the maximum compression bending stress at any location along the beam. 16.00 in. y | 7 kips | 16 kips 17 kips 1.50 in. 6 kips/ft 18.50 in. B |C D E 6 ft 4 ft 10 ft 4 ft 0.75 in. FIGURE 2 a. FIGURE 2 b.arrow_forwardConsider a point in a structural member that is subjected to plane stress. Normal and shear stresses acting on horizontal and vertical planes at the point are shown. If o = 25 MPa in the direction shown, determine the principal stresses at the point. 28 MPa 16 MPa O 39.2 MPa and -30.2 MPa O 31.6 MPa and -35.8 MPa 54.1 MPa and -41.3 MPa 35.8 MPa and -27.4 MPa O 27.7 MPa and -39.0 MPa Save for Later eTextbook and Media Attempts: 1 of 3 used Submit Answerarrow_forward
- 2.arrow_forwardThe beam is subjected to the load at its end. Take P=4.2 kN and V = 2 kN. (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 30 mm VV 60 mm 2m B The beam is subjected to the load at its end. Take P = 4.2 kN and V = 2 kN .Determine the maximum principal stress at point B.arrow_forwardThe frame supports the distributed load shown. Determine the state of stress acting at points E and D. Show the results on a differential element at this point. 4 kN/m DA -1.5m-15m+ 3 m 1 BA 20 mm 60 mm 20 mm. 5m T D 50 mmarrow_forward
- The horizontal beam is supported by a pin at A and the pin-connected link BC. It has a uniformly distributed loading w = 2.6 kN/m as shown in the figure. All the pins are in double shear and have a diameter of 20 mm. Determine the max shear stress in the pin at C. Input your answer as a value only in MPa to one decimal place without +/- sign. W 1.5 m 2 m B 1marrow_forward4.2- If positive M of 20kN.m is applied, draw the bending stress distribution. Est =200GPa and EAlu = 10GPa 180mm 20mm Wood Steel 100mmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning