
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please help with this sample problem presented in our lecture. Explain the relevant concepts on how to derive the answers. I've already submitted this initially but it was wrong. Thank you!
Sample Problem:
The rigid angle bar ABC is pinned at B with a double-shear bolt connection and is attached to a 12 mm diameter stainless-steel alloy cable at CD. The other end of the steel cable is attached to a rigid plate DE that is attached to a rubber block with dimensions of 150 mm x 25 mm x 200 mm (L x W x H) fixed on ground. Use the stress-strain diagrams for the steel cable and the rubber block in Figures 2 and 3 in answering the following questions.
Determine the following:
- The internal force in the stainless-steel alloy cable.( T = ______ kN)
- The resultant support reaction at the pin support.(R_b = _____ kN)
- The minimum required bolt diameter using a factor of safety equal to 2 and the average shear stress capacity of the bolt equal to 372 MPa. d_bolt >= ___ mm
- Axial deformation of the stainless-steel alloy cable. (Deformation_CD = ____ mm)
- Displacement of the rigid plate DE, if the dimensions of the plate is 25 mm x 150 mm while the height of the rubber is 200 mm.
- Angle of rotation of the rigid angle bar ABC and draw the corresponding sketch of the final displacement. (in rad)
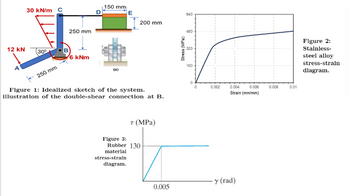
Transcribed Image Text:30 kN/m C
12 kN
300
B
250 mm
250 mm
6 kNm
150 mm
E
640
200 mm
480
(a)
Figure 1: Idealized sketch of the system.
illustration of the double-shear connection at B.
Figure 3:
7 (MPa)
Rubber 130
material
stress-strain
diagram.
Stress (MPa)
320
160
0.002
0.004
0.006
0.008
0.01
Strain (mm/mm)
y (rad)
0.005
Figure 2:
Stainless-
steel alloy
stress-strain
diagram.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please show a detailed solution and explanation including its FBD. Thank you!arrow_forwardIf the load that can be supported by the given support structure is unknown, calculate the maximum load that the structure can support by considering the maximum allowable stress for section BC is 155.8 MPa. provide your answer in kN with precision to two decimal points. 600 mm Answer: 50 mm d-20 mm 800 mm- Barrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning