
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
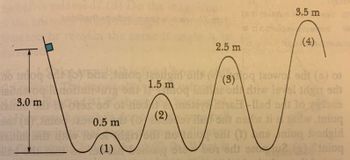
10. A stationary block is released on a frictionless ramp at a height of 3.0 m. There are other hill heights along the ramp as shown in the figure. The hills have identical circular tops, and the block does not fly off any hill. If the mass of the block is 4 Kg, what would be the velocity as it passes hill (1)?
Transcribed Image Text:no
Bir
16
3.0 m
BIDY
jszi kuke 3.5 m
m
(4) losum
2.5 m
Sahion trenghten
WFT
oq
1.5 m
(3) og Jeswo sit (s) of
Broddiw lovel idgin ods
(2) ile or now tiedwinioq
odl noniebil (1) anion feargin
ng box ods ou2 (3) Stioqg
78
HOWAR
Fondsted
\
0.5 m
(1)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Jane has a mass of 50 kg and starts from a high of 5 m above the ground. At the bottom of her swing, she grabs Tarzan (mass 70 kg standing on the ground) and they swing up together. She is aiming for branch that is 3 m above the ground. Will they make it.arrow_forwardQUESTION 7 Which of the following has the greatest kinetic energy? O a. A ball thrown at 15 m/s with a mass of 2 kg. O b. A ball rolled at 2 m/s with a mass of 15 kg. OC. A ball dropped at 0 m/s from a height of 1 meter with a mass of 1 kg. Od. A ball tossed at 5 m/s with a mass of 8 kg QUESTION 8 What quadrant will the resultant vector for the following forces? F1=250N in positive x axis, F2=300N (154 degree counterclockwise) Quadrant I (+x, +y) b. Quadrant II (-x, +y) a. C. Quadrant III (-x, -y) Quadrant IV (+x, -y) d. QUESTION 9 What is power? a. Gathering the energy to finish this lab exam. Ob. A conservative quantity intrinsic to the object. OC. A force x a distance. Od. A force x a distance per unit timearrow_forwardTwo objects are connected by a light string passing over a light, frictionless pulley. The 5.00-kg object is released from rest at a point 4.00 m above the floor. Find the speed of the 5.00-kg object when it is 1 meter above the floor. m, = 5.00 kg h = 4.00 m m, = 3.00 kg 4.756 m/s 3.834 m/s 4.475 m/s 3.942 m/s 4.135 m/s 3.384 m/s А. D. В. Е. С. F.arrow_forward
- What is the Kinetic Energy ? Cart Mass, mc . 284 kg Angle, θ 49 degrees Distance, d . 75 m Suspended Mass . 320 kg Velocity 1 1.48 m/s Velocity 2 1.43 m/s Velocity 3 1.487 m/s Average Velocity 1.466 m/sarrow_forwardTwo objects (m1 = 4.70 kg and m2 = 2.85 kg) are connected by a light string passing over a light, frictionless pulley as in the figure below. The 4.70-kg object is released from rest at a point h = 4.00 m above the table. answer all of the follwing parts (a) Determine the speed of each object when the two pass each other. m/s(b) Determine the speed of each object at the moment the 4.70-kg object hits the table. m/s(c) How much higher does the 2.85-kg object travel after the 4.70-kg object hits the table?arrow_forwardBox 1 (with mass m = 7.1 kg) is on a frictionless table moving with a velocity Vo = 7.1 m/s. It collides with an identical box (let's call it box 2). The boxes stick together and launch horizontally off the table. What is the kinetic energy of the boxes when they land on the ground a distance H = 1.4 m below the table? H 1 Vo 2 1 darrow_forward
- Assume that the force of a bow on an arrow behaves like the spring force. In aiming the arrow, an archer pulls the bow back 48 cm and holds it in position with a force of 163 N. If the mass of the arrow is 51 g and the "spring" is massless, what is the speed of the arrow immediately after it leaves the bow? v=v= m/s A boy throws a ball of mass 0.2 kg straight upward with an initial speed of 22 m/s When the ball returns to the boy, its speed is 17 m/s How much work does air resistance do on the ball during its flight? W=W= J (give the absolute value, rounded to one decimal place)arrow_forward5. As a driver steps on the gas petal, a car of mass 1160 kg accelerates from rest. During the first few seconds of motion, the car's acceleration increases with time according to the expression a = 1.16+ - 0.210+2 + 0.240+³, where t is in seconds and a is in meters/sec². (a) What is the change in kinetic energy of the car during the time interval between + = 0 sec and t = 2.5 sec? (b) What is the minimum average power output of the engine over this time interval?, (c) Why is the value in part (b) described as the minimum value?arrow_forward7. DETAILS 4 SERPSE10 8.4.OP.012. (a) With what speed does the projectile leave the barrel of the cannon? m/s (b) At what point does the ball have maximum speed? cm (from its original position) Need Help? A toy cannon uses a spring to project a 5.25-g soft rubber ball. The spring is originally compressed by 4.99 cm and has a force constant of 7.91 N/m. When the cannon is fired, the ball moves 14.4 cm through the horizontal barrel of the cannon, and the barrel exerts a constant friction force of 0.032 9 N on the ball, (c) What is this maximum speed? m/s MY NOTES Read It ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHERarrow_forward
- On the roller-coaster shown, a car is moving 10 m/s toward the right at point 1. Assuming no friction, calculate the speed of the car at point 4. 3 40 m 26 m 15 m 29.37 m/s 22.71 m/s 20.89 m/s 26.17 m/s A. D. В. 25.07 m/s Е. С. 24.29 m/s F.arrow_forwardThe desperate contestants on a TV survival show are very hungry. The only food they can see is some fruit hanging on a branch high in a tree. Fortunately, they have a spring they can use to launch a rock. The spring constant is 1300 N/m, and they can compress the spring a maximum of 38 cm. All the rocks on the island seem to have a mass of 480 g. With what speed does the rock leave the spring?arrow_forwardA ball of mass m= 0.38 kg is tied to a massless string of length L=1.2m. The ball is released at rest from point A as shown in the figure. a) What is the speed of the ball as it passes through point B? b) What is the tension in the string at point B?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON