
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780470458365
Author: Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
![Sure! Here is the transcription of the text for an educational website:
---
**3. Let**
\[
A = \begin{bmatrix}
3 & 3 & 0 & 5 \\
2 & 2 & 0 & -2 \\
0 & 1 & -3 & 0 \\
2 & 10 & 3 & 2
\end{bmatrix}.
\]
**Evaluate det(A) by a cofactor expansion along a row or column of your choice. Is A invertible?**
---](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/2ebe91de-3090-46ac-907f-d0393c4d1db8/6318710d-b899-411d-9681-2978eaabe17e/vzyik1_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:Sure! Here is the transcription of the text for an educational website:
---
**3. Let**
\[
A = \begin{bmatrix}
3 & 3 & 0 & 5 \\
2 & 2 & 0 & -2 \\
0 & 1 & -3 & 0 \\
2 & 10 & 3 & 2
\end{bmatrix}.
\]
**Evaluate det(A) by a cofactor expansion along a row or column of your choice. Is A invertible?**
---
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
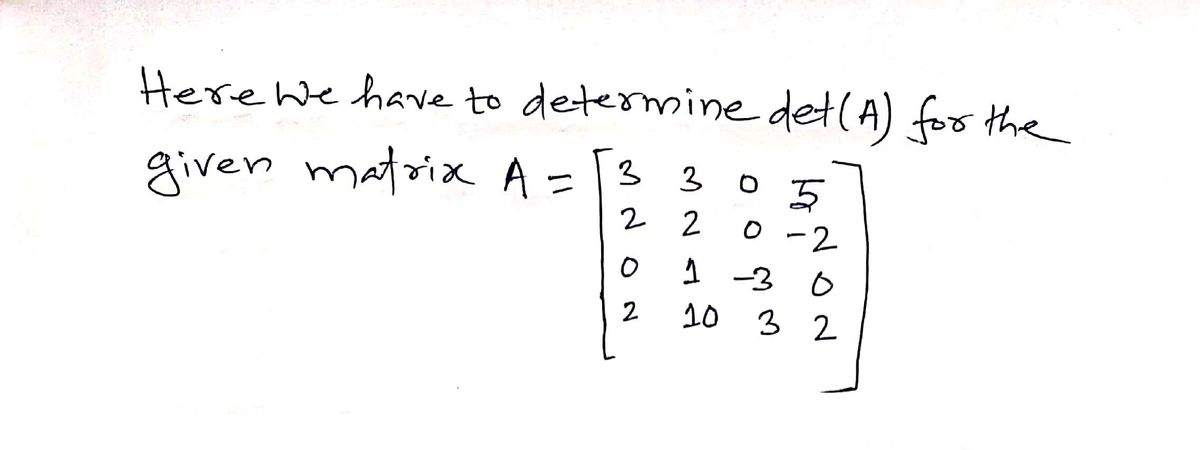
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Problem #1: Let V be the set of all ordered pairs of real numbers (µ₁, 42) with u₂ > 0. Consider the following addition and scalar multiplication operations on u = = (u₁, u₂) and v = (V₁, V2): u + v = (u₁ + v₁ + 4,7u2v2), ku = (ku1, ku2) Use the above operations for the following parts. (a) Compute u + v for u = (-2,3) and v = = (-2,2). (b) If the set V satisfies Axiom 4 of a vector space (the existence of a zero vector), what would be the zero vector? (c) If u = (5,5), what would be the negative of the vector u referred to in Axiom 5 of a vector space? (Don't forget to use your answer to part (b) here!)arrow_forwardExample:3 Verify Cayley-Hamilton theorem, and find A-1 [2 A=0 1 [1 1 2.arrow_forward3) Determine the inverse lapley transform of 105² +42s + 24 F(s) 53 + 45² +35arrow_forward
- Let A = 1₁1₁ 2 -3 0 2 12 3 1 (a) Compute det (A) using the cofactor expansion along 2nd row. (b) Compute det(A) using the cofactor expansion along 3rd column.arrow_forward1. Determine whether 3 -3 ㅠ 0 0 17 0 √2 1 is invertible using as little arithmetic as possible.arrow_forward0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 5. Let A = (a) Compute explicitly the product (I – A)(I+ A+ A²). (b) Explain why I – A is invertible and find its inverse.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780073397924
Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781118141809
Author:Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

