
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
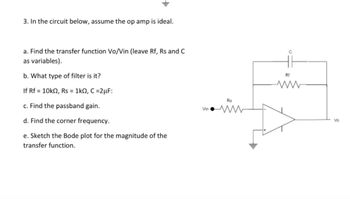
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
3. In the circuit below, assume the op amp is ideal.
- **a.** Find the transfer function Vo/Vin (leave Rf, Rs, and C as variables).
- **b.** What type of filter is it?
If Rf = 10kΩ, Rs = 1kΩ, C = 2μF:
- **c.** Find the passband gain.
- **d.** Find the corner frequency.
- **e.** Sketch the Bode plot for the magnitude of the transfer function.
**Diagram Explanation:**
The circuit is a non-inverting op-amp configuration with a feedback network consisting of a resistor (Rf) and a capacitor (C) in parallel. An input resistor (Rs) is connected to the inverting input, and the non-inverting input is grounded. The output voltage (Vo) is taken from the op-amp output.
**Important Components:**
- **Op-Amp:** Ideal operational amplifier, providing infinite gain, infinite input impedance, and zero output impedance.
- **Resistors (Rf, Rs):** Rf is the feedback resistor, and Rs is the series resistor connected to the input voltage (Vin).
- **Capacitor (C):** In parallel with Rf, forming a frequency-dependent network.
This setup is used to analyze the filter's characteristics, including its type, gain, and frequency response.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For a Fixed bias circuit having Rc-2.2K0, RB-2400, Vcc=12v and current amplification factor is 100 and the current flowing through the base is 20µA, the value if Collector current in saturation is 3mA O OA O 5.4mA O 1mAarrow_forwardIf vsig is a triangle waveform, determine the maximum amplitude that vsig can have? Showyour calculation.arrow_forwardUse the image below to help answers parts a and b.in an LRC type circuit series the inductive reactance is XL=484 ohms. and I=0.8 amps is the measured current amplitude.A) In the inductor determine the amplitude of the voltage.B)If the LRC circuit is at resonance frequency find the capacitive reactance.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,