
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
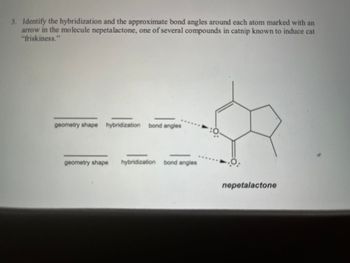
Transcribed Image Text:3. Identify the hybridization and the approximate bond angles around each atom marked with an
arrow in the molecule nepetalactone, one of several compounds in catnip known to induce cat
"friskiness."
geometry shape hybridization bond angles
geometry shape hybridization bond angles
nepetalactone
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Geometry shape is approximate arrangements of all bond pairs and loan pairs around the atom which experiences minimum hindrance between the bond pair- bond pair electrons and bond pair-loan pair electrons around that atom and gain maximum stability.
Hybridization is mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of same atome to produce degenerate and lower energy hybride orbitals. The number of hybride orbitals produced us equal to the number of atomic orbitals participated in hybridization.
Example :-
- one s-orbital and two p-orbitals hybridize then three sp2 hybride orbital will produce.
- one s-orbital and one p-orbital hybridize then two sp hybride orbital will produce.
NOTE :- Hybridize orbitals are used only to form Sigma bonds not used to form pi (π) bonds.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain a covalent bond involving four electrons between two atoms using quantum mechanics and valance bond theory. Group of answer choices Direct unhybridized s, p, or d electron overlap results in a sigma bond and hybridized indirect p electron overlap results in a pi bond. Direct unhybridized s, p, or d electron overlap results in a pi bond and hybridized indirect p electron overlap results in a sigma bond. Direct hybridized s, p, or d electron overlap results in a sigma bond and unhybridized indirect p electron overlap results in a pi bond. Direct s, p, or d electron overlap results in two unhybridized sigma bonds. Direct s, p, or d electron overlap results in two hybridized sigma bonds. Direct hybridized s, p, or d electron overlap results in a pi bond and unhybridized indirect p electron overlap results in a sigma bond.arrow_forwardDescribe each highlighted bond in terms of the overlap of atomic orbitals. (If the highlighted bond is not a pi bond, select the blank option from the dropdown menu.)arrow_forward4. Describe the hybridization of each carbon atom in the following structure.arrow_forward
- Use the References to access important values if needed for this ques Hybrid orbitals are formed by combining the valence orbitals on an atom. A molecule has sp³ d hybridization with 3 lone pairs. The electron pair geometry of this molecule is: The geometry of this molecule is: This molecule will have an approximate bond angle of (Choose all that apply.): 90° 109.5° 120° 180°arrow_forwardwhat is the geometry around the double bonds ? from left to rightarrow_forwardWhat molecular geometry does VSEPR predict for the carbon and the nitrogen in methylamine (CH3NH₂)? Choose all that apply! Trigonal pyramidal Tetrahedral T-shape Trigonal planar Linear Bentarrow_forward
- a. What is hybridization of carbon atom labeled "hybridization 3" b. Sigma (σ) bond between two carbon atoms (which DON'T have additional pi bond between them) is a combination of which two atomic orbitals according to the hybridization concept? c. Pi (π) bond between two carbon atoms is a combination of which two atomic orbitals according to the hybridization concept? d. Sigma (σ) bond between two carbon atoms (which are connected with pi bond as well) is a combination of which two atomic orbitals according to the hybridization concept? e. What is hybridization of oxygen atom labeled "hybridization 1" f. What is hybridization of carbon atom labeled "hybridization 2"arrow_forward1. a) Draw the dominant Lewis structure for the allene molecule (1,2-propyl diene, CH2CCH2 ) and use VSEPR theory to determine the molecule's geometry. In specifying the geometry give all bond angles and specify which nuclei lie in the same plane. b) Propose a hybridization and bonding scheme for the atoms in allene. That is, specify how each of the atoms is hybridized, which atomic orbitals overlap to form bonding molecular orbitals, and the nature (i.e., sigma", pi, etc.) of these molecular orbitals. c) Draw a plausible valence molecular orbital level diagram for allene (include only bonding MOs) based on the results from (b). d) Based on the work from (c) deduce the valence electronic configuration of the ground state of allene. e) Is the molecule planar or nonplanar? Explain your answer Answer subparts c, d, and earrow_forward2) a) Consider the following molecule . Given what you have learned about hybridization theory, draw an image or images explaining the bonding situation in this molecule. I want you to draw out all of the orbitals, hybrid orbitals and how they overlap to form the bonds in the molecule. Indicate the % s or p character in the given atomic and hybrid orbitals. Which C-C bond or bonds are the longest? In a paragraph or so explain the image or images you just drew. b) Lastly, consider the molecule below. Indicate the Molecular formula, the molar mass, label the hybridization of each atom except for hydrogen, indicate any chiral centers with a *, which bond or bonds are the shortest, identify by name of each functional group with an arrow pointing to the group.arrow_forward
- Chemistry Draw a three-dimensional representation of the valence orbitals and their bonding for compound CH2CHOH. Clearly show all valence electrons for each atom. Provide the following labels: atomic symbols, a code for each type of orbital used, a sigma bond, a pi bond and the molecular shape and approximate bond angles around the non- hydrogen atoms.arrow_forwardEach Carbon in benzene is sp2 hybradized. What is not true for sp2 hybridization? Question 6 options: One of the p orbitals of Carbon remains unhybradized which is utilized to form a pi bond sp2 hybrid orbital of one carbon atom overlaps with sp2 hybrid orbital of adjacent Carbon atom to give a Pi bond sp2 hybrid orbitals have 1:2 ratio of s and p One s and two p orbitals of Carbon combine to give three equivalent sp2 hybrid orbitals The sp2 hybrid orbitals are planar and arranged at an angle of 120oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY