
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
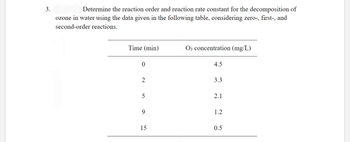
Transcribed Image Text:3.
Determine the reaction order and reaction rate constant for the decomposition of
ozone in water using the data given in the following table, considering zero-, first-, and
second-order reactions.
Time (min)
0
2
5
9
15
O3 concentration (mg/L)
4.5
3.3
2.1
1.2
0.5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following reaction: C6H11F + KBr → C6H11B1 + KF The following concentration vs. time data were collected. [CH11E]. time. min 0.400 M 0.380 M 3.00 0.350 M 7.70 0.320 M 12.87 0.300 M 16.32 0.270 M 22.64 0.250 M 27.24 A. Graph the data to determine the order. B. What is the order with respect to [C6H11F]? C. Calculate the rate constant, k. D. Write the rate law (equation). E. Calculate the half-life. F. How many minutes will it take to reach a concentration of 0.280 M? Upload the graphs with correlation coefficients and trendline equations and calculations.arrow_forward1. An investigator measured the concentration of a reactant A as a function of time. Part of his data are as follows: time / min [A]/mol dm³ 17.5 0.02566 39.6 0.01300 83.8 0.00650 Using these data, what can we say about the kinetics of the reaction? Determine the rate constant and the initial concentration. Calculate the half-life at time zero.arrow_forwardNumber 4arrow_forward
- Evaluate the following data to determine whether the reaction is first or second order. Calculate the rate constant and be certain to give its unit. A → Product A (mmol/L) Time (sec) 1.00 0 0.50 11 0.25 20 0.10 48 0.05 105arrow_forwardInitial rates were measured for the following reaction and are listed in the table. A + 2B ⎯→ products Expt. Initial Concentrations Initial Rate (mol/L·s) [A] [B] 1 0.115 0.135 2.70 × 10−3 2 0.115 0.270 2.16 × 10−2 3 0.345 0.135 8.10 × 10−3 What is the order of the reaction with respect to A, with respect to B, and overall?arrow_forwardPlease help to understandarrow_forward
- 8. Rates for a certain chemical reaction involving the reactant A were measured as a function of the concentration of A, and these data were plotted in the graph below. What is the order of the reaction with respect to A, and what is the rate constant for the reaction? 0.012 0.010 0.008 0.006· 0.004 0.002 0. 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 [A](M) A) order with respect to A = 0, k = 0.010 s-l B) órder with respect to A = 1, k = 0.010 s C) order with respect to A = 2, k = 0.00 s- D) order with respect to A = 0, k = 10 s E) order with respect to A = 1, k = 100 s- 11:2 a 2/18 Cop Rate (M/s)arrow_forward36 The reaction C2H5Cl →C2H4 + HCl is first order in C2H5Cl. The rate constant is 1.60 x 10-6/s. In an investigation of the decomposition of C2H5Cl an initial concentration of 0.165 mol/L was used. What will the concentration of C2H5Cl be after 125 hours? Select one: a. 0.0803 M b. 0.0703 M c. 0.0603 M d. 0.0503Marrow_forwardB 8. D Trial 1 2 3 4 [A₂] 0.10 0.20 0.30 0.30 [B] 0.50 0.50 0.05 0.10 An experiment was conducted to determine the rate law for the reaction A2(g) + B(9) A₂B(g). The table above shows the data collected. Based on the data in the table. which statement is correct? Initial rate (Ms-¹) 2.5 x 10 5.0 x 10-4 5.0 × 10-5 1.0 x 10-4 Since the rate law can be expressed as ratek[A₂), tripling the concentration of A2 will cause a 9-fold increase in the rate of the reaction. Since the rate law can be expressed as rate k[A₂][B], doubling the concentrations of A₂ and B will quadruple the rate of the reaction. Since the rate law can be expressed as rate k[A] [B], tripling the concentration of A2 while keeping the concentration of B constant will triple the rate of the reaction. Since the rate law can be expressed as rate=k[A₂][B], doubling the concentration of B while keeping the concentration of A₂ constant will double the rate of the reaction.arrow_forward
- The reaction between hydrogen and chlorine is as follows: Cl2(g) + H2(g) → 2HCl(g) Experiments show that this reaction is first order with respect to H2 and one-half order with respect to Cl2. What is the rate law? a. Rate = k [H2]1/2 [Cl2] b. Rate = k [Cl2] [H2]2 c. Rate = k [Cl2]1/2 [H2] d. Rate = k [Cl2]2 [H2]arrow_forwardDo not give handwriting solution.arrow_forward1. For an irreversible reaction A products, the graph of 1/[A] as a function of time is linear. What is the reaction order in A? a. Zeroth-order b. First-order c. Second-order d. The order in A cannot be determined based on the information given. 2. A proposed mechanism for the reduction of nitrogen as NO by hydrogen is: Step 1: H₂(g) + 2 NO (g) → N₂O (g) + H₂O (g) Step 2: N₂O (g) + H₂ (g) → N2 (g) + H₂O (g) What is the molecularity of Step 2? a. unimolecular b. bimolecular c. termolecular d. zero molecular (spontaneous) e. More information is needed to answer this question. 3. Which one of the following will change the value of an equilibrium constant? a. changing temperature b. adding other substances that do not react with any of the species involved in the equilibrium c. varying the initial concentrations of reactants d. varying the initial concentrations of products e. changing the volume of the reaction vesselarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY