
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:3. Column ABC has a uniform rectangular cross-section and is braced in the xz plane at its
midpoint C is shown Figure Q3(a). Given, the factor of safety is 2.7, P=5.4 kN, L=600
mm and E=70 GPa, determine the ratio b/d for which the factor of safety is the same with
respect to buckling in the xz and yz planes
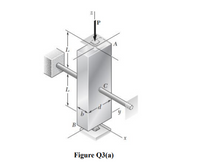
Transcribed Image Text:A
L
B
Figure Q3(a)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The plate shown in (Figure is supported by a roller and a cable in the x-direction at A, a ball-and-socket joint at B, and a roller at C. A force F = 8.1 kN is applied at the centroid of the plate parallel to the yz-plane and making an angle of θ = 40 ∘ with the xy-plane. The sides AB and BC of the plate have length L = 1.5 m . 1) What is the reaction force in the z-direction at point B? 2) What is the tension T in the cable? 3) What is the reaction force in the x-direction at point B? Let a positive force act in the positive x-direction.arrow_forwardGiven the structure shown in the figure below, determine:the support reactions in the structure. (the positive * signs correspond to the directions "up" in y and "to the right" in x)arrow_forward1. Three cubes of side l0, 2l0, and 3l0, are placed next to another (in contact) with their centers along a straight line and the l = 2l0 cube is in the middle (see Figure below).a) If the cubes are made of the same uniform material, find along this line the position of the center of mass of the system.b) We now replace the cube in the middle (l = 2l0) by another cube of the same volume but made of a different uniform material. What would be the mass density of this cube compared to the mass density 0 of the initial cube if we want to locate the center of mass of the new system at the interface between the cube in the middle (l = 2l0) and the right-hand cube (l = 3l0)?arrow_forward
- 4-83 that's what I nearrow_forwardFor the composite beam section in Figure Q6a, calculate the second moment of areaabout its centroidal x-x axis (Ixx centroid), where b1 = 125.50 mm, b2 = 25.75 mm,b3 = 36.35 mm, d1 = 78.00 mm and d2 = 24.00 mm Give your answer to 2 decimalplaces.arrow_forwardplease solve with stepsarrow_forward
- A sign for a pizza restaurant hangs from a 2.60-m long rod extended out from a building. A cable, attached to the building, is attached to the rod at a point that is 2.10 m from the hidge. (See the figure.) The mass of the rod is 3.20 kg. The mass of the sign is 7.10 kg. The angle between the building and the rod is 69.0 degrees. The angle between the cable and the horizontal is 36.0 degrees. The tension in the cable is 117.5 N. What is the vertical component of the reaction force from then hinge on the rod?arrow_forwardComplete Solutionarrow_forward2. The steel beam ABCD shown is simply supported at A and supported at B and D by steel cables, each having an effective diameter of 0.5 in. The moment of inertia of the beam is I = 1.2 inª. A force of 5 kips is applied at point C. Determine the deflections of B, C, and D using Superposition method. A 16 in E B 16 in C 5 kips 16 in F D 38 inarrow_forward
- 2. The structure is connected by a pin joint at point A and by a cable of length L at points B and C, respectively.When load P is given at point D as shown below, what is the vertical displacement at point D?arrow_forwardbar AB is Q1) A homogeneous of M supported at either end by a cable as shown in figure beside. If the stress is not to exceed 75 MPa in bronze and 110 MPa in steel. And the diameter of bronze cable is 25 mm while for steel cable is 20 mm. Calculate the maximum safe mass M that can be carried by these cables. (1300) Bronze A 8m Steelarrow_forwardPLEASE BOX THE FINAL ANSWER, A LOT OF SOLVER'S SOLUTIONS ARE MESSY. Please give me explanationarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY