
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
3. Calculate the value of ΔSo for the formation of POCl3 from its constituent elements, as shown below. P2(g) + O2(g) + 3Cl2(g) → 2POCl3(g)
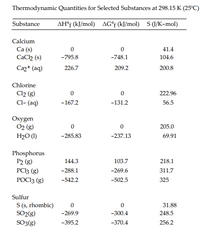
Transcribed Image Text:Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25°C)
AH°f (kJ/mol) AG°f (kJ/mol) S (J/K-mol)
Substance
Calcium
Ca (s)
CaCh (s)
41.4
-795.8
-748.1
104.6
Caz+ (aq)
226.7
209.2
200.8
Chlorine
Cl2 (g)
Cl- (aq)
222.96
-167.2
-131.2
56.5
Oxygen
02 (g)
205.0
H2O (1)
-285.83
-237.13
69.91
Phosphorus
Р2 (g)
PC3 (g)
РОС13 (3)
144.3
103.7
218.1
-288.1
-269.6
311.7
-542.2
-502.5
325
Sulfur
S (s, rhombic)
SO2(g)
SO3(g)
31.88
-269.9
-300.4
248.5
-395.2
-370.4
256.2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using the following thermochemical data: 2Sb(s) + 6HF(g) → 2SbF3(s) + 3H2(g) ΔH° = –1631.8 kJ/mol 2Sb(s) + 6HCl(g) → 2SbCl3(s) + 3H2(g) ΔH° = –210.6 kJ/mol calculate ΔH° for the following reaction: SbF3(s) + 3HCl(g) → SbCl3(s) + 3HF(g)arrow_forwardPlease answer question 20 part Aarrow_forwardEthanol can be made from the fermentation of crops and has been used as a fuel additive to gasoline. C2H5OH(l)+3O2(g)→2CO2(g)+3H2O(g)C2H5OH(l)+3O2(g)→2CO2(g)+3H2O(g) Part B Calculate ΔrH∘ (The standard enthalpy of formation of liquid ethanol is −277.6 kJmol−1, of gaseous carbon dioxide is −393.5 kJmol−1, and of gaseous water is −241.8 kJmol−1.) Express your answer in kilojoules per mole to one decimal place.arrow_forward
- Determine the ΔH of formation for sulfur trioxide gas if: 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) --> 2 SO3 (g) ΔH = -300 kJ SO2 (g) --> O2 (g) + S (s) ΔH = 200 kJ The standard state of sulfur is S (s). -500 kJ/mol -400 kJ/mol - 350 kJ/mol +200 kJ/mol +100 kJ/molarrow_forwardThe ΔH°rxn for the following reaction: NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) is –55.7 kJ/mol. Given the following enthalpies of formation, determine ΔH°f of H2O(l). ΔH°f NaOH(aq) = −470.1 kJ/mol ΔH°f HCl(aq) = −167.2 kJ/mol ΔH°f NaCl(aq) = −407.2 kJ/molarrow_forwardDetermine the ΔH of formation for sulfur trioxide gas if: 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) --> 2 SO3 (g) ΔH = -300 kJ SO2 (g) --> O2 (g) + S (s) ΔH = 200 kJ The standard state of sulfur is S (s). - 350 kJ/mol -500 kJ/mol +200 kJ/mol +100 kJ/mol -400 kJ/molarrow_forward
- The following is the balanced equation for the reaction of gaseous ammonia with oxygen gas. 4NH3 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 4NO (g) + 6H2O (g) Using the ΔHf° values shown below, calculate the ΔHrxn° for the overall reaction. ΔHf°(NO (g)) = 91.3 kJ/mol ΔHf°(NH3 (g)) = −45.9 kJ/mol ΔHf°(H2O (l)) = −241.8 kJ/mol A) −294.8 kJ/mol B) −731.5 kJ/mol C) −902.0 kJ/mol D) −468.2 kJ/molarrow_forwardConsider the reaction 2H2O(g) →2H2(g) + O2(g) ΔH = +483.60 kJ/mol at a certain temperature. If the increase in volume is 52.7 L against an external pressure of 1.00 atm, calculate ΔU for this reaction. (The conversion factor is 1 L · atm = 101.3 J.) put your answer in KJarrow_forwardConsider the reaction. 2 Fe₂0₂4Fe +30₂ AHin = +824.2 kJ The formation of 62.0 g of Fe results in the release of 229 kJ of heat. the absorption of 229 kJ of heat. O the release of 12800 kJ of heat. the release of 915 kJ of heat. the absorption of 12800 kJ of heat. the absorption of 915 kJ of heat.arrow_forward
- Using the equations 2 Fe (s) + 3 Cl₂ (g) → 2 FeCl₃ (s) ∆H° = -800.0 kJ/mol Si(s) + 2 Cl₂ (g) → SiCl₄ (s) ∆H° = -640.1 kJ/mol Determine the molar enthalpy (in kJ/mol) for the reaction 3 SiCl₄ (s) + 4 Fe (s) → 4 FeCl₃ (s) + 3 Si (s)arrow_forwardTitanium(IV) oxide is commonly used as a white paint pigment. The compound is produced by the reaction TiCl 4(g) + 2 H 2O(g)↔ TiO 2(s) + 4 HCl(g) What is ΔH° rxn (in kilojoules)? TiCl 4(g) ΔH f o = -763 kJ/molH 2O(g) ΔH f o = -241.8 kJ/mol.HCl(g) ΔH f o = -92 kJ/mol.TiO 2(s) ΔH f o = -945 kJ/mol.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY